之所以选择example/tutorial里的seven.cc,是因为在统计数据画图时,不仅仅存在常有的Trace机制如ASCII trace file和PCAP文件,还存在利用GNUPLOT Helper和File Helper实现。具有代表意义。
#include <fstream>
#include "ns3/core-module.h"
#include "ns3/network-module.h"
#include "ns3/internet-module.h"
#include "ns3/point-to-point-module.h"
#include "ns3/applications-module.h"
#include "ns3/stats-module.h"
using namespace ns3;
NS_LOG_COMPONENT_DEFINE ("SeventhScriptExample");
// ===========================================================================
//
// node 0 node 1
// +----------------+ +----------------+
// | ns-3 TCP | | ns-3 TCP |
// +----------------+ +----------------+
// | 10.1.1.1 | | 10.1.1.2 |
// +----------------+ +----------------+
// | point-to-point | | point-to-point |
// +----------------+ +----------------+
// | |
// +---------------------+
// 5 Mbps, 2 ms
//
//
// We want to look at changes in the ns-3 TCP congestion window. We need
// to crank up a flow and hook the CongestionWindow attribute on the socket
// of the sender. Normally one would use an on-off application to generate a
// flow, but this has a couple of problems. First, the socket of the on-off
// application is not created until Application Start time, so we wouldn't be
// able to hook the socket (now) at configuration time. Second, even if we
// could arrange a call after start time, the socket is not public so we
// couldn't get at it.
//
// So, we can cook up a simple version of the on-off application that does what
// we want. On the plus side we don't need all of the complexity of the on-off
// application. On the minus side, we don't have a helper, so we have to get
// a little more involved in the details, but this is trivial.
//
// So first, we create a socket and do the trace connect on it; then we pass
// this socket into the constructor of our simple application which we then
// install in the source node.
// ===========================================================================
//
class MyApp : public Application
{
public:
MyApp ();
virtual ~MyApp ();
/**
* Register this type.
* \return The TypeId.
*/
static TypeId GetTypeId (void);
void Setup (Ptr<Socket> socket, Address address, uint32_t packetSize, uint32_t nPackets, DataRate dataRate);
private:
virtual void StartApplication (void);
virtual void StopApplication (void);
void ScheduleTx (void);
void SendPacket (void);
Ptr<Socket> m_socket;
Address m_peer;
uint32_t m_packetSize;
uint32_t m_nPackets;
DataRate m_dataRate;
EventId m_sendEvent;
bool m_running;
uint32_t m_packetsSent;
};
MyApp::MyApp ()
: m_socket (0),
m_peer (),
m_packetSize (0),
m_nPackets (0),
m_dataRate (0),
m_sendEvent (),
m_running (false),
m_packetsSent (0)
{
}
MyApp::~MyApp ()
{
m_socket = 0;
}
/* static */
TypeId MyApp::GetTypeId (void)
{
static TypeId tid = TypeId ("MyApp")
.SetParent<Application> ()
.SetGroupName ("Tutorial")
.AddConstructor<MyApp> ()
;
return tid;
}
void
MyApp::Setup (Ptr<Socket> socket, Address address, uint32_t packetSize, uint32_t nPackets, DataRate dataRate)
{
m_socket = socket;
m_peer = address;
m_packetSize = packetSize;
m_nPackets = nPackets;
m_dataRate = dataRate;
}
void
MyApp::StartApplication (void)
{
m_running = true;
m_packetsSent = 0;
if (InetSocketAddress::IsMatchingType (m_peer))
{
m_socket->Bind ();
}
else
{
m_socket->Bind6 ();
}
m_socket->Connect (m_peer);
SendPacket ();
}
void
MyApp::StopApplication (void)
{
m_running = false;
if (m_sendEvent.IsRunning ())
{
Simulator::Cancel (m_sendEvent);
}
if (m_socket)
{
m_socket->Close ();
}
}
void
MyApp::SendPacket (void)
{
Ptr<Packet> packet = Create<Packet> (m_packetSize);
m_socket->Send (packet);
if (++m_packetsSent < m_nPackets)
{
ScheduleTx ();
}
}
void
MyApp::ScheduleTx (void)
{
if (m_running)
{
Time tNext (Seconds (m_packetSize * 8 / static_cast<double> (m_dataRate.GetBitRate ())));
