Redis 源码解读之事件循环机制
背景和问题
本文想要解决的问题:
- Redis 事件循环(EventLoop)是怎样的?
- Redis 有几类事件,分别是怎么执行的?
- 如果事件循环没有文件事件(只有定时事件或没有任何事件),那么整个事件循环系统是怎么运行的?
结论
- Redis 事件循环(EventLoop)是怎样的?
见源码解读。
- Redis 有几类事件,分别是怎么执行的?
Redis 共有两类事件:文件事件(
aeFileEvent) 和 时间事件(aeTimeEvent)。
- 文件事件: 负责监听文件读/写事件
- 时间事件: 负责维护定时任务
- 如果事件循环没有文件事件(只有定时事件或没有任何事件),那么整个事件循环系统是怎么运行的?如果只有文件事件(没有时间事件)呢?
- 没有文件事件:
epoll_wait等待的文件事件列表为空时,会等待到下一个时间事件的触发。- 只有文件事件:
epoll_wait的等待时间设为NULL, 阻塞等待文件事件激活。(有时间事件时,等待时间为到aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop)的时间间隔。)
源码解读
redis 提供了
kqueue,select,epoll等多种多路复用 IO 的方式,本文采用的是epoll:#define HAVE_EPOLL // added by yanglingwell /* Include the best multiplexing layer supported by this system. * The following should be ordered by performances, descending. */ #ifdef HAVE_EVPORT #include "ae_evport.c" #else #ifdef HAVE_EPOLL #include "ae_epoll.c" #else #ifdef HAVE_KQUEUE #include "ae_kqueue.c" #else #include "ae_select.c" #endif #endif #endif
-
Demo
为了理解 Redis 事件循环系统的逻辑,我将 redis 的时间循环相关的文件 ae.h, ae.c, ae_epoll.c 摘取出来,写了个样例。源码见 redis-ae_event-example。

-
EventLoop结构

Redis 事件循环系统主要由 aeEventLoop 结构维护。
beforesleep和aftersleep是每次等待事件循环前/后执行的函数。
events保存注册的文件事件的文件描述符和回调信息aeFileEvent的映射关系(文件描述符数字的生成规则保证了数组下标作为文件描述符数字的可行性)。fired,apidata保存激活的文件描述符信息。timeEventHead是一个保存定时事件列表的双向链表。// in ae.h /* Types and data structures */ typedef void aeFileProc(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, void *clientData, int mask); typedef int aeTimeProc(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData); typedef void aeEventFinalizerProc(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, void *clientData); typedef void aeBeforeSleepProc(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop); /* File event structure */ typedef struct aeFileEvent { int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE|BARRIER) */ aeFileProc *rfileProc; aeFileProc *wfileProc; void *clientData; } aeFileEvent; /* Time event structure */ typedef struct aeTimeEvent { long long id; /* time event identifier. */ long when_sec; /* seconds */ long when_ms; /* milliseconds */ aeTimeProc *timeProc; aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc; void *clientData; struct aeTimeEvent *prev; struct aeTimeEvent *next; } aeTimeEvent; /* A fired event */ typedef struct aeFiredEvent { int fd; int mask; } aeFiredEvent; /* State of an event based program */ typedef struct aeEventLoop { int maxfd; /* highest file descriptor currently registered */ int setsize; /* max number of file descriptors tracked */ long long timeEventNextId; time_t lastTime; /* Used to detect system clock skew */ aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events */ aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events */ aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead; int stop; void *apidata; /* This is used for polling API specific data */ aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep; aeBeforeSleepProc *aftersleep; } aeEventLoop; // in ae_epoll.c typedef struct aeApiState { int epfd; struct epoll_event *events; } aeApiState;
