Map
HashMap
jdk1.7与jdk1.8的区别
-
底层数据结构,jdk1.7为数组 + 链表,jdk1.8为数组 + 链表 + 红黑树,HashMap本质上是用的数组,链表是用来解决hash冲突的
-
链表添加元素的位置,jdk1.7为头插法(循环引用问题),jdk1.8为尾插法
-
对于key==null的处理,jdk1.7为添加前独立判断,jdk1.8为综合到hash()函数里面
-
先添加再扩容还是先扩容再添加。jdk1.7为先扩容再添加,jdk1.8为先添加再扩容
-
hash()函数的异或次数,jdk1.7为4次,jdk1.8为1次(高16位和低16位异或)
jdk1.8要比jdk1.7多一步考虑红黑树的操作,为什么需要多加一个红黑树呢?主要是为了避免数组的长度过长,链表的的效率是O(n),随着链表的长度增加效率会下降,红黑树的效率是O(logn),在存储大量元素的时候会更占优势
-
比如插入考虑树化,删除考虑反树化,查找考虑树的递归查找
-
扩容的时候会把每个索引位置后边的链表或者红黑树都拆分成两个部分(i、i + oldcap),比如 1 和 17 在容量为 16 的hashmap都是在索引为1的位置,扩容后 1 还是在索引为 1 的位置,但是 17 到了索引为 17 的位置
对于负载因子为什么是0.75而不是更大或者更小的值?
在HashMap里面有个成员变量是threshold,也就是扩容阈值,它等于当前数组的长度 * 负载因子,也就是说扩容阈值正比于负载因子,当负载因子更大,也就是扩容阈值更大,那么HashMap的冲突会增加,当负载因子更小,也就是扩容阈值更小,那么HashMap扩容的次数会增加,元素rehash的次数会增加,效率肯定是没有那么好的,对于0.75我想是原作者思考和实验出来的一个合适的值,能保证冲突减少以及一定的效率
对于HashMap来说,解决hash冲突的办法是链地址法
所以可以看到HashMap底层的数据结构是数组 + 链表这么一种形式,那还有一些其他的解决hash冲突的办法,比如说开放定址法(再次hash找位置)、再hash法(第一个hash函数冲突,使用第二个hash函数,知道找到位置)
HashMap如何实现去重的?
首先判断HashMap中是否存在相同hashCode的元素,如果不存在直接放入,如果存在那么再用equals()比较,相同则不放入HashMap
-
只重写hashcode()不行,默认用的就是Object的equals(),Object类的equals()方法直接用==实现,无法实现语义上的去重
-
只重写equals()不行,默认不同对象的hashcode不同,无法实现语义上的去重(如属性相同的User对象),就不会用到equals()比较
jdk1.7实现
底层是数组 + 链表

static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
}初始化
调用inflateTable()方法进行初始化
初始数组大小默认为16个,负载因子为3/4,数组达到负载因子则进行扩容
hash()函数
先取得key的hashCode,再经过4次异或得到最后hash值

put()
-
如果table[]为空,创建table[]数组
-
如果key == null,会在下标为0位置放入
-
通过hash函数计算key的hashCode的hash值
-
通过hash值和数组长度-1进行&运算(取模运算),得到key在哪个桶
-
如果桶内没有元素,创建新节点,直接插入
-
否则判断首元素是否key相同,是的话,进行 value 替换
-
否则,进行链表查找插入,如果找到了key相同的元素,进行value替换
-
否则插入元素,如果总节点数到达阈值64,先扩容,再头插法添加元素
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 初始化table[]
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
// key为null的entry放到下标为0的地方
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 四次异或hashcode
int hash = hash(key);
// 计算存放的数组下标,hash和数组长度减一进行&运算
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 从数组下标位置开始,遍历链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
// 比较hash和key,判断这个key是否在链表中
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
// key相同,替换链表节点的值
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
// 当前map元素总数 + 1
modCount++;
// 如果总节点数达到阈值并且当前下标不是null,先扩容,再头插法添加元素
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 当前hashMap内节点数量达到阈值,并且这个下标的第一个元素不是null
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
// 2倍扩容
resize(2 * table.length);
// 重新计算这个key在新的table[]的下标位置
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}get()
-
如果key == null,会在下标为0位置查询
-
通过hash函数计算出key的hashCode的hash值
-
如果桶内位置首元素符合,返回结果
-
否则遍历链表
-
找不到返回null
public V get(Object key) {
// key为null的查找
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
// 遍历链表查找
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
// hash扰乱
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
// 计算出下标后,开始链表遍历
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
扩容resize()
-
由于java的数组是没有扩容机制的,HashMap会创建一个更大容量的数组(原容量的2倍)
-
调用transfer()函数,遍历所有桶,把每个桶内所有的元素重新rehash到新的数组
-
更新扩容阈值threshold
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
// 默认以两倍大小扩容
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
// 重新hash原来的元素放到新的table
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
// 更新扩容阈值
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}并发问题
循环死链问题
扩容的时候线程并发产生的循环引用,主要是前插法同时线程并发导致的
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
// 这里很重要
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
// 重新计算下标
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
// 头插法
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
初始转态:(1) -> (35) -> null
// 由于头插法
thread1扩容成功后:(35) -> (1) -> null
// thraed阻塞前的 next 指向的是 (1),恢复后会把(1)又插到新的数组那个位置的链表头
假设thread0卡了一会才进行扩容的时候:(1) -> (35) -> (1)数据覆盖问题
比如A、B线程同时判断出同一个桶内没有元素,一起插入的时候,会存在一个覆盖掉另一个的问题
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
jdk1.8实现
数组 + 链表 + 红黑树

