Cesium高级教程-后处理体积云-实现简单的体积云效果
博客参考
实现简单的体积云,我们先参考这篇博客 体积云渲染实战:ray marching,体积云与体积云光照 ,这是一篇基于opengl的体积云实现,为什么选择此示例参考呢?因为该示例一是相对简单,并且流程比较完善,二是涉及到的引擎代码比较少,不像其他示例有很多c#或者c++代码,参考起来难度很大。
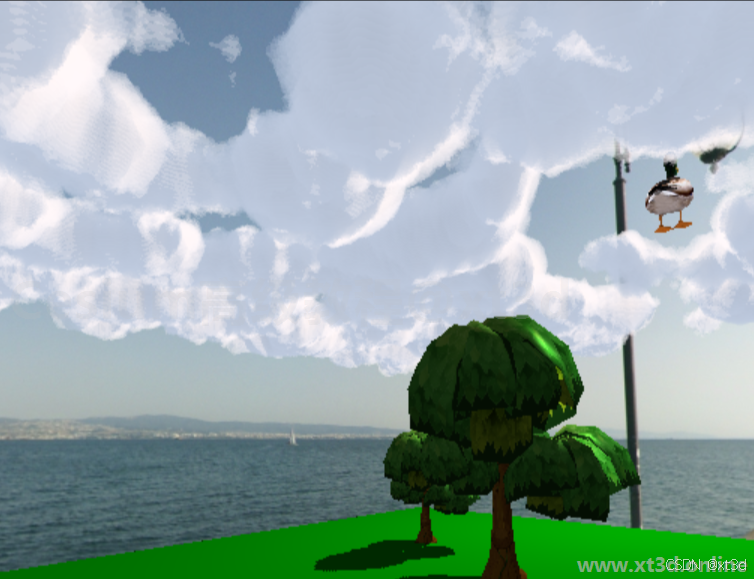

你可以先看看文章,然后自己思考有没有难点,如果觉得没有,可以自己先实现一遍,看能不能做出来,因为学习其实最重要的是过程,而不是结果。如果照着文章就能把效果实现出来,您会信心倍增,成就感满满。

