加入神经网络的意义
* 前面也讲到了,使用普通的训练方法,也可以进行识别,但是识别的精度不够高,因此我们需要对其进行提升,其实MNIST官方提供了很多的组合方法以及测试精度,并做成了表格供我们选用,谷歌官方为了保证教学的简单性,所以用了最简单的卷积神经网络来提升这个的识别精度,原理是通过强化它的特征(比如轮廓等),其实我也刚学,所以能看懂就说明它确实比较简单。 * 我的代码都是在0.7版本的tensorflow上实现的,建议看一下前两篇文章先。
流程和步骤
其实流程跟前面的差不多,只是在softmax前进行了卷积神经网络的操作,所也就不仔细提出了,这里只说卷积神经网络的部分。 如第一篇文章所说,我们的卷积神经网络的,过程是卷积->池化->全连接.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding, use_cudnn_on_gpu=None, name=None)
Computes a 2-D convolution given 4-D input and filter tensors.
Given an input tensor of shape [batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels] and a filter / kernel tensor of shape [filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels], this op performs the following:
Flattens the filter to a 2-D matrix with shape [filter_height * filter_width * in_channels, output_channels].
Extracts image patches from the the input tensor to form a virtual tensor of shape [batch, out_height, out_width, filter_height * filter_width * in_channels].
For each patch, right-multiplies the filter matrix and the image patch vector.
In detail,output[b, i, j, k] =
sum_{di, dj, q} input[b, strides[1] * i + di, strides[2] * j + dj, q] *
filter[di, dj, q, k]Must have strides[0] = strides[3] = 1. For the most common case of the same horizontal and vertices strides, strides = [1, stride, stride, 1].
Args:
input: A Tensor. Must be one of the following types: float32, float64.
filter: A Tensor. Must have the same type as input.
strides: A list of ints. 1-D of length 4. The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of input.
padding: A string from: “SAME”, “VALID”. The type of padding algorithm to use.
use_cudnn_on_gpu: An optional bool. Defaults to True.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A Tensor. Has the same type as input.
tf.nn.max_pool(value, ksize, strides, padding, name=None)
Performs the max pooling on the input.
Args:
value: A 4-D Tensor with shape [batch, height, width, channels] and type float32, float64, qint8, quint8, qint32.
ksize: A list of ints that has length >= 4. The size of the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
strides: A list of ints that has length >= 4. The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor.
padding: A string, either ‘VALID’ or ‘SAME’. The padding algorithm.
name: Optional name for the operation.
Returns:
A Tensor with the same type as value. The max pooled output tensor.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
然后得到的结果再跟之前的一样,使用softmax等方法训练即可得到参数。
RELU激活函数
激活函数有很多种,最常用的是以下三种
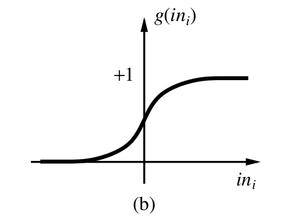
Sigmoid
将数据映射到0-1范围内
#### 公式如下
####函数图像如下
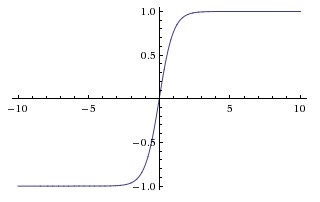
Tanh
将数据映射到-1-1的范围内
公式如下
函数图像如下
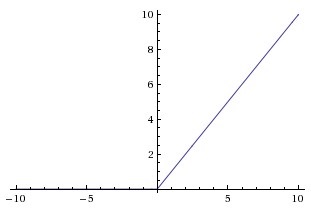
RELU
小于0的值就变成0,大于0的等于它本身
函数图像
具体的参考这个http://blog.csdn.net/u012526120/article/details/49149317
dropout的作用
以前学习数学我们常用到一种方法,叫做待定系数法,就是给定2次函数上的几个点,然后求得2次函数的参数。
一样的道理,我们这里用格式训练集训练,最后训练得到参数,其实就是在求得一个模型(函数),使得它能跟原始数据的曲线进行拟合(说白了,就是假装原始数据都在我们计算出来的函数上)
但是这样不行啊,因为我们还需要对未知数据进行预测啊,如果原始的数据点都在(或者大多数都在)函数上了(这就是过拟合),那会被很多训练数据误导的,所以其实只要一个大致的趋势函数就可以了
所以Dropout函数就是用来,减少某些点的全连接(可以理解为把一些点去掉了),来防止过拟合
具体的看这个http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/p/3258122.html
代码
- 水完了,看代码吧,注释上有写一些变量的维度,大家可以一步步地看过去,计算过去
- https://github.com/wlmnzf/tensorflow-train/blob/master/mnist/cnn_mnist.py








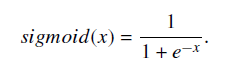
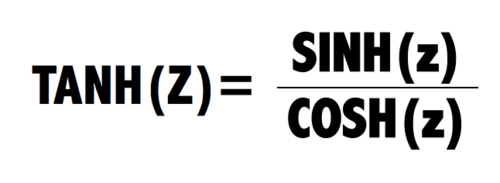














 1926
1926

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