m_sendEvent = Simulator::Schedule (tNext, &MyApp::SendPacket, this);
}
}
static void
CwndChange (Ptr<OutputStreamWrapper> stream, uint32_t oldCwnd, uint32_t newCwnd)
{
NS_LOG_UNCOND (Simulator::Now ().GetSeconds () << "\t" << newCwnd);
*stream->GetStream () << Simulator::Now ().GetSeconds () << "\t" << oldCwnd << "\t" << newCwnd << std::endl;
}
static void
RxDrop (Ptr<PcapFileWrapper> file, Ptr<const Packet> p)
{
NS_LOG_UNCOND ("RxDrop at " << Simulator::Now ().GetSeconds ());
file->Write (Simulator::Now (), p);
}
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
bool useV6 = false;
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.AddValue ("useIpv6", "Use Ipv6", useV6);
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
NodeContainer nodes;
nodes.Create (2);
PointToPointHelper pointToPoint;
pointToPoint.SetDeviceAttribute ("DataRate", StringValue ("5Mbps"));
pointToPoint.SetChannelAttribute ("Delay", StringValue ("2ms"));
NetDeviceContainer devices;
devices = pointToPoint.Install (nodes);
Ptr<RateErrorModel> em = CreateObject<RateErrorModel> ();
em->SetAttribute ("ErrorRate", DoubleValue (0.00001));
devices.Get (1)->SetAttribute ("ReceiveErrorModel", PointerValue (em));
InternetStackHelper stack;
stack.Install (nodes);
uint16_t sinkPort = 8080;
Address sinkAddress;
Address anyAddress;
std::string probeType;
std::string tracePath;
if (useV6 == false)
{
Ipv4AddressHelper address;
address.SetBase ("10.1.1.0", "255.255.255.0");
Ipv4InterfaceContainer interfaces = address.Assign (devices);
sinkAddress = InetSocketAddress (interfaces.GetAddress (1), sinkPort);
anyAddress = InetSocketAddress (Ipv4Address::GetAny (), sinkPort);
probeType = "ns3::Ipv4PacketProbe";
tracePath = "/NodeList/*/$ns3::Ipv4L3Protocol/Tx";
}
else
{
Ipv6AddressHelper address;
address.SetBase ("2001:0000:f00d:cafe::", Ipv6Prefix (64));
Ipv6InterfaceContainer interfaces = address.Assign (devices);
sinkAddress = Inet6SocketAddress (interfaces.GetAddress (1,1), sinkPort);
anyAddress = Inet6SocketAddress (Ipv6Address::GetAny (), sinkPort);
probeType = "ns3::Ipv6PacketProbe";
tracePath = "/NodeList/*/$ns3::Ipv6L3Protocol/Tx";
}
PacketSinkHelper packetSinkHelper ("ns3::TcpSocketFactory", anyAddress);
ApplicationContainer sinkApps = packetSinkHelper.Install (nodes.Get (1));
sinkApps.Start (Seconds (0.));
sinkApps.Stop (Seconds (20.));
Ptr<Socket> ns3TcpSocket = Socket::CreateSocket (nodes.Get (0), TcpSocketFactory::GetTypeId ());
Ptr<MyApp> app = CreateObject<MyApp> ();
app->Setup (ns3TcpSocket, sinkAddress, 1040, 1000, DataRate ("1Mbps"));
nodes.Get (0)->AddApplication (app);
app->SetStartTime (Seconds (1.));
app->SetStopTime (Seconds (20.));
AsciiTraceHelper asciiTraceHelper;
Ptr<OutputStreamWrapper> stream = asciiTraceHelper.CreateFileStream ("seventh.cwnd");
ns3TcpSocket->TraceConnectWithoutContext ("CongestionWindow", MakeBoundCallback (&CwndChange, stream));
PcapHelper pcapHelper;
Ptr<PcapFileWrapper> file = pcapHelper.CreateFile ("seventh.pcap", std::ios::out, PcapHelper::DLT_PPP);
devices.Get (1)->TraceConnectWithoutContext ("PhyRxDrop", MakeBoundCallback (&RxDrop, file));
// Use GnuplotHelper to plot the packet byte count over time
GnuplotHelper plotHelper;
// Configure the plot. The first argument is the file name prefix
// for the output files generated. The second, third, and fourth
// arguments are, respectively, the plot title, x-axis, and y-axis labels
plotHelper.ConfigurePlot ("seventh-packet-byte-count",//文件名前缀
"Packet Byte Count vs. Time",//图题
"Time (Seconds)",//x标签
"Packet Byte Count");//y标签
// Specify the probe type, trace source path (in configuration namespace), and
// probe output trace source ("OutputBytes") to plot. The fourth argument
// specifies the name of the data series label on the plot. The last
// argument formats the plot by specifying where the key should be placed.