本节最后的效果
实现过程
一、 光线步进创建Box
需要注意他的盒子中心应该就是世界坐标系的中心点,所以他直接使用相关坐标进行计算,而我们的盒子中心并不在世界坐标的中心,所以不能直接算,需要像上一节那样建立一个局部坐标系当做世界坐标系。
#define bottom 13 // 云层底部
#define top 20 // 云层顶部
#define width 5 // 云层 xz 坐标范围 [-width, width]
// 获取体积云颜色
vec4 getCloud(vec3 worldPos, vec3 cameraPos) {
vec3 direction = normalize(worldPos - cameraPos); // 视线射线方向
vec3 step = direction * 0.25; // 步长
vec4 colorSum = vec4(0); // 积累的颜色
vec3 point = cameraPos; // 从相机出发开始测试
// ray marching
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
point += step;
if(bottom>point.y || point.y>top || -width>point.x || point.x>width || -width>point.z || point.z>width) {
continue;
}
float density = 0.1;
vec4 color = vec4(0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 1.0) * density; // 当前点的颜色
colorSum = colorSum + color * (1.0 - colorSum.a); // 与累积的颜色混合
}
return colorSum;
}
这里可以参考上一节的代码
let shader=`
uniform sampler2D colorTexture;
uniform sampler2D depthTexture;
in vec2 v_textureCoordinates;
uniform mat4 inverse;
vec4 rayBoxDst(vec3 boundsMin, vec3 boundsMax, vec3 rayOrigin, vec3 invRaydir)
{
vec3 t0 = (boundsMin - rayOrigin) * invRaydir;
vec3 t1 = (boundsMax - rayOrigin) * invRaydir;
vec3 tmin = min(t0, t1);
vec3 tmax = max(t0, t1);
float dstA = max(max(tmin.x, tmin.y), tmin.z); //进入点
float dstB = min(tmax.x, min(tmax.y, tmax.z)); //出去点
float dstToBox = max(0., dstA);
...
return vec4(dstToBox, dstInsideBox,dstA,dstB);
}
void main(){
out_FragColor = texture(colorTexture, v_textureCoordinates);
vec4 rawDepthColor = texture(czm_globeDepthTexture, v_textureCoordinates);
float depth = czm_unpackDepth(rawDepthColor);
if (depth == 0.0) {
depth = 1.0;
}
vec4 eyeCoordinate4 = czm_windowToEyeCoordinates(gl_FragCoord.xy, depth);
vec3 eyeCoordinate3 = eyeCoordinate4.xyz/eyeCoordinate4.w;
vec4 worldCoordinate4 = czm_inverseView * vec4(eyeCoordinate3,1.) ;
vec3 worldCoordinate = worldCoordinate4.xyz / worldCoordinate4.w;
vec4 worldPos= inverse * vec4(worldCoordinate,1.);
vec4 cameraPos= inverse * vec4(czm_viewerPositionWC,1.);
vec3 vDirection=worldPos.xyz-cameraPos.xyz;//方向
vec3 rayDir = normalize( vDirection );
vec3 dim= vec3(20.,20.,20.);//盒子长宽高
vec3 box_min = vec3(0.) - dim / 2.;
vec3 box_max = vec3(0.) + dim / 2.;
vec4 bounds =rayBoxDst(box_min,box_max,cameraPos.xyz,1.0 / rayDir);