Node结构
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
}TreeNode树节点的结构
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent;
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // 初始化成链表用
boolean red; //是否是红色节点
}初始化
调用resize()方法创建table[]数组
初始数组大小默认为16个,负载因子为3/4,数组达到负载因子则进行扩容

hash()函数
取hashCode的高低16位互相异或

put()
-
通过hash函数计算出key的hashCode的hash值
-
如果table[]为空,通过resize()方法创建table[]数组
-
通过hash值和数组长度-1进行&运算,得到key在哪个桶
-
桶为空,创建新节点,直接插入
-
否则判断桶内元素是否key相同,是的话,进行 value 替换
-
否则判断桶内元素是否是TreeNode,是的话,红黑树插入
-
否则,进行链表查询插入,如果中途找到了key相同的元素,那么进行value替换
-
看看当前链表节点数是否到达8,再看看总节点数是否到达64,到8没到64就扩容;大于8大于64就树化
-
++size > threshold,判断是否需要扩容

public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
++size > threshold
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// table[]为null,调用resize()创建table[]数组
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 如果对应下标没有元素,那么直接创建节点
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 红黑树查找
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
// 链表查找
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// 尾插法
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 链表节点数量到达8,考虑树化,不一定树化,还需要总节点数到达64
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
// p是用来遍历的指针,前面e = p.next,即p = p.next
p = e;
}
}
// key已经在hashMap中存在,只需要替换value即可
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 检查是否需要扩容,和JDK1.7相反,是先插入再检查是否需要扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
红黑树插入putTreeVal()
根据hash值来排序,放左边或者右边
final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,
int h, K k, V v) {
Class<?> kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this;
// 从根节点开始遍历红黑树
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
// 根据hash值判断放左边还是右边
// ph是当前遍历节点的 hash,h是要放置的目标节点的hash
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
// hash相同,如果key相等,return p,外面的函数会对这个节点进行value覆盖
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
// hash相同,则由Comparable接口的比较方法判定
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {
// 在左右子树递归的寻找 是否有key的hash相同,并且equals相同的节点
if (!searched) {
TreeNode<K,V> q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))
return q;
}
// 否则,通过Native方法,决定放置的位置
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
}
// 插入节点
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
// 遍历找到一个叶子节点为空的节点
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next;
TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);
// 根据dir在左边还是右边插入新节点
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
// 还需要维护节点之间的前后关系,这里似乎同时是在维护双向链表关系
xp.next = x;
x.parent = x.prev = xp;
if (xpn != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x;
// balanceInsertion保证红黑树平衡
moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));
return null;
}
}
}get()
-
通过hash函数计算出key的hashCode的hash值
-
如果桶内首元素符合,返回结果
-
首元素是否是TreeNode,是的话,红黑树搜索
-
否则遍历链表
-
找不到返回null
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n, hash; K k;
// first代表下标位置首个元素
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & (hash = hash(key))]) != null) {
// 如果下标位置首个元素就符合,返回
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 否则
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 遍历红黑树
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// e为指针遍历链表
// 因为判断下标首个元素和遍历链表分开了,所以用do while循环
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
// 找不到
return null;
}红黑树搜索getTreeNode()
final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) {
return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null);