plotHelper.PlotProbe (probeType,
tracePath,//trace source path
"OutputBytes",//probe output trace source
"Packet Byte Count",//legend
GnuplotAggregator::KEY_BELOW);//在图中key的位置,默认在inside
// Use FileHelper to write out the packet byte count over time
FileHelper fileHelper;
// Configure the file to be written, and the formatting of output data.
fileHelper.ConfigureFile ("seventh-packet-byte-count",
FileAggregator::FORMATTED);
// Set the labels for this formatted output file.
fileHelper.Set2dFormat ("Time (Seconds) = %.3e\tPacket Byte Count = %.0f");
// Specify the probe type, trace source path (in configuration namespace), and
// probe output trace source ("OutputBytes") to write.
fileHelper.WriteProbe (probeType,
tracePath,
"OutputBytes");
Simulator::Stop (Seconds (20));
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy ();
return 0;
}
对于plothelper对象的第一个函数ConfigurePlots四个参数分别如下:
文件名前缀;
图片名;
x标签;
y标签;
该函数主要完成对于图文件格式的定义。而第二个函数PlotProbe是获得的原始数据,
第一个参数是probetype,这里是
"ns3::Ipv4PacketProbe"vim src/internet/model/ipv4-packet-probe.cc#include "ns3/ipv4-packet-probe.h"
#include "ns3/object.h"
#include "ns3/log.h"
#include "ns3/names.h"
#include "ns3/config.h"
#include "ns3/trace-source-accessor.h"
namespace ns3 {
NS_LOG_COMPONENT_DEFINE ("Ipv4PacketProbe");
NS_OBJECT_ENSURE_REGISTERED (Ipv4PacketProbe);
TypeId
Ipv4PacketProbe::GetTypeId ()
{
static TypeId tid = TypeId ("ns3::Ipv4PacketProbe")
.SetParent<Probe> ()
.SetGroupName ("Internet")
.AddConstructor<Ipv4PacketProbe> ()
.AddTraceSource ( "Output",
"The packet plus its IPv4 object and interface "
"that serve as the output for this probe",
MakeTraceSourceAccessor (&Ipv4PacketProbe::m_output),
"ns3::Ipv4L3Protocol::TxRxTracedCallback")
.AddTraceSource ( "OutputBytes",
"The number of bytes in the packet",
MakeTraceSourceAccessor (&Ipv4PacketProbe::m_outputBytes),
"ns3::Packet::SizeTracedCallback")
;
return tid;
}
Ipv4PacketProbe::Ipv4PacketProbe ()
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
m_packet = 0;
m_packetSizeOld = 0;
m_ipv4 = 0;
m_interface = 0;
}
Ipv4PacketProbe::~Ipv4PacketProbe ()
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
}
void
Ipv4PacketProbe::SetValue (Ptr<const Packet> packet, Ptr<Ipv4> ipv4, uint32_t interface)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << packet << ipv4 << interface);
m_packet = packet;
m_ipv4 = ipv4;
m_interface = interface;
m_output (packet, ipv4, interface);
uint32_t packetSizeNew = packet->GetSize ();
m_outputBytes (m_packetSizeOld, packetSizeNew);
m_packetSizeOld = packetSizeNew;
}
void