...; //盒子外
out_FragColor=vec4(0.,0.,1.,1.);
}
`;
二、提高光线步进的性能
为了提高光线步进的性能,需要将射线的起点设置到与盒子最近的点,从该点开始前进,这就省去了相机到盒子这段的距离
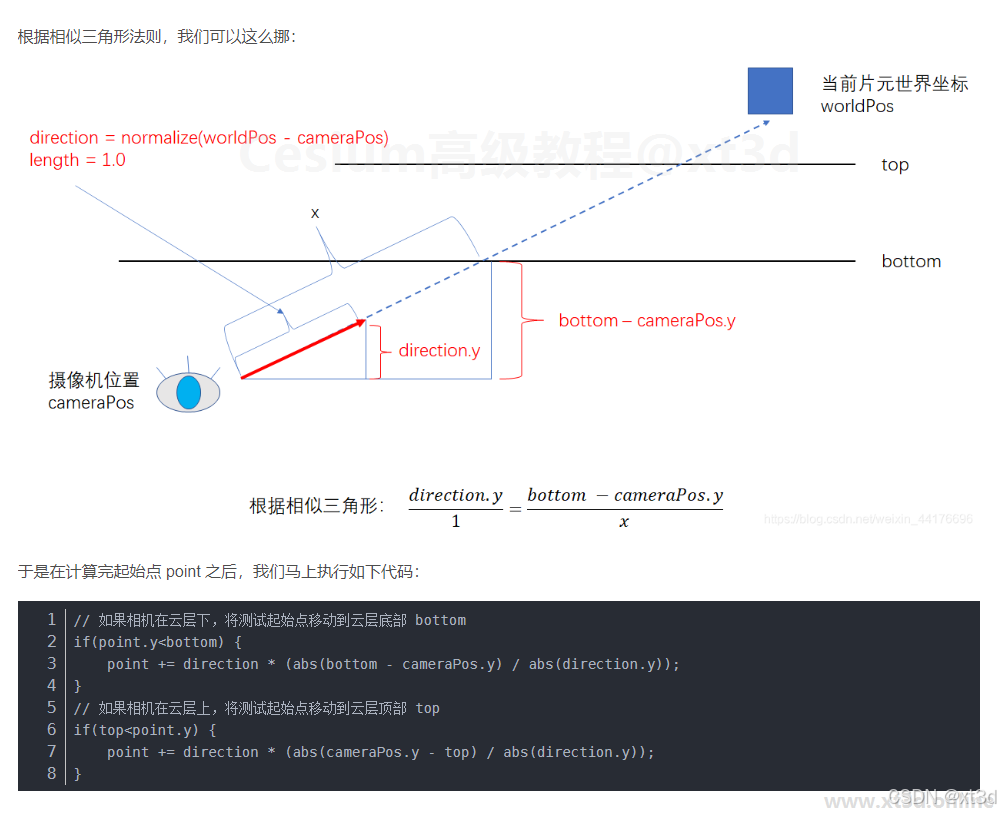
这里我们还可以更加优化,因为我们的vec4 rayBoxDst(vec3 boundsMin, vec3 boundsMax, vec3 rayOrigin, vec3 invRaydir) 方法其实能够获取到射线与盒子的距离,以及射线在光线中的行驶距离,分别为dstToBox, dstInsideBox,我们通过dstToBox和射线方向,就可以将光线步进的起点设置到与盒子最近的点,通过dstInsideBox可以知道在盒子内的步进距离。
修改shader如下
let shader=`
uniform sampler2D colorTexture;
uniform sampler2D depthTexture;
in vec2 v_textureCoordinates;
uniform mat4 inverse;
vec4 rayBoxDst(vec3 boundsMin, vec3 boundsMax, vec3 rayOrigin, vec3 invRaydir)
{
vec3 t0 = (boundsMin - rayOrigin) * invRaydir;
vec3 t1 = (boundsMax - rayOrigin) * invRaydir;
vec3 tmin = min(t0, t1);
vec3 tmax = max(t0, t1);
float dstA = max(max(tmin.x, tmin.y), tmin.z); //进入点
float dstB = min(tmax.x, min(tmax.y, tmax.z)); //出去点
float dstToBox = max(0., dstA);
...
return vec4(dstToBox, dstInsideBox,dstA,dstB);
}
void main(){
out_FragColor = texture(colorTexture, v_textureCoordinates);
vec4 rawDepthColor = texture(czm_globeDepthTexture, v_textureCoordinates);
float depth = czm_unpackDepth(rawDepthColor);
if (depth == 0.0) {
depth = 1.0;
}
vec4 eyeCoordinate4 = czm_windowToEyeCoordinates(gl_FragCoord.xy, depth);
vec3 eyeCoordinate3 = eyeCoordinate4.xyz/eyeCoordinate4.w;
vec4 worldCoordinate4 = czm_inverseView * vec4(eyeCoordinate3,1.) ;
vec3 worldCoordinate = worldCoordinate4.xyz / worldCoordinate4.w;
...
vec3 vDirection=worldPos.xyz-cameraPos.xyz;//方向
vec3 rayDir = normalize( vDirection );
vec3 dim= vec3(20.,20.,20.);//盒子长宽高
vec3 box_min = vec3(0.) - dim / 2.;
vec3 box_max = vec3(0.) + dim / 2.;
vec4 bounds =rayBoxDst(box_min,box_max,cameraPos.xyz,1.0 / rayDir);
bounds.x = max( bounds.x, 0.0 );
... //盒子外
...; //射线起点
float distance=bounds.y;//盒子内的步进总距离
float stepDis=1.5;//每次步进的距离
int totalStep=int(distance/stepDis);
vec4 colorSum = vec4(0); // 积累的颜色
for ( int t =0; t < totalStep ; t++) {
float density = .1; // 当前点云密度
vec4 color = vec4(0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 1.0) * density; // 当前点的颜色
colorSum = colorSum + color * (1.0 - colorSum.a); // 与累积的颜色混合
p += rayDir * stepDis;
}
out_FragColor=colorSum;
}
`;
此时运行代码,会看到一个中间到边缘渐变的盒子,因为边缘步进次数少,而中间步进次数多,颜色累加次数就多。

