一、首先根据HDFS的API写一段程序,然后是用Eclipse进行debug 单步跟踪,从而查看源码执行流程:
import java.net.URI;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
public class testRead1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//String uri = args[0];
String uri = "hdfs://localhost:9000/user/mmliu/test01.txt";
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(URI.create(uri), conf);
FSDataInputStream in = null;
try {
in = fs.open(new Path(uri));
IOUtils.copyBytes(in, System.out, 4096, false);
in.seek(0);
IOUtils.copyBytes(in, System.out, 4096, false);
} finally {
IOUtils.closeStream(in);
}
}
}
先给出整体的序列图以便后边分析:
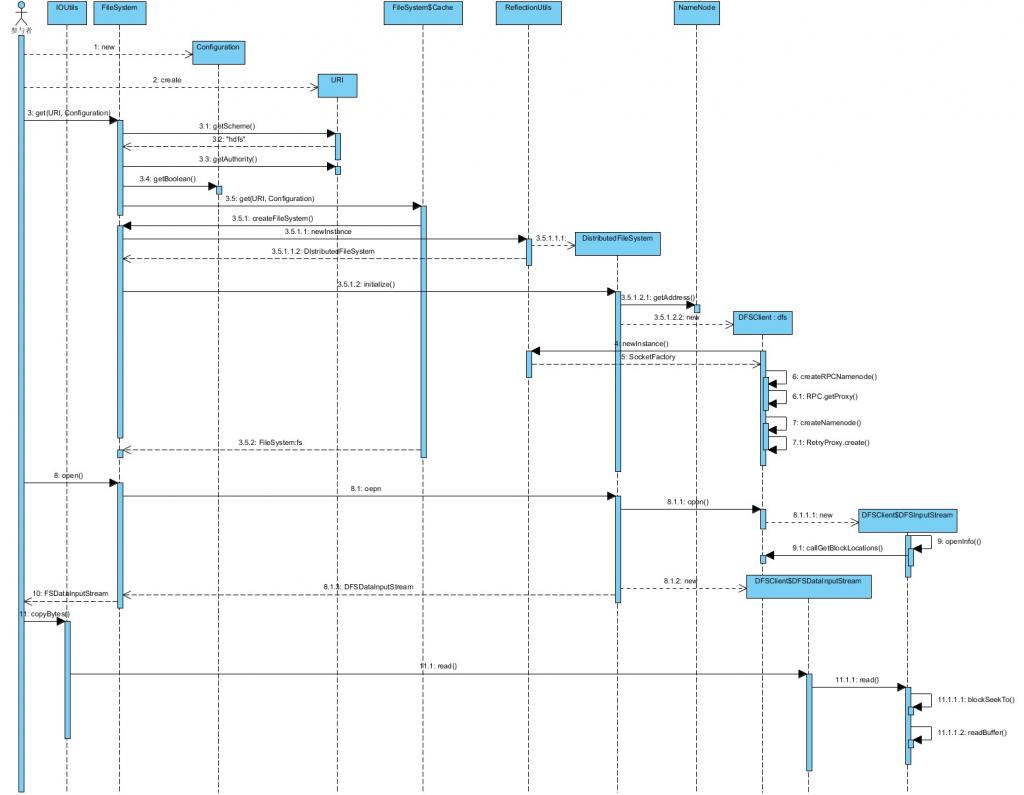
1、单步追踪client端的代码:
可以看到一开始当get一个FileSystem类的实例的时候,最终会根据我们提供的uri和conf 创建了一个DistributedFileSystem的实例对象,并完成了初始化的过程,初始化函数主要是完成了RPCNamenode和namenode的创建,而这两个变量都是ClientProtocol类型的,ClientProtocol本质上是一个接口,最终完成的是RPC操作。
private static ClientProtocol createRPCNamenode(InetSocketAddress nameNodeAddr,
Configuration conf, UserGroupInformation ugi)
throws IOException {
return (ClientProtocol)RPC.getProxy(ClientProtocol.class,
ClientProtocol.versionID, nameNodeAddr, ugi, conf,
NetUtils.getSocketFactory(conf, ClientProtocol.class));
}Open阶段,HDFS调用了DistributedFileSystem的open函数:
public FSDataInputStream open(Path f, int bufferSize) throws IOException {
statistics.incrementReadOps(1);
return new DFSClient.DFSDataInputStream(
dfs.open(getPathName(f), bufferSize, verifyChecksum, statistics));
}
/****************************************************************
* DFSInputStream provides bytes from a named file. It handles
* negotiation of the namenode and various datanodes as necessary.