Ipv4PacketProbe::SetValueByPath (std::string path, Ptr<const Packet> packet, Ptr<Ipv4> ipv4, uint32_t interface)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (path << packet << ipv4 << interface);
Ptr<Ipv4PacketProbe> probe = Names::Find<Ipv4PacketProbe> (path);
NS_ASSERT_MSG (probe, "Error: Can't find probe for path " << path);
probe->SetValue (packet, ipv4, interface);
}
bool
Ipv4PacketProbe::ConnectByObject (std::string traceSource, Ptr<Object> obj)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << traceSource << obj);
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Name of probe (if any) in names database: " << Names::FindPath (obj));
bool connected = obj->TraceConnectWithoutContext (traceSource, MakeCallback (&ns3::Ipv4PacketProbe::TraceSink, this));
return connected;
}
void
Ipv4PacketProbe::ConnectByPath (std::string path)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << path);
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Name of probe to search for in config database: " << path);
Config::ConnectWithoutContext (path, MakeCallback (&ns3::Ipv4PacketProbe::TraceSink, this));
}
void
Ipv4PacketProbe::TraceSink (Ptr<const Packet> packet, Ptr<Ipv4> ipv4, uint32_t interface)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << packet << ipv4 << interface);
if (IsEnabled ())
{
m_packet = packet;
m_ipv4 = ipv4;
m_interface = interface;
m_output (packet, ipv4, interface);
uint32_t packetSizeNew = packet->GetSize ();
m_outputBytes (m_packetSizeOld, packetSizeNew);
m_packetSizeOld = packetSizeNew;
}
}
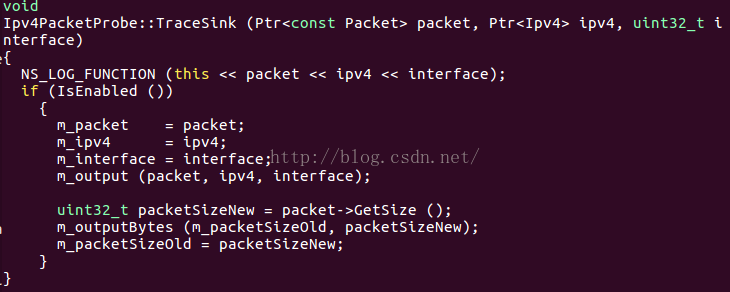
} // namespace ns3m_output设置traced source,分组加上Ipv4对象及其接口,记为Output,由回调签名ns3::Ipv4L3Protocol::TxRxTracedCallback调用
m_outputBytes设置traced source,分组中Bytes数目,记为OutputBytes,由回调签名ns3::Packet::SizeTracedCallback调用
第二个参数是tracepath,这里是
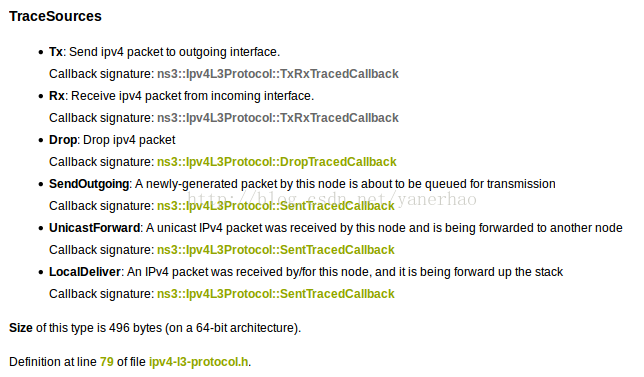
/NodeList/*/$ns3::Ipv4L3Protocol/Tx各TraceSources对应的回调签名为:
Tx对应的回调签名为:TxRxTracedCallback函数指针,其格式为
typedef void(* ns3::Ipv4L3Protocol::TxRxTracedCallback) (Ptr< const Packet > packet, Ptr< Ipv4 > ipv4, uint32_t interface)第四个参数是图中数据标签如”Packet Byte Count“
第五个参数是图中key的位置,默认inside,如这里的”KEY_BELOW“
对于GnuplotHelper类的两个函数,第一个函数ConfigurePlot比较简单,不用多说,这里主要分析第二个函数PlotProbe。进入src/stats/helper/,打开gnuplot-helper.cc,截取该函数定义:
void
GnuplotHelper::PlotProbe (const std::string &typeId,
const std::string &path,
const std::string &probeTraceSource,
const std::string &title,
enum GnuplotAggregator::KeyLocation keyLocation)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << typeId << path << probeTraceSource << title << keyLocation);
// Get a pointer to the aggregator.
