Time Limit: 2.0 Seconds Memory Limit:65536K
Total Runs: 225 Accepted Runs:55
There are N birds in a 2D space, let x and y denote their coordinate in each dimension.
As an excellent shooter, you can shoot down all the birds in the 2D space. But you think that's too cruel.
In order to make the shooting procedure more interesting, you come up with a rule:
At the beginning, you can choose any bird to shoot.
Afterwards, you can only shoot the bird whose coordinate is not smaller than the previous one in each dimension.
For example, if you want to shoot three birds a, b and c then the following relationship must hold:
xa≤xb, ya≤yb, xb≤xc, yb≤yc.
With this rule and coordinates of all the N birds, can you figure out how many birds you can shoot as many as possible?
Input
First line will be a positive integer T indicating the test case number. Following there are T (1≤T≤10) test cases.
Each test case begins with a positive integer N (1≤N≤100000), the number of birds.
Then following N lines with two positive integers x and y (1≤x,y≤100000), which are the coordinates of each bird (you can assume no two birds have the same coordinates).
Output
For each test case output only one integer representing the maximal number of birds you can shoot.
Sample Input
2 3 1 1 2 2 3 3 3 1 1 2 3 3 2
Sample Output
3 2
直接按照x排序,求y的最长不下降子序列,nlogn写法
感谢王大神指导
#define DeBUG #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <string> #include <set> #include <sstream> #include <map> #include <list> #include <bitset> using namespace std ; #define zero {0} #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define EPS 1e-6 typedef long long LL; const double PI = acos(-1.0); //#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") inline int sgn(double x) { return fabs(x) < EPS ? 0 : (x < 0 ? -1 : 1); } #define N 100005 struct Point { int x, y; }; int cmp(Point a, Point b) { if (a.x == b.x) return a.y < b.y; return a.x < b.x; } int main() { #ifdef DeBUGs freopen("C:\\Users\\Sky\\Desktop\\1.in", "r", stdin); #endif int T; scanf("%d", &T); while (T--) { int n; Point p[N]; int a[N]; scanf("%d", &n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &p[i].x, &p[i].y); } sort(p, p + n, cmp); int top = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int l = 0, r = top - 1, mid; while (l <= r) { mid = (l + r) >> 1; if (a[mid] <= p[i].y) l = mid + 1; else r = mid - 1; } if (l == top) a[top++] = p[i].y; else a[l] = p[i].y; } // for(int i=0;i<top;i++) // { // printf("%d,", a[i]); // } // printf("\n"); printf("%d\n", top); } return 0; }
最长上升子序列nlogn
HDU1024 Constructing Roads In JGShining's Kingdom
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65536/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 3 Accepted Submission(s) : 1
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
JGShining's kingdom consists of 2n(n is no more than 500,000) small cities which are located in two parallel lines. Half of these cities are rich in resource (we call them rich cities) while the others are short of resource (we call them poor cities). Each poor city is short of exactly one kind of resource and also each rich city is rich in exactly one kind of resource. You may assume no two poor cities are short of one same kind of resource and no two rich cities are rich in one same kind of resource. With the development of industry, poor cities wanna import resource from rich ones. The roads existed are so small that they're unable to ensure the heavy trucks, so new roads should be built. The poor cities strongly BS each other, so are the rich ones. Poor cities don't wanna build a road with other poor ones, and rich ones also can't abide sharing an end of road with other rich ones. Because of economic benefit, any rich city will be willing to export resource to any poor one. Rich citis marked from 1 to n are located in Line I and poor ones marked from 1 to n are located in Line II. The location of Rich City 1 is on the left of all other cities, Rich City 2 is on the left of all other cities excluding Rich City 1, Rich City 3 is on the right of Rich City 1 and Rich City 2 but on the left of all other cities ... And so as the poor ones. But as you know, two crossed roads may cause a lot of traffic accident so JGShining has established a law to forbid constructing crossed roads. For example, the roads in Figure I are forbidden.In order to build as many roads as possible, the young and handsome king of the kingdom - JGShining needs your help, please help him. ^_^ 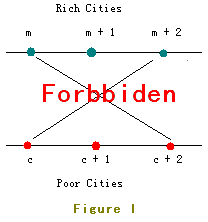
Input
Each test case will begin with a line containing an integer n(1 ≤ n ≤ 500,000). Then n lines follow. Each line contains two integers p and r which represents that Poor City p needs to import resources from Rich City r. Process to the end of file.Output
For each test case, output the result in the form of sample. You should tell JGShining what's the maximal number of road(s) can be built.Sample Input
2 1 2 2 1 3 1 2 2 3 3 1Sample Output
Case 1: My king, at most 1 road can be built. Case 2: My king, at most 2 roads can be built.
#define DeBUG #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <string> #include <set> #include <sstream> #include <map> #include <list> #include <bitset> using namespace std ; #define zero {0} #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define EPS 1e-6 #define TRUE true #define FALSE false typedef long long LL; const double PI = acos(-1.0); //#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") inline int sgn(double x) { return fabs(x) < EPS ? 0 : (x < 0 ? -1 : 1); } #define N 500010 struct Node { int a, b; }; Node c[N]; int B[N] = zero; int cmp(Node a1, Node a2) { if (a1.a == a2.a) return a1.b < a2.b; return a1.a < a2.a; } int Bsearch(int *b, int len, int w) { int left = 0, right = len - 1; int mid; while (left <= right) { mid = (left + right) >> 1; if (b[mid] > w) right = mid - 1; else if (b[mid] < w) left = mid + 1; else return mid; } return left; } int LIS(int n) { memset(B,0,sizeof(B)); int len = 1; B[0] = c[0].b; int pos = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { if (c[i].b > B[len - 1]) { B[len] = c[i].b; len++; } else { pos = Bsearch(B, len, c[i].b); B[pos] = c[i].b; } } return len; } int cnt = 1; int main() { #ifdef DeBUGs freopen("C:\\Users\\Sky\\Desktop\\1.in", "r", stdin); #endif int n; while (scanf("%d", &n) + 1) { printf("Case %d:\n", cnt++); memset(c, 0, sizeof(c)); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &c[i].a, &c[i].b); } sort(c, c + n, cmp); int num = LIS(n); if (num == 1) printf("My king, at most %d road can be built.\n\n", num); else printf("My king, at most %d roads can be built.\n\n", num); } return 0; }






















 250
250

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