****************************************************************/
public class DFSInputStream extends FSInputStream {openInfo函数主要与namenode通信,从namenode上预取file的block信息,其中perfetchSize可以设定预取的block的块数,默认为10.
private long prefetchSize = 10 * defaultBlockSize;
/**
* Grab the open-file info from namenode
*/
synchronized void openInfo() throws IOException {
LocatedBlocks newInfo = callGetBlockLocations(namenode, src, 0, prefetchSize);
if (newInfo == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("File does not exist: " + src);
}
// I think this check is not correct. A file could have been appended to
// between two calls to openInfo().
if (locatedBlocks != null && !locatedBlocks.isUnderConstruction() &&
!newInfo.isUnderConstruction()) {
Iterator<LocatedBlock> oldIter = locatedBlocks.getLocatedBlocks().iterator();
Iterator<LocatedBlock> newIter = newInfo.getLocatedBlocks().iterator();
while (oldIter.hasNext() && newIter.hasNext()) {
if (! oldIter.next().getBlock().equals(newIter.next().getBlock())) {
throw new IOException("Blocklist for " + src + " has changed!");
}
}
}
updateBlockInfo(newInfo);
this.locatedBlocks = newInfo;
this.currentNode = null;
}private static LocatedBlocks callGetBlockLocations(ClientProtocol namenode,
String src, long start, long length) throws IOException {
try {
return namenode.getBlockLocations(src, start, length);
} catch(RemoteException re) {
throw re.unwrapRemoteException(AccessControlException.class,
FileNotFoundException.class);
}
}
private Block b;
private long offset; // offset of the first byte of the block in the file
private DatanodeInfo[] locs;根据在get阶段的追踪记录我们可以得知namenode.getBlockLocations函数调用是一个RPC调用,最终调用到namenode的getBlockLocations函数上,接下来我们就开始单步调试namenode
2、NameNode端getBlockLocations函数分析
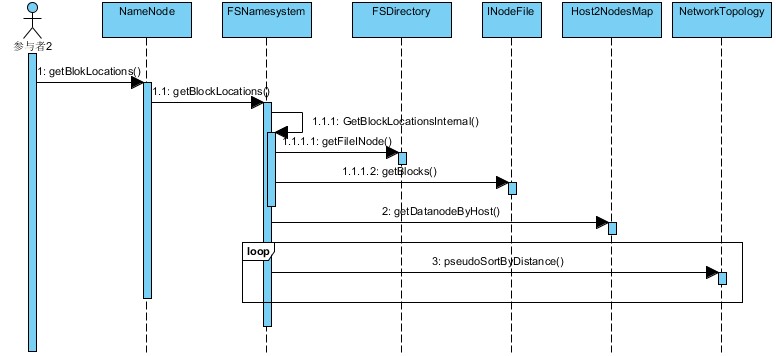
NameNode类的getBlocksLocation函数实现为:
/** {@inheritDoc} */
public LocatedBlocks getBlockLocations(String src,
long offset,
long length) throws IOException {
myMetrics.incrNumGetBlockLocations();
return namesystem.getBlockLocations(getClientMachine(),
src, offset, length);
}其中namesystem在为一个FSNameSystem类型的成员变量, 保存的是NameNode的name space树,其中一个重要的成员变量为FSDirectory dir。 FSDirectory主要包括FSImage fsImage,用于读写硬盘上的fsimage文件,FSImage类有成员变量FSEditLog editLog,用于读写硬盘上的edit文件,这两个文件的关系和作用已经在之前的文章中提到过了,并且也解释了INode, INodeFile, 以及INodeDeirectory等之间的关系。
/**
* Get block locations within the specified range.
*
* @see #getBlockLocations(String, long, long)
*/
LocatedBlocks getBlockLocations(String clientMachine, String src,
long offset, long length) throws IOException {
LocatedBlocks blocks = getBlockLocations(src, offset, length, true, true);
if (blocks != null) {
//sort the blocks
DatanodeDescriptor client = host2DataNodeMap.getDatanodeByHost(
clientMachine); // 根据client的主机IP等找到一个在该主机上运行的DataNode(如果存在的话)
for (LocatedBlock b : blocks.getLocatedBlocks()) {
clusterMap.pseudoSortByDistance(client, b.getLocations()); // 根据网络拓扑结构,将每个block的datanode按照距离client最近的标准进行排序
}
}
return blocks;
} /**
* Get block locations within the specified range.