- EventLoop 的创建和删除
呃…… 这个没啥说的,简单罗列下吧。
aeCreateEventLoop: 创建和初始化事件循环相关变量aeDeleteEventLoop: 清理事件循环占用的内存资源//in ae.c aeEventLoop *aeCreateEventLoop(int setsize) { aeEventLoop *eventLoop; int i; if ((eventLoop = zmalloc(sizeof(*eventLoop))) == NULL) goto err; eventLoop->events = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFileEvent)*setsize); eventLoop->fired = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFiredEvent)*setsize); if (eventLoop->events == NULL || eventLoop->fired == NULL) goto err; eventLoop->setsize = setsize; eventLoop->lastTime = time(NULL); eventLoop->timeEventHead = NULL; eventLoop->timeEventNextId = 0; eventLoop->stop = 0; eventLoop->maxfd = -1; eventLoop->beforesleep = NULL; eventLoop->aftersleep = NULL; if (aeApiCreate(eventLoop) == -1) goto err; /* Events with mask == AE_NONE are not set. So let's initialize the * vector with it. */ for (i = 0; i < setsize; i++) eventLoop->events[i].mask = AE_NONE; return eventLoop; err: if (eventLoop) { zfree(eventLoop->events); zfree(eventLoop->fired); zfree(eventLoop); } return NULL; } void aeDeleteEventLoop(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { aeApiFree(eventLoop); zfree(eventLoop->events); zfree(eventLoop->fired); zfree(eventLoop); }
- 定时事件的创建和删除
-
EventLoop 的时间事件由双向链表
timeEventHead维护。新建时间事件,即是将新的时间事件插入时间事件链表头。
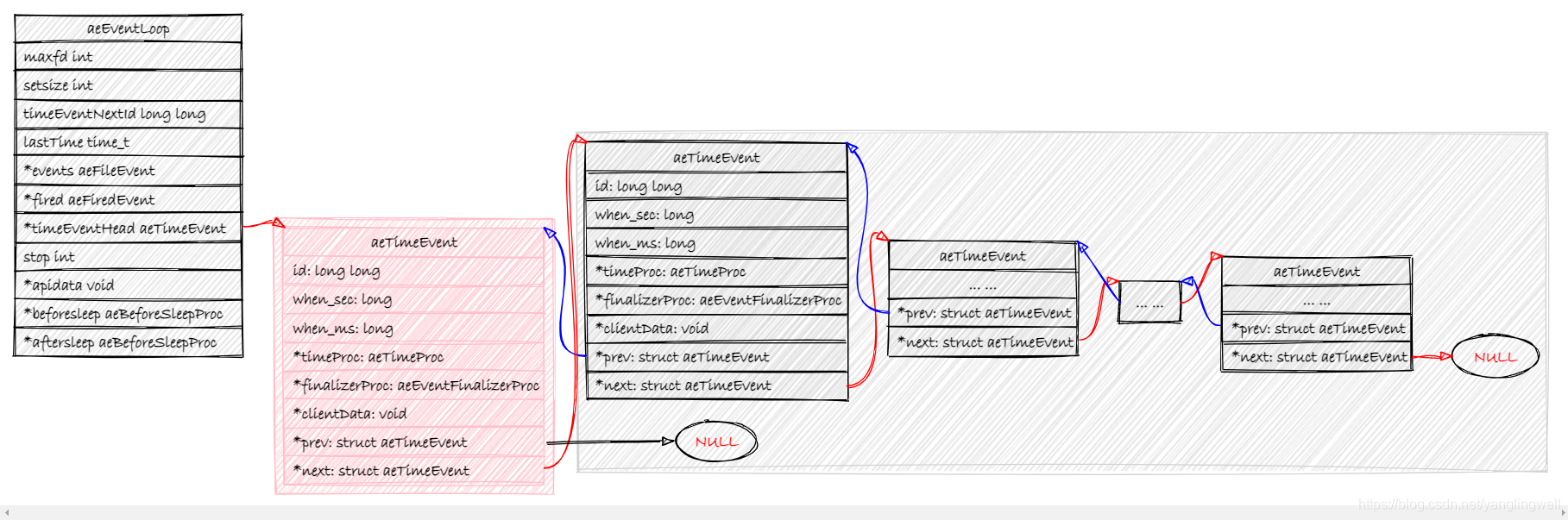
-
aeDeleteTimeEvent删除时间事件实际上是将该时间事件标记为AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID, 在下一次事件循环时,实际实际执行删除操作。long long aeCreateTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long milliseconds, aeTimeProc *proc, void *clientData, aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc) { long long id = eventLoop->timeEventNextId++; aeTimeEvent *te; te = zmalloc(sizeof(*te)); if (te == NULL) return AE_ERR; te->id = id; aeAddMillisecondsToNow(milliseconds,&te->when_sec,&te->when_ms); te->timeProc = proc; te->finalizerProc = finalizerProc; te->clientData = clientData; te->prev = NULL; te->next = eventLoop->timeEventHead; if (te->next) te->next->prev = te; eventLoop->timeEventHead = te; return id; } int aeDeleteTimeEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id) { aeTimeEvent *te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; while(te) { if (te->id == id) { te->id = AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID; return AE_OK; } te = te->next; } return AE_ERR; /* NO event with the specified ID found */ }
- 文件事件的创建和删除
aeCreateFileEvent创建文件读/写事件,并注册该时间到epoll事件循环中。
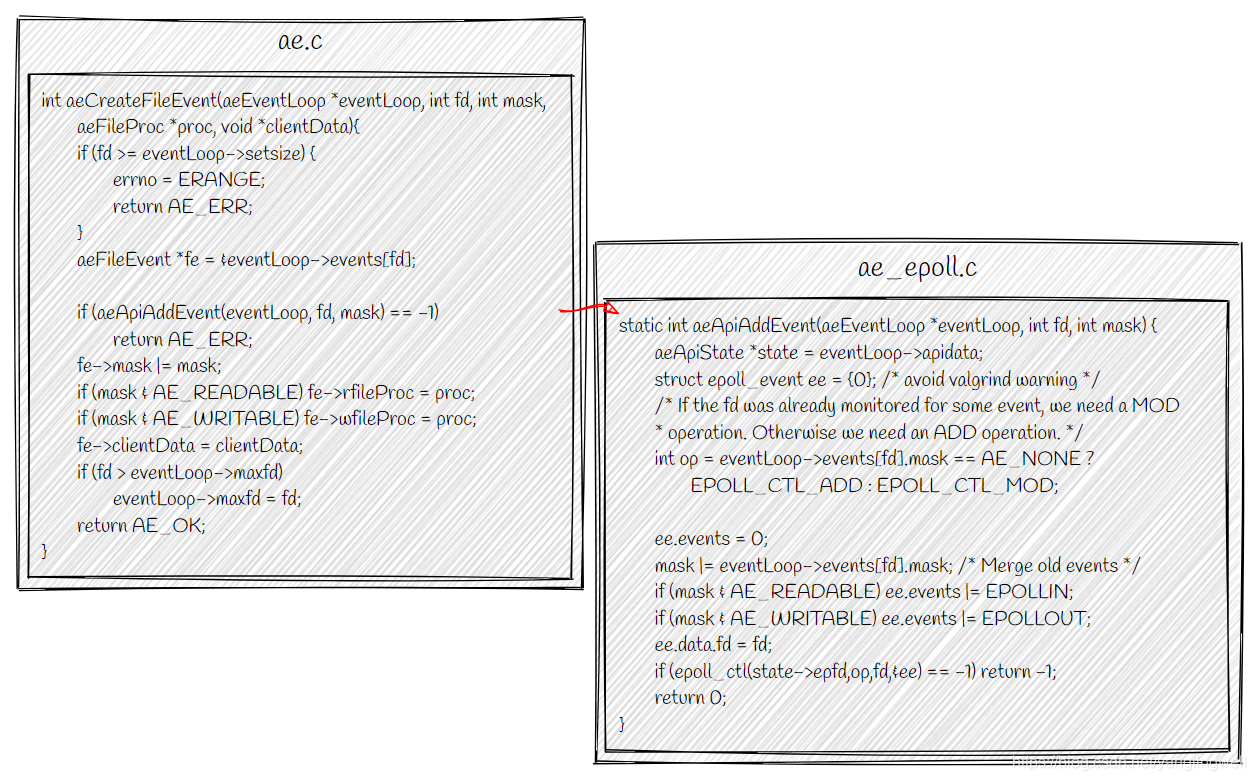
