最近刷题遇到很多与最长公共子序列或者子串有关的题,这里回顾一下两者的求解过程以及怎么输出打印。
最长公共子串(Longest Common Substring)与最长公共子序列(Longest Common Subsequence)的区别: 子串要求在原字符串中是连续的,而子序列则只需保持相对顺序,并不要求连续。
问题描述:
给定两个序列:X[1…m]和Y[1…n],求在两个序列中同时出现的最长子序列的长度。
假设 X 和 Y 的序列如下:
str1:"ABCBDAB"
str2:"BDCABA"经典的解法是使用动态规划来解:
假设Z=z1,z2,⋯,zk>是X与Y的LCS, 我们观察到
如果Xm=Yn,则Zk=Xm=Yn,有Zk−1是Xm−1与Yn−1的LCS;
如果Xm≠Yn,则Zk是Xm与Yn−1的LCS,或者是Xm−1与Yn的LCS。
因此,求解LCS的问题则变成递归求解的两个子问题。但是,上述的递归求解的办法中,重复的子问题多,效率低下。改进的办法——用空间换时间,用数组保存中间状态,方便后面的计算。这就是动态规划(DP)的核心思想了。
状态转移方程式如下:
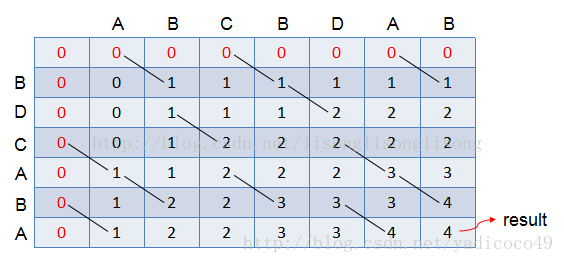
其实用矩阵图来表示会更加清楚:
矩阵的最后的值就是最长公共子序列的长度,而在打印所有的最长公共子序列时,也是沿着最后一个点向上溯源找,如果str1.charAt(i) == str2.charAt(j),记录这个序列点,然后向斜对角线方向继续寻找。而当table[i-1][j] > table[i][j-1](这里的table指上面的二维数组),向左边方向继续寻找序列点;当table[i-1][j] < table[i][j-1],向上方向寻找序列点。而当存在table[i-1][j]==table[i][j-1]时,说明存在不同的最长公共子序列,则进一步递归寻找。
public class LongestCommonSubsequence {
private String X;
private String Y;
private int[][] table; // 动态规划表
private TreeSet<String> set = new TreeSet<String>();
/**
* 功能:带参数的构造器
*/
public LongestCommonSubsequence(String X, String Y) {
this.X = X;
this.Y = Y;
}
/**
* 功能:求两个数中的较大者
*/
private int max(int a, int b) {
return (a>b) ? a:b;
}
/**
* 功能:构造表,并返回X和Y的LCS的长度
*/
private int lcs(int m, int n) {
table = new int[m+1][n+1]; // 表的大小为(m+1)*(n+1)
for(int i=0; i<m+1; ++i) {
for(int j=0; j<n+1; ++j) {
// 第一行和第一列置0
if (i == 0 || j == 0)
table[i][j] = 0;
else if(X.charAt(i-1) == Y.charAt(j-1))
table[i][j] = table[i-1][j-1] + 1;
else
table[i][j] = max(table[i-1][j], table[i][j-1]);
}
}
return table[m][n];
}
/**
* 功能:回溯,求出所有的最长公共子序列,并放入set中
*/
private void traceBack(int i, int j, String lcs_str) {
while (i>0 && j>0) {
if (X.charAt(i-1) == Y.charAt(j-1)) {
lcs_str += X.charAt(i-1);
--i;
--j;
}
else {
if (table[i-1][j] > table[i][j-1])
--i;
else if (table[i-1][j] < table[i][j-1])
--j;
else { // 相等的情况
traceBack(i-1, j, lcs_str);
traceBack(i, j-1, lcs_str);
return;
}
}
}
set.add(reverse(lcs_str));
}
/**
* 功能:字符串逆序
*/
private String reverse(String str) {
StringBuffer strBuf = new StringBuffer(str).reverse();
return strBuf.toString();
}
/**
* 功能:外部接口 —— 打印输出
*/
public void printLCS() {
int m = X.length();
int n = Y.length();
int length = lcs(m,n);
String str = "";
traceBack(m,n,str);
System.out.println("The length of LCS is: " + length);
for(String s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
/**
* 功能:main方法 —— 程序的入口
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence("ABCBDAB","BDCABA");
lcs.printLCS();
}
}
而最长公共子串则强调连续的条件,因此其状态转移方程式为:
最长公共子串在二维数组中则表现为连续的对角线数值不为0。其中数值最大则为最长公共子串的长度。而在输出打印所有最长公共子串时,可以遍历寻找数值为最长公共子串的长度,之后沿着对角线遍历寻找最长公共子串。
public class LongestCommonSubstring {
private String X;
private String Y;
private int[][] table; // 动态规划表
private TreeSet<String> set = new TreeSet<String>();
/**
* 功能:带参数的构造器
*/
public LongestCommonSubstring(String X, String Y) {
this.X = X;
this.Y = Y;
int m=X.length();
int n=Y.length();
System.out.println("The length of the longest substring is "+lcs(m,n));
}
/**
* 功能:构造表,并返回X和Y的LCS的长度
*/
private int lcs(int m, int n) {
int result=0;//记录最长公共子串的长度
table = new int[m+1][n+1]; // 表的大小为(m+1)*(n+1)
for(int i=0;i<=X.length();i++){
for(int j=0;j<=Y.length();j++){
if(i==0||j==0){
table[i][j]=0;
}else if(X.charAt(i-1)==Y.charAt(j-1)){
table[i][j]=table[i-1][j-1]+1;
result=Math.max(table[i][j], result);
}else{
table[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
traceBack(table, m, n, result);
return result;
}
/**
* 功能:(用一个比较笨的方法,遍历array,找出result所在的位置,对角线遍历最长公共字串)
*/
private void traceBack(int[][] lcsArray,int i, int j,int result) {
while (i>0 && j>0) {
if(lcsArray[i][j]==result){
printLCS(lcsArray, i, j);
}
--i;
--j;
}
}
public void printLCS(int[][] lcsArray,int i,int j){
String str="";
while(i>0&&j>0&&lcsArray[i][j]!=0){
str+=X.charAt(i-1);
--i;
--j;
}
System.out.println(reverse(str));
}
/**
* 功能:字符串逆序
*/
private String reverse(String str) {
StringBuffer strBuf = new StringBuffer(str).reverse();
return strBuf.toString();
}
/**
* 功能:main方法 —— 程序的入口
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongestCommonSubstring lcs = new LongestCommonSubstring("ABCBDQIENAB","BDDCAQISBNA");
}
}























 1094
1094

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








