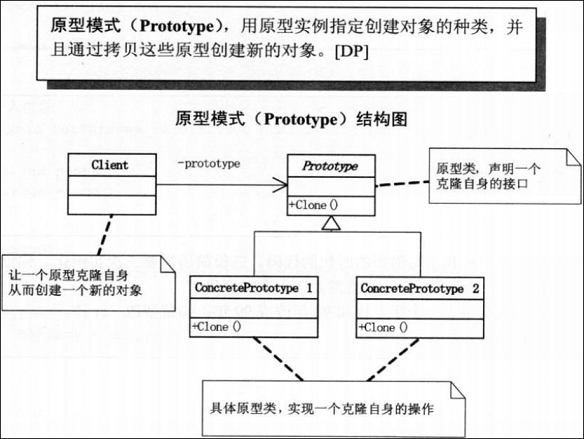
1. 原型模式: 用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。。。
注意: 拷贝的时候是浅拷贝 还是 深拷贝, 来考虑是否需要重写拷贝构造函数。
关键在于: virtual Prototype* clone(); 克隆函数。。。返回一个克隆的对象。
实例: 以深拷贝为例
prototype.h prototype.cpp
#ifndef PROTOTYPE_H
#define PROTOTYPE_H
class Prototype
{
public:
int a;
char *str;
Prototype(int b, char* cstr);
Prototype(const Prototype &cp);
~Prototype();
void show();
virtual Prototype* clone();
};
#endif // PROTOTYPE_H
#include "prototype.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
Prototype::Prototype(int b, char* cstr)
{
a = b;
str = new char[b];
strcpy(str, cstr);
}
Prototype::~Prototype()
{
delete str;
}
Prototype::Prototype(const Prototype &cp)
{
a = cp.a;
str = new char[a];
if(str!=0)
strcpy(str, cp.str);
}
Prototype* Prototype::clone()
{
return new Prototype(a, str);
}
void Prototype::show()
{
printf("a: %d, str: %s\n", a, str);
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "prototype.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Prototype test !" << endl;
Prototype *p = new Prototype(6, "hello");
Prototype *p1 = p->clone();
p1->show();
return 0;
}






















 459
459

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