Ptr<GnuplotAggregator> aggregator = GetAggregator ();
// Add a subtitle to the title to show the trace source's path.
aggregator->SetTitle ( m_title + " \\n\\nTrace Source Path: " + path);
// Set the default dataset plotting style for the values.
aggregator->Set2dDatasetDefaultStyle (Gnuplot2dDataset::LINES_POINTS);
// Set the location of the key in the plot.
aggregator->SetKeyLocation (keyLocation);
std::string pathWithoutLastToken;
std::string lastToken;
// See if the path has any wildcards.
bool pathHasNoWildcards = path.find ("*") == std::string::npos;
// Remove the last token from the path; this should correspond to the
// trace source attribute.
size_t lastSlash = path.find_last_of ("/");
if (lastSlash == std::string::npos)
{
pathWithoutLastToken = path;
lastToken = "";
}
else
{
// Chop off up to last token.
pathWithoutLastToken = path.substr (0, lastSlash);
// Save the last token without the last slash.
lastToken = path.substr (lastSlash + 1, std::string::npos);
}
// See if there are any matches for the probe's path with the last
// token removed; this corresponds to the traced object itself.
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Searching config database for trace source " << path);
Config::MatchContainer matches = Config::LookupMatches (pathWithoutLastToken);
uint32_t matchCount = matches.GetN ();
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Found " << matchCount << " matches for trace source " << path);
// This is used to make the probe's context be unique.
std::string matchIdentifier;
// Hook one or more probes and the aggregator together.
if (matchCount == 1 && pathHasNoWildcards)
{
// Connect the probe to the aggregator only once because there
// is only one matching config path. There is no need to find
// the wildcard matches because the passed in path has none.
matchIdentifier = "0";
ConnectProbeToAggregator (typeId,
matchIdentifier,
path,
probeTraceSource,
title);
}
else if (matchCount > 0)
{
// Handle all of the matches if there are more than one.
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < matchCount; i++)
{
// Set the match identifier.
std::ostringstream matchIdentifierStream;
matchIdentifierStream << i;
matchIdentifier = matchIdentifierStream.str ();
// Construct the matched path and get the matches for each
// of the wildcards.
std::string wildcardSeparator = " ";
std::string matchedPath = matches.GetMatchedPath (i) + lastToken;
std::string wildcardMatches = GetWildcardMatches (path,
matchedPath,
wildcardSeparator);
// Connect the probe to the aggregator for this match.
ConnectProbeToAggregator (typeId,
matchIdentifier,
matchedPath,
probeTraceSource,
title + "-" + wildcardMatches);
}
}
else
{
// There is a problem if there are no matching config paths.
NS_FATAL_ERROR ("Lookup of " << path << " got no matches");
}
}
void
GnuplotHelper::ConnectProbeToAggregator (const std::string &typeId,
const std::string &matchIdentifier,
const std::string &path,
const std::string &probeTraceSource,
const std::string &title)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << typeId << matchIdentifier << path << probeTraceSource
<< title);
Ptr<GnuplotAggregator> aggregator = GetAggregator ();
// Increment the total number of plot probes that have been created.
m_plotProbeCount++;
// Create a unique name for this probe.
std::ostringstream probeNameStream;
probeNameStream << "PlotProbe-" << m_plotProbeCount;
std::string probeName = probeNameStream.str ();
// Create a unique dataset context string for this probe.
std::string probeContext = probeName
+ "/" + matchIdentifier + "/" + probeTraceSource;
// Add the probe to the map of probes, which will keep the probe in
// memory after this function ends.