示例效果可到 xt3d 官网 运行查看
三、采样噪声数据
接下来从噪声图中采样云的形状,将噪声图传入着色器,是通过Cesium.Texture类,相信您对此已经没问题。

Cesium.Resource.createIfNeeded("./noise.png")
.fetchImage().then(res => {
let texture = new Cesium.Texture({
context: viewer.scene.context,
source: res,
sampler: new Cesium.Sampler({
wrapS: Cesium.TextureWrap.REPEAT,
wrapT: Cesium.TextureWrap.REPEAT,
minificationFilter: Cesium.TextureMinificationFilter.LINEAR,
magnificationFilter: Cesium.TextureMagnificationFilter.LINEAR,
})
})
})
修改着色器
let shader=`
uniform sampler2D colorTexture;
uniform sampler2D depthTexture;
in vec2 v_textureCoordinates;
uniform mat4 inverse;
uniform sampler2D noiseMap;
...
// 计算 云密度
float getDensity(vec3 pos) {
// 采样噪声图
vec2 coord = pos.xy * 0.00025;
float noise = texture (noiseMap, coord).x;
// 截断
// if(noise<0.4) {
// noise = 0.;
// }
return noise;
}
void main(){
...
vec3 dim= vec3(1000.,1000.,100.);//盒子长宽高
vec3 box_min = vec3(0.) - dim / 2.;
vec3 box_max = vec3(0.) + dim / 2.;
vec4 bounds =rayBoxDst(box_min,box_max,cameraPos.xyz,1.0 / rayDir);
bounds.x = max( bounds.x, 0.0 );
if ( bounds.z > bounds.w ) return; //盒子外
vec3 p = cameraPos.xyz + bounds.x * rayDir; //射线起点
float distance=bounds.y;//盒子内的步进总距离
float stepDis=1.5;//每次步进的距离
int totalStep=int(distance/stepDis);
vec4 colorSum = vec4(0); // 积累的颜色
for ( int t =0; t < totalStep ; t++) {
float density = getDensity(p) * 0.1; // 当前点云密度
vec4 color = vec4(0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 1.0) * density; // 当前点的颜色
colorSum = colorSum + color * (1.0 - colorSum.a); // 与累积的颜色混合
p += rayDir * stepDis;
}
out_FragColor.rgb= out_FragColor.rgb*(1.0 - colorSum.a) + colorSum.rgb;
}
`;

示例效果可到 xt3d 官网 运行查看
四、高度衰减
let shader=`
uniform sampler2D colorTexture;
uniform sampler2D depthTexture;
in vec2 v_textureCoordinates;
uniform mat4 inverse;
uniform sampler2D noiseMap;
// 计算 云密度
float getDensity(vec3 pos,float bottom,float top) {
// 高度衰减
float mid = (bottom + top) / 2.0;
float h = top - bottom;
float weight = 1.0 - 2.0 * abs(mid - pos.z) / h;
weight = pow(weight, 0.5);
// 采样噪声图
vec2 coord = pos.xy * 0.00025;
float noise = texture (noiseMap, coord).x;
noise *= weight;
// 截断
if(noise<0.3) {
noise = 0.;
}
return noise;
}
void main(){
...
vec3 p = cameraPos.xyz + bounds.x * rayDir; //射线起点
p.z+=50.;
float distance=bounds.y;//盒子内的步进总距离
float stepDis=1.5;//每次步进的距离
int totalStep=int(distance/stepDis);
vec4 colorSum = vec4(0); // 积累的颜色
for ( int t =0; t < totalStep ; t++) {
float density = getDensity(p,-2.,102.) * 0.1; // 当前点云密度
vec4 color = vec4(0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 1.0) * density; // 当前点的颜色
colorSum = colorSum + color * (1.0 - colorSum.a); // 与累积的颜色混合
if(colorSum.a>1.)break;
p += rayDir * stepDis;
}
out_FragColor.rgb= out_FragColor.rgb*(1.0 - colorSum.a) + colorSum.rgb;
}
`;

示例效果可到 xt3d 官网 运行查看
五、多次采样噪声
// 计算 云密度
float getDensity(vec3 pos,float bottom,float top) {
// 高度衰减
float mid = (bottom + top) / 2.0;
float h = top - bottom;
float weight = 1.0 - 2.0 * abs(mid - pos.z) / h;
weight = pow(weight, 0.5); // 采样噪声图
vec2 coord = pos.xy * 0.00025;
float noise = texture (noiseMap, coord).x;
noise += texture (noiseMap, coord*3.5).x/3.5;
noise += texture (noiseMap, coord*12.5).x/12.5;
noise += texture (noiseMap, coord*42.87).x/42.87;
noise/=1.6472;
noise *= weight;
noise *= weight; // 截断
if(noise<0.3) {
noise = 0.;
}
return noise;
}