}
final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
TreeNode<K,V> p = this;
// 不断遍历红黑树查找
do {
int ph, dir; K pk;
TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
p = pl;
else if (ph < h)
p = pr;
// 如果key相同就返回节点
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if (pl == null)
p = pr;
else if (pr == null)
p = pl;
// 调用Compare接口比较
else if ((kc != null ||
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)
p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;
else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null)
return q;
else
p = pl;
} while (p != null);
return null;
}
扩容resize()
如果是初始化,会默认初始化容量和加载因子
正常扩容的话
-
数组两倍扩容
-
遍历所有桶,重新rehash桶内所有的元素
-
当前桶内位置的首元素后面没有链表或者树,直接插入到新数组
-
首元素后面是红黑树的话,执行split()函数,遍历树所有节点,分成两部分,如果某个部分元素个数<=6,那么退化为链表
-
首元素后面是链表的话,根据e.hash & oldCap == 0,将链表分成lo,hi两个链表,一点点优化(不用rehash),分别放在下标为 j 和 j + oldCap位置,比如原始容量为4,扩容后为8,对于3和5这两个key,3(011)&4(100)的首位是0、5(101)&4(100)的首位是1,就区分开了
-
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
// 两倍扩容
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
//
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
// 初始化走这里,默认初始化
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
//
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
// 遍历Entry数组,开始扩容
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
// 当前下标的首元素后面没有链表或者树,直接插入
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
// 当前下标的首元素后面是树
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
// 当前下标的首元素后面是链表
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
// 尾插法插入
do {
next = e.next;
// e.hash & oldCap == 0,意思是找到分离点
// 比如oldCap = 8(1000),如果结果为0,那么e.hash首位是0,即0~7(0111)
// lo链表放在原位置,hi链表放在j + oldCap
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
// 首个元素为空,直接插入
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
// 链表尾部插入
else
loTail.next = e;
// 修改链表尾部
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
// e指针往后移动,遍历原数组当前下标的链表
} while ((e = next) != null);
// 让链表尾部指向null
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}树化treeifyBin()
-
遍历原链表,把Node转为TreeNode,来创建一个TreeNode链表
-
遍历TreeNode链表,把每个TreeNode加入到红黑树当中
-
没有根节点,直接创建新的根节点,颜色为黑色
-
否则从根节点开始遍历,对比当前节点和叶子节点的hash值得出不同的dir,判断叶子节点插入当前节点左边(-1)还是右边(1),并且要进行左旋或者右旋,来维护红黑树的特性
-
确保给定的根节点是所在桶的第一个节点
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// hd指向链表头,tl指向链表尾部
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
// new一个TreeNode
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
// 尾插法构造TreeNode链表
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
// 把链表转成树
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
TreeNode<K,V> root = null;
// 遍历TreeNode链表
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
// 构造黑色根节点
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
// 已经设置了根节点了
else {
// x是当前TreeNode节点
K k = x.key;
// h是当前节点的hash值
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
// 从根节点开始遍历 准备插入叶子节点
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
// 父节点和当前节点比较hash值
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
// 父节点的hash值大于当前节点hash,插入左边
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
// 否则插入右边
dir = 1;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
// 父节点
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
// 根据上面的dir判断插入哪边
// 假设为左边,左边是null就插入,不为null就继续遍历
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
// 插入
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
// 平衡二叉树,执行左旋还是右旋
