io分类
在JDK中提供了IO类的支持。这些类都在java.io包中。
1. 根据方向的划分: 输入流和输出流
2. 根据数据的单位划分: 字节流和字符流。
3. 根据功能的划分: 节点流和处理流(缓冲流)
字节流就是流中数据以字节为单位(byte)。特别适用于音频、视频、图片等二进制文件的输入、输出操作。
字符流就是流中数据以字符为单位。存在的意义:高效、方便的读取文本数据。此处需要注意的是字符流单位可能是一个字节,可能是多个字节。
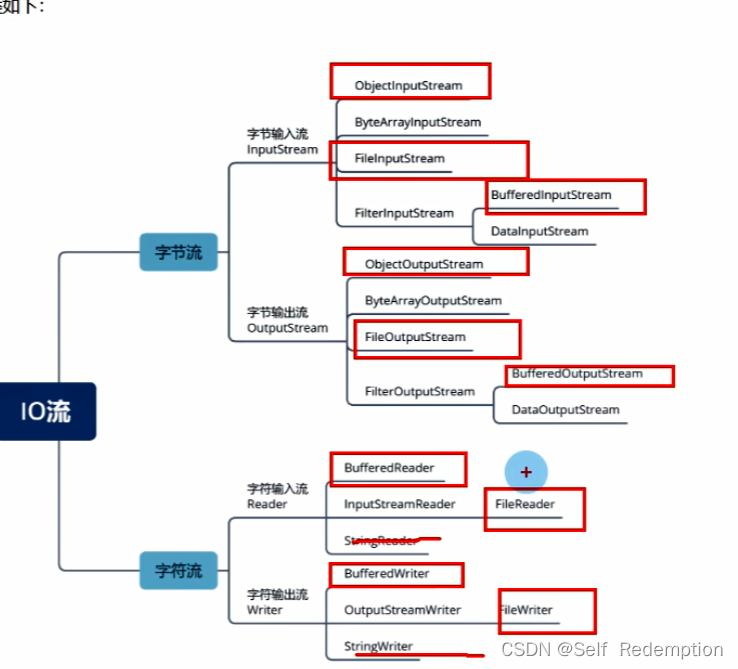
API解析

字符输入流使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建文件对象
File file = new File("D:/io/a.txt");
//使用字节输入流读取文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int read;//读取文件中的内容
while ((read = fis.read()) != -1){
System.out.println(read);
}
fis.close();
}
字符输出流使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建文件对象
File file = new File("D:/io/d.txt");
//创建字节输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
//向文件中输出
fos.write("abc".getBytes());
fos.close();
}
使用字节流复制文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建字节输入流读取文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("d:/io/test.png"));
//创建字节输出流输出文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("d:/io/test_copy.png"));
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int length; //每一次读取的长度, 全部读取完成返回-1
while ((length = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
//System.out.println(red);
fos.write(bytes, 0, length);
}
long l1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(l1 - l);
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
字符输出流,输出流的api

字符输入流代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建字符输入流对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("d:/io/a.txt"));
int read;
while ((read = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)read); //你好吗
}
fr.close();
//创建字节输入流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("d:/io/a.txt"));
int read1;
while ((read1 = fis.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char) read1); //ä½å
}
fis.close();
}
字符输出流代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*
* 参数1: 输出文件对象
* 参数2: true: 追加
* false: 覆盖原有内容
* */
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File("d:/io/aa.txt"),true);
//可以写字符串
fw.write("你好吗");
fw.close();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("d:/io/abc.txt"));
//只能写字节
fos.write("你好吗".getBytes());
fos.close();
}
总结
其实只有字节流,没有字符流。字符流的底层还是字节流,进行了封装转换,是开发者可以更简单的来处理非英文字符
字节流可以完成所有类型文件的复制(文本、音频、视频、图片、chm)
字符流只可以完成文本文件的复制(txt、java), 字符流一般用来处理中文的文本文件
try-with-source
try-with-source 是java 7引入的。主要是为了解决因为忘记关闭资源而导致的性能问题和调用关闭方法而导致的代码结构乱的问题。
语法
try(需要在finally关闭的资源对象定义,可以写多条代码){
}catch(){
}
我们发现和普通的try-catch相似, 但是在try后面多个一个括号。
定义到括号里面的对象会自动关闭资源。
字符流, 将a.txt中的文本内容拷贝到b.txt中
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
//1.创建字符输入流对象
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("D:/io/a.txt");
//2.创建字符输出流对象
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("D:/io/b.txt");)
{
//3.读取
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int length; //每次读取的长度
while ((length = fileReader.read(chars)) != -1) {
//4.输出
fileWriter.write(chars, 0, length);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}```
缓冲流
Java IO中BufferedXXX相关的流统称缓冲流。其本质就是在输入输出时添加缓冲区,减少磁盘IO的次数, 这样可以提高读写效率,同时也可以反复读取。
缓冲流称为上层流(高效流),其底层必须有字节流或字符流。当使用完成后关闭缓冲流,字节流或字符流也会随之关闭。
可以使用flush()刷新(清空)缓冲区内容,把内容输出到目的地。
当缓存区满了以后会自动刷新。在代码中当关闭流时,底层自动调用flush()方法。
字节缓冲流
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建一个输入流和输出流
InputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("e:/JDK_API.CHM"));
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("e:/JDK_API2.CHM"));
//默认输入缓冲区大小8192
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
//默认输出缓冲区大小8192
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//2.使用输入流和输出流完成文件复制
/*
int n; //读取一个字节,赋给n
while((n = bis.read()) != -1){
//写一个字节
bos.write(n);
}
*/
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int n; //每次读取数组长度放入输入缓存池
while((n = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){
//输出数组中指定长度的字节到输出缓存池
bos.write(bytes, 0, n);
}
//3.关闭输入流和输出流
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
字符缓冲流
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建两个流
BufferedReader br =
new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("d:/io/a.txt")));
BufferedWriter bw =
new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("d:/io/a_copy.txt"));
//使用两个缓冲流完成按行输入, 输出的功能
String str;//每次读取一行
while((str = br.readLine()) != null ){
bw.write(str); //每次写一行
bw.newLine(); //bw.write("\r\n");不同操作系统中换行符是不同的
}
//关闭两个流
br.close();
bw.close();
}
总结
总结1:BufferedReader和BufferedWriter的优点
- 速度快
- 简化编程
总结2:readLine()底层的原理
- 底层还是一个一个字符的读取,append()放入到StringBuilder(或者char[] )中,遇到换行符 ,将StringBuilder(char[])转换成String并返回
总结3:不同的操作系统中换行符是不同的
- Unix系统里,每行结尾只有“<换行>”,即“\n”;
- Windows系统里面,每行结尾是“<回车><换行>”,即“\r\n”;
- Mac系统里,每行结尾是“<回车>”,即“\r”。




















 142
142











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