示例效果可到 xt3d 官网 运行查看
五、 设置颜色,加入动效
完整的shader如下
let shader=`
uniform sampler2D colorTexture;
uniform sampler2D depthTexture;
in vec2 v_textureCoordinates;
uniform mat4 inverse;
uniform sampler2D noiseMap;
vec4 rayBoxDst(vec3 boundsMin, vec3 boundsMax, vec3 rayOrigin, vec3 invRaydir)
{
vec3 t0 = (boundsMin - rayOrigin) * invRaydir;
vec3 t1 = (boundsMax - rayOrigin) * invRaydir;
vec3 tmin = min(t0, t1);
vec3 tmax = max(t0, t1);
float dstA = max(max(tmin.x, tmin.y), tmin.z); //进入点
float dstB = min(tmax.x, min(tmax.y, tmax.z)); //出去点
...;
return vec4(dstToBox, dstInsideBox,dstA,dstB);
}
// 计算 云密度
float getDensity(vec3 pos,float bottom,float top) {
// 高度衰减
float mid = (bottom + top) / 2.0;
...;
// 采样噪声图
vec2 coord = pos.xy * 0.00025;
float noise = texture (noiseMap, coord).x;
noise += texture (noiseMap, coord*3.5).x/3.5;
noise += texture (noiseMap, coord*12.5).x/12.5;
noise += texture (noiseMap, coord*42.87).x/42.87;
noise/=1.6472;
noise *= weight;
// 截断
if(noise<0.3) {
noise = 0.;
}
return noise;
}
#define baseBright vec3(1.26,1.25,1.29) // 基础颜色 -- 亮部
#define baseDark vec3(0.31,0.31,0.32) // 基础颜色 -- 暗部
#define lightBright vec3(1.29, 1.17, 1.05) // 光照颜色 -- 亮部
#define lightDark vec3(0.7,0.75,0.8) // 光照颜色 -- 暗部
void main(){
out_FragColor = texture(colorTexture, v_textureCoordinates);
vec4 rawDepthColor = texture(czm_globeDepthTexture, v_textureCoordinates);
float depth = czm_unpackDepth(rawDepthColor);
if (depth == 0.0) {
depth = 1.0;
}
vec4 eyeCoordinate4 = czm_windowToEyeCoordinates(gl_FragCoord.xy, depth);
vec3 eyeCoordinate3 = eyeCoordinate4.xyz/eyeCoordinate4.w;
vec4 worldCoordinate4 = czm_inverseView * vec4(eyeCoordinate3,1.) ;
vec3 worldCoordinate = worldCoordinate4.xyz / worldCoordinate4.w;
...
vec3 vDirection=worldPos.xyz-cameraPos.xyz;//方向
vec3 rayDir = normalize( vDirection );
vec3 dim= vec3(1000.,1000.,100.);//盒子长宽高
vec3 box_min = vec3(0.) - dim / 2.;
vec3 box_max = vec3(0.) + dim / 2.;
vec4 bounds =rayBoxDst(box_min,box_max,cameraPos.xyz,1.0 / rayDir);
...; //盒子外
...;//盒子内的步进总距离
float stepDis=1.5;//每次步进的距离
int totalStep=int(distance/stepDis);
vec4 colorSum = vec4(0); // 积累的颜色
for ( int t =0; t < totalStep ; t++) {
...; // 当前点云密度
...; // 当前点的颜色
colorSum = colorSum + color * (1.0 - colorSum.a); // 与累积的颜色混合
if(colorSum.a>1.)break;
p += rayDir * stepDis;
}
out_FragColor.rgb= out_FragColor.rgb*(1.0 - colorSum.a) + colorSum.rgb;
}
`;
此时的效果

示例效果可到 xt3d 官网 运行查看
更多内容见 Cesium高级教程-教程简介
本节到此结束,至于后面的改进,如果您有时间,可以继续研究,作为教程,到此已经包含所有体积云的关键知识点。

























 458
458

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