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
// 确保给定的根节点是所在桶的第一个节点
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
}取消树化untreeify()
TreeNode转Node,树转成链表
final Node<K,V> untreeify(HashMap<K,V> map) {
Node<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
for (Node<K,V> q = this; q != null; q = q.next) {
Node<K,V> p = map.replacementNode(q, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else
tl.next = p;
tl = p;
}
return hd;
}维护红黑树特性balanceInsertion()
可能涉及左旋或者右旋
static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceInsertion(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> x) {
// 当前节点先设为红色,后面会调整的
x.red = true;
/**
* x: 当前节点
* xp: x的父节点
* xpp: x父节点的父节点
* xppl: x父节点的父节点左子节点
* xppr: x父节点的父节点右子节点
*/
for (TreeNode<K,V> xp, xpp, xppl, xppr;;) {
// 插入的是根节点,直接是黑色
if ((xp = x.parent) == null) {
x.red = false;
return x;
}
// 插入节点的父节点是黑色或者是根节点,红黑树没有被破坏,不需要调整
else if (!xp.red || (xpp = xp.parent) == null)
return root;
// 父节点是红色
// 父节点是祖父节点的左节点
if (xp == (xppl = xpp.left)) {
// 叔叔节点存在且为红色,同时父节点也是红色
if ((xppr = xpp.right) != null && xppr.red) {
// (3)
// 父节点和叔叔节点都改为黑色
// 祖父节点改成红色
// 当前节点变成祖父节点
xppr.red = false;
xp.red = false;
xpp.red = true;
x = xpp;
}
// 叔叔节点为黑色
else {
// (5)当前节点的父节点是红色,且叔叔节点是黑色,当前节点是其父右子节点
if (x == xp.right) {
// 左旋转
root = rotateLeft(root, x = xp);
xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
}
// (4)
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
if (xpp != null) {
// 右旋转
xpp.red = true;
root = rotateRight(root, xpp);
}
}
}
}
// 父节点是祖父节点的右节点,流程和上面一样,只是换了个方向而已
else {
if (xppl != null && xppl.red) {
xppl.red = false;
xp.red = false;
xpp.red = true;
x = xpp;
}
else {
// (7)
if (x == xp.left) {
// 右旋转
root = rotateRight(root, x = xp);
xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
}
// (6)
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
if (xpp != null) {
// 左旋转
xpp.red = true;
root = rotateLeft(root, xpp);
}
}
}
}
}
}
static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateLeft(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> p) {
// p: 当前节点
// r: 当前节点的右儿子
// rl: 当前节点的右儿子的左儿子
TreeNode<K,V> r, pp, rl;
if (p != null && (r = p.right) != null) {
// 当前节点的右儿子的左儿子成为当前节点的右儿子
if ((rl = p.right = r.left) != null)
rl.parent = p;
// 当前节点的右儿子成为当前节点的父节点
if ((pp = r.parent = p.parent) == null)
// 如果当前节点是根节点,那么r的颜色必须是黑色
(root = r).red = false;
else if (pp.left == p)
pp.left = r;
else
pp.right = r;
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
return root;
}
static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateRight(TreeNode<K,V> root,
TreeNode<K,V> p) {
TreeNode<K,V> l, pp, lr;
if (p != null && (l = p.left) != null) {
if ((lr = p.left = l.right) != null)
lr.parent = p;
if ((pp = l.parent = p.parent) == null)
(root = l).red = false;
else if (pp.right == p)
pp.right = l;
else
pp.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
return root;
}左旋右旋
以下红黑树部分参考HashMap源码分析putTreeVal(红黑树部分)——java学习总结(11)-CSDN博客
插入的节点一开始默认都为红色,左左(指的是父节点是祖父节点的左孩子,自己是父节点的左孩子)
-
无需调整:父节点是黑色
-
变色:父节点是红色并且叔父节点也是红色
-
变色 + 旋转:父节点是红色,叔父节点是黑色
| 无需调整 | 【变色】即可实现平衡 | 【旋转+变色】才可实现平衡 |
|---|---|---|
| (1)当父节点为黑色时直接插入子节点 | (2)空树插入根节点,将根节点红色变为黑色 | (4)父节点为红色左节点,叔父节点为黑色,插入左子节点,那么通过【左左节点旋转】 |
| (3)父节点和叔父节点都为红色,则将父节点和叔父结点置为黑色,再将祖父结点置为红色,再递归向上处理(将祖父结点视为新插入的结点,将父节点和叔父节点看作黑色的null) | (5)父节点为红色左节点,叔父节点为黑色,插入右子节点,那么通过【左右节点旋转】 | |
| (6)父节点为红色右节点,叔父节点为黑色,插入左子节点,那么通过【右左节点旋转】 | ||
| (7)父节点为红色右节点,叔父节点为黑色,插入右子节点,那么通过【右右节点旋转】 |
(4)左左节点旋转