aeDeleteFileEvent将指定文件描述符的特定事件移除。// in ae.c int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask, aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData) { if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) { errno = ERANGE; return AE_ERR; } aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1) return AE_ERR; fe->mask |= mask; if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc; if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc; fe->clientData = clientData; if (fd > eventLoop->maxfd) eventLoop->maxfd = fd; return AE_OK; } void aeDeleteFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask) { if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) return; aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; if (fe->mask == AE_NONE) return; /* We want to always remove AE_BARRIER if set when AE_WRITABLE * is removed. */ if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) mask |= AE_BARRIER; aeApiDelEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask); fe->mask = fe->mask & (~mask); if (fd == eventLoop->maxfd && fe->mask == AE_NONE) { /* Update the max fd */ int j; for (j = eventLoop->maxfd-1; j >= 0; j--) if (eventLoop->events[j].mask != AE_NONE) break; eventLoop->maxfd = j; } } // in ae_epoll.c static int aeApiAddEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask) { aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata; struct epoll_event ee = {0}; /* avoid valgrind warning */ /* If the fd was already monitored for some event, we need a MOD * operation. Otherwise we need an ADD operation. */ int op = eventLoop->events[fd].mask == AE_NONE ? EPOLL_CTL_ADD : EPOLL_CTL_MOD; ee.events = 0; mask |= eventLoop->events[fd].mask; /* Merge old events */ if (mask & AE_READABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLIN; if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLOUT; ee.data.fd = fd; if (epoll_ctl(state->epfd,op,fd,&ee) == -1) return -1; return 0; } static void aeApiDelEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int delmask) { aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata; struct epoll_event ee = {0}; /* avoid valgrind warning */ int mask = eventLoop->events[fd].mask & (~delmask); ee.events = 0; if (mask & AE_READABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLIN; if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLOUT; ee.data.fd = fd; if (mask != AE_NONE) { epoll_ctl(state->epfd,EPOLL_CTL_MOD,fd,&ee); } else { /* Note, Kernel < 2.6.9 requires a non null event pointer even for * EPOLL_CTL_DEL. */ epoll_ctl(state->epfd,EPOLL_CTL_DEL,fd,&ee); } }
-
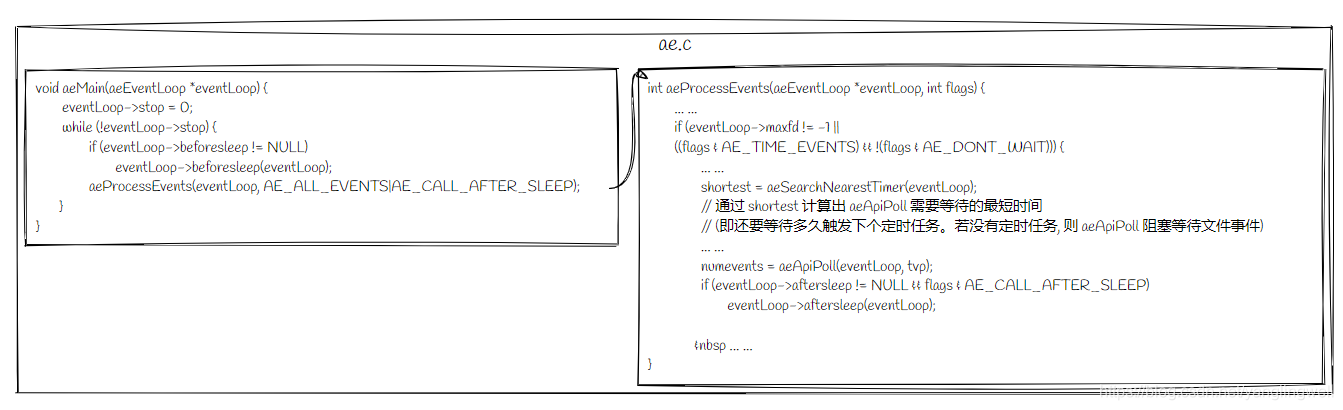
事件循环

aeProcessEvents通过aeSearchNearestTimer获取下一个定时事件的执行时间,并以此计算aeApiPoll需要等待的时间。如果没有定时事件,则
aeApiPoll将会阻塞到文件事件触发。当文件事件触发时,会根据文件事件激活情况,依次执行读/写回调函数。
当文件事件回调函数执行完后,
processTimeEvents才开始执行定时任务。processTimeEvents依次遍历时间事件链表timeEventHead:
如果当前事件被标记为AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID, 则执行该事件的finalizerProc回调函数,并将其从时间事件链表中移除。