* @see ClientProtocol#getBlockLocations(String, long, long)
*/
public LocatedBlocks getBlockLocations(String src, long offset, long length,
boolean doAccessTime, boolean needBlockToken) throws IOException {
if (isPermissionEnabled) {
checkPathAccess(src, FsAction.READ);
}
if (offset < 0) {
throw new IOException("Negative offset is not supported. File: " + src );
}
if (length < 0) {
throw new IOException("Negative length is not supported. File: " + src );
}
final LocatedBlocks ret = getBlockLocationsInternal(src,
offset, length, Integer.MAX_VALUE, doAccessTime, needBlockToken); // 实际工作者
if (auditLog.isInfoEnabled() && isExternalInvocation()) {
logAuditEvent(UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser(),
Server.getRemoteIp(),
"open", src, null, null);
}
return ret;
}可以看到最终是调用的getBlockLocationsInternal函数完成的LocatedBlocks的构建过程:
private synchronized LocatedBlocks getBlockLocationsInternal(String src,
long offset,
long length,
int nrBlocksToReturn,
boolean doAccessTime,
boolean needBlockToken)
throws IOException {
INodeFile inode = dir.getFileINode(src); // 通过路径名从文件系统树中找到要打开的文件的INodeFile,其中保存了该文件的INode信息
if(inode == null) {
return null;
}
if (doAccessTime && isAccessTimeSupported()) {
dir.setTimes(src, inode, -1, now(), false);
}
Block[] blocks = inode.getBlocks();
if (blocks == null) {
return null;
}
if (blocks.length == 0) {
return inode.createLocatedBlocks(new ArrayList<LocatedBlock>(blocks.length));
}
List<LocatedBlock> results;
results = new ArrayList<LocatedBlock>(blocks.length);
int curBlk = 0;
long curPos = 0, blkSize = 0;
int nrBlocks = (blocks[0].getNumBytes() == 0) ? 0 : blocks.length;
for (curBlk = 0; curBlk < nrBlocks; curBlk++) { // 这个循环的目的是找到offset所在的block的位置 blkSize = blocks[curBlk].getNumBytes(); // curBlk就指向了offset所在的block
assert blkSize > 0 : "Block of size 0";
if (curPos + blkSize > offset) {
break;
}
curPos += blkSize;
}
if (nrBlocks > 0 && curBlk == nrBlocks) // offset >= end of file
return null;
long endOff = offset + length; // 找到用户请求的length长度的data在文件中的结束位置
do { // 该循环将涉及到从offset开始到endOff结束这段长度的data的block信息收集起来,然后组合成LocatedBlock
// get block locations
int numNodes = blocksMap.numNodes(blocks[curBlk]);
int numCorruptNodes = countNodes(blocks[curBlk]).corruptReplicas();
int numCorruptReplicas = corruptReplicas.numCorruptReplicas(blocks[curBlk]);
if (numCorruptNodes != numCorruptReplicas) {
LOG.warn("Inconsistent number of corrupt replicas for " +
blocks[curBlk] + "blockMap has " + numCorruptNodes +
" but corrupt replicas map has " + numCorruptReplicas);
}
DatanodeDescriptor[] machineSet = null;
boolean blockCorrupt = false;
if (inode.isUnderConstruction() && curBlk == blocks.length - 1
&& blocksMap.numNodes(blocks[curBlk]) == 0) {
// get unfinished block locations
INodeFileUnderConstruction cons = (INodeFileUnderConstruction)inode;
machineSet = cons.getTargets();
blockCorrupt = false;
} else {
blockCorrupt = (numCorruptNodes == numNodes);
int numMachineSet = blockCorrupt ? numNodes :
(numNodes - numCorruptNodes);
machineSet = new DatanodeDescriptor[numMachineSet]; // 找到block对应的machineSet信息并将为损坏的放入集合中
if (numMachineSet > 0) {
numNodes = 0;
for(Iterator<DatanodeDescriptor> it =
blocksMap.nodeIterator(blocks[curBlk]); it.hasNext();) {
DatanodeDescriptor dn = it.next();
boolean replicaCorrupt = corruptReplicas.isReplicaCorrupt(blocks[curBlk], dn);
if (blockCorrupt || (!blockCorrupt && !replicaCorrupt))
machineSet[numNodes++] = dn;
}
}
}
LocatedBlock b = new LocatedBlock(blocks[curBlk], machineSet, curPos,
blockCorrupt);
if(isAccessTokenEnabled && needBlockToken) {
b.setBlockToken(accessTokenHandler.generateToken(b.getBlock(),
EnumSet.of(BlockTokenSecretManager.AccessMode.READ)));
}
results.add(b); // 将machineSet以及block构造的LocatedBlock放入到链表中
curPos += blocks[curBlk].getNumBytes();
curBlk++;
} while (curPos < endOff
&& curBlk < blocks.length
&& results.size() < nrBlocksToReturn);
return inode.createLocatedBlocks(results); // 使用LocatedBlock链表构造一个LocatedBlocks对象然后返回
}
通过RPC调用,在NameNode得到的LocatedBlocks对象,作为成员变量构造DFSInputStream对象,最后包装为FSDataInputStream返回给用户






















 3221
3221

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