(5)左右节点旋转

(6)右左节点旋转

(7)右右节点旋转

数据覆盖问题
比如A、B线程同时判断出同一个桶内没有元素,一起插入的时候,会存在一个覆盖掉另一个的问题
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap是线程并发安全的hashmap,所以他会解决hashmap的一些线程问题(使用CAS或者锁),比如jdk1.7的循环引用问题或者说是数据覆盖问题
jdk1.7与jdk1.8的区别
jdk1.7可以理解为hashmap拆成了很多份,把每个小的hashmap锁起来了,只有获取到锁才能写这个小的hashmap,读不受影响
jdk1.8沿用了原生的hashmap,只不过在写操作的时候,索引首元素用CAS,首元素后面的插入会用synchronized锁起来
-
数据结构:取消了 Segment 分段锁的数据结构,取而代之的是数组+链表+红黑树的结构。
-
保证线程安全机制:JDK1.7 采用 Segment 的分段锁机制实现线程安全,其中 Segment 继承自 CAS + ReentrantLock 。JDK1.8 采用 CAS + synchronized 保证线程安全。
-
锁的粒度降低:JDK1.7 是对需要进行数据操作的 Segment 加锁,JDK1.8 调整为对每个数组元素加锁(Node)。
jdk1.7实现
segment数组 + hashEntry数组 + 链表

初始化
-
初始化segment数组的大小,默认为16,如果不是2^n,则向上取整(比如segment数组的大小传入10,其实还是16)
-
初始化entry数组的大小,默认是2,同样需要向上取整,为什么要向上取整,因为hash函数要与操作
-
然后segment数组首个元素先创造一个segment对象,方便之后put()快速创建新的segment对象
// initialCapacity是entry数组的初始容量
// concurrencyLevel是segment数组的初始容量
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS)
concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS;
// Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments
int sshift = 0;
// segment数组的长度,一定是2的倍数
int ssize = 1;
while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {
++sshift;
ssize <<= 1;
}
this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;
this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
// c代表每个entry数组至少要有的初始容量
int c = initialCapacity / ssize;
if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)
++c;
// 和c比较,找到entry数组的初始容量cap,一定是2的倍数,最小是2
int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;
while (cap < c)
cap <<= 1;
// 创建 segments and segments[0],创建segments[0]是为了加快以后创建segment[?]
Segment<K,V> s0 =
new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor),
(HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]);
Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize];
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0]
this.segments = ss;
}put()
-
通过第一次hash函数(hashcode和segment数组长度减一进行与运算)算出key对应的segment数组的下标
-
判断这个位置是否需要创建segment对象,如果需要,获取segment[0]的信息可以快速创建segment对象,通过CAS保证创建segment对象是并发安全的
-
trylock()尝试上锁,获取锁成功才能插入元素,否则进入自旋锁操作(期间可以遍历链表,看看是否要创建新元素,如果别的线程插入修改了链表的头节点,就去重新遍历链表,如果自旋次数太多就阻塞)
-
获取锁成功的话,后续流程参照HashMap,每个Segment都是一个小的HashMap嘛