否则,执行该时间事件回调函数timeProc。该回调函数返回AE_NOMORE(-1)下次事件循环时将该时间事件删除。否则,返回值作为该时间事件下次执行的时间间隔。// in ae.c /* Process time events */ static int processTimeEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { int processed = 0; aeTimeEvent *te; long long maxId; time_t now = time(NULL); /* If the system clock is moved to the future, and then set back to the * right value, time events may be delayed in a random way. Often this * means that scheduled operations will not be performed soon enough. * * Here we try to detect system clock skews, and force all the time * events to be processed ASAP when this happens: the idea is that * processing events earlier is less dangerous than delaying them * indefinitely, and practice suggests it is. */ if (now < eventLoop->lastTime) { te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; while(te) { te->when_sec = 0; te = te->next; } } eventLoop->lastTime = now; te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; maxId = eventLoop->timeEventNextId-1; while(te) { long now_sec, now_ms; long long id; /* Remove events scheduled for deletion. */ if (te->id == AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID) { aeTimeEvent *next = te->next; if (te->prev) te->prev->next = te->next; else eventLoop->timeEventHead = te->next; if (te->next) te->next->prev = te->prev; if (te->finalizerProc) te->finalizerProc(eventLoop, te->clientData); zfree(te); te = next; continue; } /* Make sure we don't process time events created by time events in * this iteration. Note that this check is currently useless: we always * add new timers on the head, however if we change the implementation * detail, this check may be useful again: we keep it here for future * defense. */ if (te->id > maxId) { te = te->next; continue; } aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms); if (now_sec > te->when_sec || (now_sec == te->when_sec && now_ms >= te->when_ms)) { int retval; id = te->id; retval = te->timeProc(eventLoop, id, te->clientData); processed++; if (retval != AE_NOMORE) { aeAddMillisecondsToNow(retval,&te->when_sec,&te->when_ms); } else { te->id = AE_DELETED_EVENT_ID; } } te = te->next; } return processed; } /* Process every pending time event, then every pending file event * (that may be registered by time event callbacks just processed). * Without special flags the function sleeps until some file event * fires, or when the next time event occurs (if any). * * If flags is 0, the function does nothing and returns. * if flags has AE_ALL_EVENTS set, all the kind of events are processed. * if flags has AE_FILE_EVENTS set, file events are processed. * if flags has AE_TIME_EVENTS set, time events are processed. * if flags has AE_DONT_WAIT set the function returns ASAP until all * if flags has AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP set, the aftersleep callback is called. * the events that's possible to process without to wait are processed. * * The function returns the number of events processed. */ int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags) { int processed = 0, numevents; /* Nothing to do? return ASAP */ if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0; /* Note that we want call select() even if there are no * file events to process as long as we want to process time * events, in order to sleep until the next time event is ready * to fire. */ if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 || ((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) { int j; aeTimeEvent *shortest = NULL; struct timeval tv, *tvp; if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT)) shortest = aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop); if (shortest) { long now_sec, now_ms; aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms); tvp = &tv; /* How many milliseconds we need to wait for the next * time event to fire? */ long long ms = (shortest->when_sec - now_sec)*1000 + shortest->when_ms - now_ms; if (ms > 0) { tvp->tv_sec = ms/1000; tvp->tv_usec = (ms % 1000)*1000; } else { tvp->tv_sec = 0; tvp->tv_usec = 0; } } else { /* If we have to check for events but need to return * ASAP because of AE_DONT_WAIT we need to set the timeout * to zero */ if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) { tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0; tvp = &tv; } else { /* Otherwise we can block */ tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */ } } /* Call the multiplexing API, will return only on timeout or when * some event fires. */ numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp); /* After sleep callback. */ if (eventLoop->aftersleep != NULL && flags & AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP) eventLoop->aftersleep(eventLoop); for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd]; int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask; int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd; int fired = 0; /* Number of events fired for current fd. */ /* Normally we execute the readable event first, and the writable * event laster. This is useful as sometimes we may be able * to serve the reply of a query immediately after processing the * query. * * However if AE_BARRIER is set in the mask, our application is * asking us to do the reverse: never fire the writable event * after the readable. In such a case, we invert the calls. * This is useful when, for instance, we want to do things * in the beforeSleep() hook, like fsynching a file to disk, * before replying to a client. */ int invert = fe->mask & AE_BARRIER; /* Note the "fe->mask & mask & ..." code: maybe an already * processed event removed an element that fired and we still * didn't processed, so we check if the event is still valid. * * Fire the readable event if the call sequence is not * inverted. */ if (!invert && fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) { fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); fired++; } /* Fire the writable event. */ if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) { if (!