AddProbe (typeId, probeName, path);
// Because the callbacks to the probes' trace sources don't use the
// probe's context, a unique adaptor needs to be created for each
// probe context so that information is not lost.
AddTimeSeriesAdaptor (probeContext);
// Connect the probe to the adaptor.
if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::DoubleProbe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkDouble,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::BooleanProbe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkBoolean,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::PacketProbe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger32,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::ApplicationPacketProbe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger32,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::Ipv4PacketProbe")//probename 是”Ipv4PacketProbe“
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger32,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::Ipv6PacketProbe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger32,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::Uinteger8Probe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger8,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::Uinteger16Probe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger16,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::Uinteger32Probe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger32,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::TimeProbe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkDouble,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
}
else
{
NS_FATAL_ERROR ("Unknown probe type " << m_probeMap[probeName].second << "; need to add support in the helper for this");
}
// Connect the adaptor to the aggregator.
std::string adaptorTraceSource = "Output";
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]->TraceConnect
(adaptorTraceSource,
probeContext,
MakeCallback (&GnuplotAggregator::Write2d, aggregator));
// Add the dataset to the plot.
aggregator->Add2dDataset (probeContext, title);
}
} // namespace ns3
else if (m_probeMap[probeName].second == "ns3::Ipv4PacketProbe")
{
m_probeMap[probeName].first->TraceConnectWithoutContext
(probeTraceSource,
MakeCallback (&TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger32,
m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap[probeContext]));
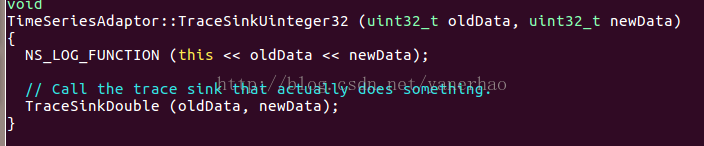
}TimeSeriesAdaptor::TraceSinkUinteger32函数与回调关联,该函数是类 TimeSeriesAdaptor类对象一成员函数,对应指针m_timeSeriesAdaptorMap。
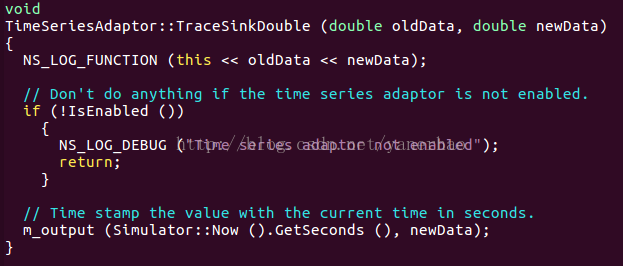
查询API发现在src/stats/model,打开time-series-adaptor.cc,找到TraceSinkUinteger32
里面调用的TraceSinkDouble为:
故最终输出形式两列:第一列为时间(s),第二列为最新值。
总结思路:
选择gnuplot helper 画图后,选择需要统计画图的标准,这里是分组的bytes数目,故probetype这里选择ipv4packetprobe;
选择trace sources集合,这里从ipv4l3protocol里选择
选择待画图的一个source
关联source和sink。
probetype 例如ipv4--packet-probe,打开src/internet/model/ipv4-packet-probe.cc,
且存在ConnectByObject函数和ConnectByPath,将外来trace source与该probe相关联,即通TraceConnectWithoutContext或者Config::ConnectWithoutContext实现与ipv4packetprobe::TraceSInk函数的关联:
可见完成外来trace source与probe关联后,外来trace source变化--->在probe的Enabled=1时对应的sink函数TraceSink接收这种变化并被调用---->m_output 和m_outputBytes被赋值即Output 和OutputBuyes这两个内部trace source变化---->对应的sink函数调用,输出trace soucre对应内容。
























 2598
2598

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