private Segment<K,V> ensureSegment(int k) {
final Segment<K,V>[] ss = this.segments;
long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; // raw offset
Segment<K,V> seg;
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) {
// 构造器有先创建segment[0],这时候获取,方便快速生成segment[?]
Segment<K,V> proto = ss[0]; // use segment 0 as prototype
int cap = proto.table.length;
float lf = proto.loadFactor;
int threshold = (int)(cap * lf);
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap];
// 双重检查,避免调用UNSAFE开销
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) { // recheck
Segment<K,V> s = new Segment<K,V>(lf, threshold, tab);
// 自旋的CAS操作compareAndSwapObject,尝试创建segment[?],保证只有一个线程创建成功
while ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s))
break;
}
}
}
return seg;
}
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// 调用lock.tryLock()尝试获取锁,有了锁才能进行写操作,保证线程安全
// 如果获取锁失败,调用scanAndLockForPut()等待
HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
// 计算出key在entry数组的位置
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index);
// 遍历链表
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
// 如果key相同,则覆盖旧value
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first);
int c = count + 1;
// entry数组当前元素到达阈值threshold,entry数组扩容
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
rehash(node);
else
// 找到了空位,直接放到entry数组对应位置
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}获取锁的自旋操作scanAndLockForPut()
先做一些准备工作,直到获取锁
-
准备个新节点,找到它的位置
-
获取锁一直失败导致循环次数太多,那么直接lock()阻塞
-
偶数次循环的时候如果发现链表头节点变化,那么重新遍历
private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash);
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
HashEntry<K,V> node = null;
// 用于记录获取锁的次数
int retries = -1; // negative while locating node
// 如果获取失败,就会去进行一些准备工作
while (!tryLock()) {
HashEntry<K,V> f; // to recheck first below
if (retries < 0) {
// entry数组该位置没有元素,先准备个新节点,让获取锁后插入速度更快
if (e == null) {
if (node == null) // speculatively create node
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null);
retries = 0;
}
// 判断 key 是否有重复的,进行替换value就好了
else if (key.equals(e.key))
retries = 0;
// 否则顺着链表往下走
else
e = e.next;
}
// 重试次数太多,使用lock()阻塞方法,避免CPU空转,消耗CPU资源
else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {
lock();
break;
}
// (retries & 1) == 0 是偶数次数才进行后面的判断
// f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first 新元素插入使得表头被改变了
else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&
(f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {
// 修改当前节点,重新开始遍历
e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changed
retries = -1;
}
}
// 将准备工作制作好的节点返回
return node;
}
get()
无锁,因为Node的value和next是用volatile修饰了,其他线程的修改对本线程可见
public V get(Object key) {
Segment<K,V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab;
int h = hash(key);
// 计算segment的下标位置
long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
// UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile()保证segment可见性
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&
(tab = s.table) != null) {
// 遍历查找
// UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile()确保不会和写操作产生并发问题
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile
(tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);
e != null; e = e.next) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}扩容机制rehash()
segment数组大小初始化之后不会改变,hashentry数组的扩容和hashMap一样
遍历一遍链表,找到一个lastRun/lastIdx(通过hashCode & oldtable.length看1、0),这个节点以后都是要rehash到相同位置的
private void rehash(HashEntry<K,V> node) {
HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable =
(HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity];
int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) {
HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i];
if (e != null) {
HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
// idx 是要存放的新的下标位置
int idx = e.hash & sizeMask;
// 只有1个节点,直接放入就好了
if (next == null) // Single node on list
newTable[idx] = e;
// 遍历链表
else { // Reuse consecutive sequence at same slot
HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e;
int lastIdx = idx;
// 找到一个lastRun,这个节点后面都是一起要放到newTable[?]或者newTable[? + oldcap]
for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next;
last != null;
last = last.next) {
int k = last.hash & sizeMask;
// 这里的意思是后续节点必须计算下标是同一个下标
// 要么都是?,要么都是? + oldcap,不断更新lastRun
if (k != lastIdx) {
lastIdx = k;
lastRun = last;
}
}
// 虽然会多遍历1次链表,但是如果lastRun在链表前半部分,这样节省很多功夫
newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun;
// lastRun之前的节点遍历放到正确位置
for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
V v = p.value;
int h = p.hash;
int k = h & sizeMask;
HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k];
newTable[k] = new HashEntry<K,V>(h, p.key, v, n);
}
}
}
}
// 将新的 node 放到新数组中刚刚的两个链表之一的头部
int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; // add the new node
node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]);
newTable[nodeIndex] = node;
table = newTable;
}remove()
final V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) {
// 获取锁
if (!tryLock())
scanAndLock(key, hash);
V oldValue = null;
try {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
// 计算下标位置
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry<K,V> e = entryAt(tab, index);
// 前驱节点,用来删除元素
HashEntry<K,V> pred = null;
// 遍历链表
while (e != null) {
K k;
HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
// 找到了被删除的元素
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
V v = e.value;
if (value == null || value == v || value.equals(v)) {
// 只有下标一个元素,下标位置置为null
if (pred == null)
setEntryAt(tab, index, next);
// 删除节点
else
pred.setNext(next);
++modCount;
--count;
oldValue = v;
}
break;
}
pred = e;
e = next;
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}jdk1.8实现
node数组 + 链表 + 红黑树