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc) { fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); fired++; } } /* If we have to invert the call, fire the readable event now * after the writable one. */ if (invert && fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) { if (!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc) { fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); fired++; } } processed++; } } /* Check time events */ if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop); return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */ } void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { eventLoop->stop = 0; while (!eventLoop->stop) { if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL) eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop); aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP); } } /* Search the first timer to fire. * This operation is useful to know how many time the select can be * put in sleep without to delay any event. * If there are no timers NULL is returned. * * Note that's O(N) since time events are unsorted. * Possible optimizations (not needed by Redis so far, but...): * 1) Insert the event in order, so that the nearest is just the head. * Much better but still insertion or deletion of timers is O(N). * 2) Use a skiplist to have this operation as O(1) and insertion as O(log(N)). */ static aeTimeEvent *aeSearchNearestTimer(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { aeTimeEvent *te = eventLoop->timeEventHead; aeTimeEvent *nearest = NULL; while(te) { if (!nearest || te->when_sec < nearest->when_sec || (te->when_sec == nearest->when_sec && te->when_ms < nearest->when_ms)) nearest = te; te = te->next; } return nearest; } // in ae_epoll.c static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp) { aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata; int retval, numevents = 0; retval = epoll_wait(state->epfd,state->events,eventLoop->setsize, tvp ? (tvp->tv_sec*1000 + tvp->tv_usec/1000) : -1); if (retval > 0) { int j; numevents = retval; for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { int mask = 0; struct epoll_event *e = state->events+j; if (e->events & EPOLLIN) mask |= AE_READABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLOUT) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLERR) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLHUP) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; eventLoop->fired[j].fd = e->data.fd; eventLoop->fired[j].mask = mask; } } return numevents; }








 本文深入解读Redis的事件循环机制,包括文件事件与时间事件的工作原理,以及如何在不同情况下(如仅存在定时事件或文件事件)运行事件循环系统。
本文深入解读Redis的事件循环机制,包括文件事件与时间事件的工作原理,以及如何在不同情况下(如仅存在定时事件或文件事件)运行事件循环系统。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