初始化
如果node数组为空,利用CAS创建node数组,默认大小为16个,默认扩展因子是0.75
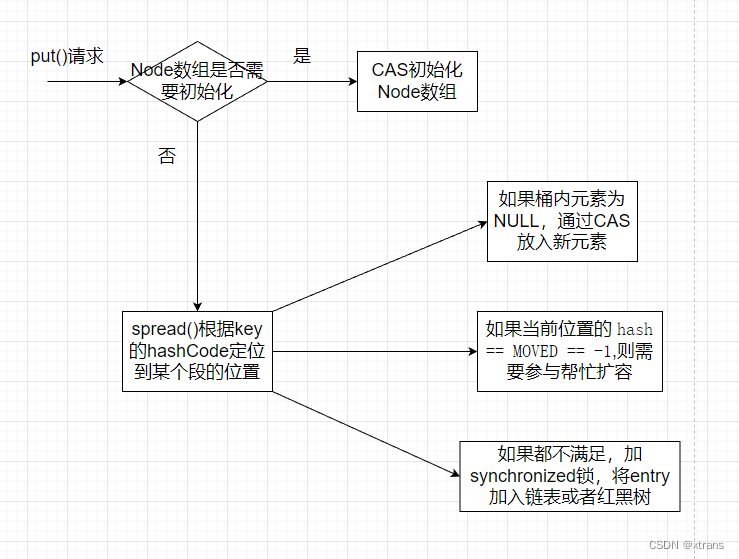
put()
-
根据 key 计算出 hash
-
判断node数组是否已经初始化,没有就初始化node数组
-
hash出下标,如果为空,CAS尝试写入
-
如果当前位置的
hash == MOVED == -1,则需要参与帮忙扩容 -
如果都不满足,加synchronized锁,将entry加入链表或者红黑树
-
判断是否需要树化
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
// CAS操作创建
else if (U.compareAndSetInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; K fk; V fv;
// node数组为空,先创建ndoe数组
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// 下标位置没有元素,CAS尝试放入
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// 树化或者在扩容
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else if (onlyIfAbsent // check first node without acquiring lock
&& fh == hash
&& ((fk = f.key) == key || (fk != null && key.equals(fk)))
&& (fv = f.val) != null)
return fv;
else {
V oldVal = null;
// 当前node加synchronized锁,后面的操作和HashMap基本一样了
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
else if (f instanceof ReservationNode)
throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update");
}
}
// 判断链表是否需要树化
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 里面看看是否需要扩容
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}get()
无锁,因为Node的value和next是用volatile修饰了,其他线程的修改对本线程可见
-
根据key计算出hash
-
查找到指定位置,如果头节点是key相同,直接返回
-
如果hash<0,说明在扩容或者是红黑树,查找红黑树
-
否则查找链表
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
// 下标位置的节点就是要找的节点
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
// 在红黑树上或者正在扩容
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
// 遍历链表
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
// 找不到返回null
return null;
}扩容机制transfer()
运用到了多线程,每个线程默认处理16个桶
ForwardingNode结构表示这个节点开头的那部分节点们正在迁移,用CAS操作让线程去取得迁移这个部分节点的权力
当所有节点迁移完成,finish = true
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
// 做扩容的线程至少处理16个桶
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("uncheckzheed")
// 容量翻倍
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
// 正在被迁移的 Node
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
// 做完了一个位置的迁移工作,可以准备做下一个位置的了
boolean advance = true;
// 所有桶是否都已迁移完成
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
else if (U.compareAndSetInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
if (U.compareAndSetInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
// 具体的扩容迁移操作
else {
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
if (fh >= 0) {
// 下面这一块和 Java7 中的 ConcurrentHashMap 迁移是差不多的,
// 需要将链表一分为二,
// 找到原链表中的 lastRun,然后 lastRun 及其之后的节点是一起进行迁移的
// lastRun 之前的节点需要进行克隆,然后分到两个链表中
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
// 红黑树的迁移
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
// 如果一分为二后,节点数少于 8,那么将红黑树转换回链表
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
else if (f instanceof ReservationNode)
throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update");
}
}
}
}
}remove()
final V replaceNode(Object key, V value, Object cv) {
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||
(f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null)
break;
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
boolean validated = false;
// 获取锁
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 遍历链表
if (fh >= 0) {
validated = true;
for (Node<K,V> e = f, pred = null;;) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
V ev = e.val;
if (cv == null || cv == ev ||
(ev != null && cv.equals(ev))) {
oldVal = ev;
if (value != null)
e.val = value;
else if (pred != null)
pred.next = e.next;
else
setTabAt(tab, i, e.next);
}
break;
}
pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null)
break;
}
}
// 遍历红黑树
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
validated = true;
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> r, p;
if ((r = t.root) != null &&
(p = r.findTreeNode(hash, key, null)) != null) {
V pv = p.val;
if (cv == null || cv == pv ||
(pv != null && cv.equals(pv))) {
oldVal = pv;
if (value != null)
p.val = value;
else if (t.removeTreeNode(p))
setTabAt(tab, i, untreeify(t.first));
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof ReservationNode)
throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update");
}
}
if (validated) {
if (oldVal != null) {
if (value == null)
addCount(-1L, -1);
return oldVal;
}
break;
}
}
}
return null;
}




















 2387
2387











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








