---------------------- ASP.Net+Android+IOS开发、.Net培训、期待与您交流! ----------------------
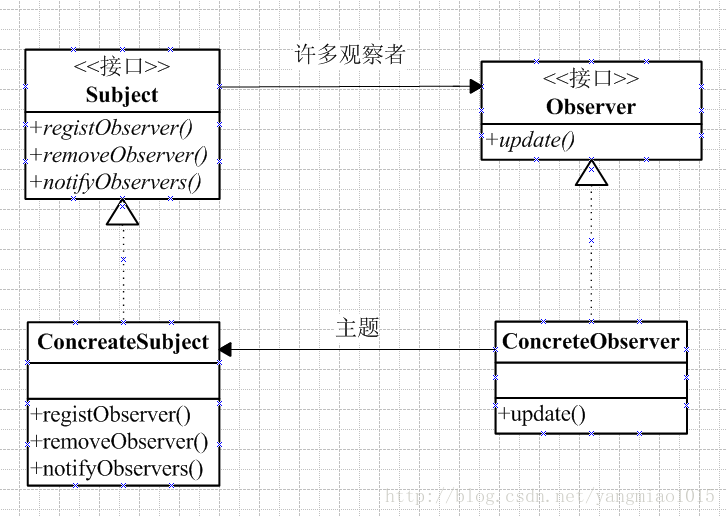
1.观察者模式
观察者模式: 定义了对象之间的一对多依赖,这样一来,当一个对象改变状态时,它的所有依赖者都会收到通知并自动更新。
首先我们需要一个 主题接口,对象可以使用该接口注册为观察者或者将自己从观察者中删除:
Subject接口:
/*
* 主题接口,对象使用此接口注册为观察者或者将自己从观察着中删除
*/
public interface Subject {
/*
* 注册观察者
*/
public void registObserver(Observer observer);
/*
* 删除观察者
*/
public void removeObserver(Observer observer);
/*
* 提醒观察者更新数据
*/
public void notifyObserver();
}Observer接口:
public interface Observer {
/*
* 更新数据
*/
public void update(String team,String score);
}
public class MatchData implements Subject{
public void registObserver(Observer observer) {
this.observers.add(observer);
}
public void removeObserver(Observer observer) {
int i = observers.indexOf(observer);
if(i >= 0){
observers.remove(i);
}
}
public void notifyObserver() {
for(int i=0; i<observers.size(); i++){
Observer observer = observers.get(i);
observer.update(team, score);
}
}
public void setMatchData(String team,String score){
this.team = team;
this.score = score;
notifyObserver();
}
private String team;
private String score;
private List<Observer> observers = new ArrayList<Observer>();
}Observer实现类TVObserver、WebsitObserver:
public class TVObserver implements Observer{
public TVObserver(Subject subject){
this.subject = subject;
this.subject.registObserver(this);
}
public void update(String team, String score) {
this.team = team;
this.score = score;
this.display();
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("现在是TV直播,正在播放的比赛是 : " + team + " 现在的比分是:" + score);
}
private Subject subject;
private String team;
private String score;
}public class WebsitObserver implements Observer{
public WebsitObserver(Subject subject){
this.subject = subject;
this.subject.registObserver(this);
}
public void update(String team, String score) {
this.team = team;
this.score = score;
this.display();
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("这里是比赛直播网站,比赛的最新赛况 : " + team + " 比分 : " + score);
}
private String team;
private String score;
private Subject subject;
}使用代码:
public static void main(String[] args){
MatchData matchData = new MatchData();
Observer websit = new WebsitObserver(matchData);
Observer tvObserver = new TVObserver(matchData);
matchData.setMatchData("西班牙VS巴西", "1:2");
matchData.setMatchData("美国VS英国", "0:1");
matchData.setMatchData("西班牙VS葡萄牙", "1:1");
}
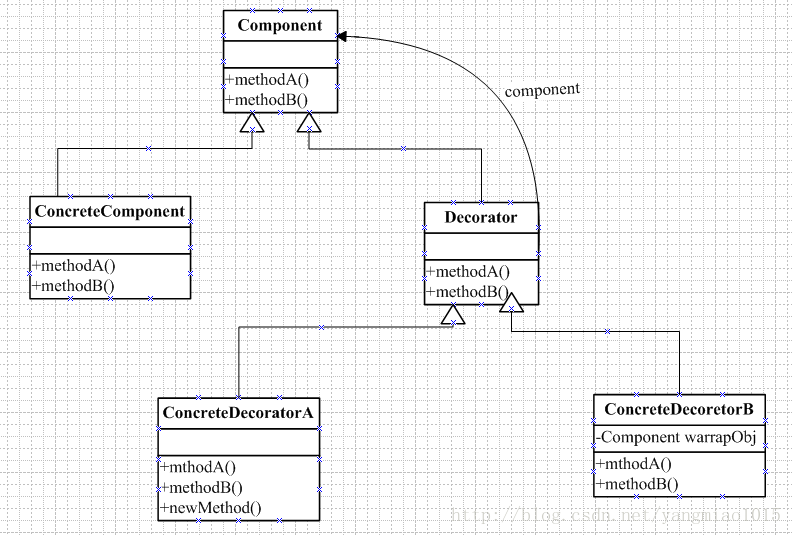
2.装饰模式
装饰模式:动态的将责任附加到对象上,若要扩展功能,装饰着提供了比继承更有弹性的替代方案。
具体的用法用代码演示:
定义一个抽象的Food抽象类
public abstract class Food {
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
protected String description = "Just Rice";
}public class Rice extends Food{
public Rice(){
this.description = "Rice";
}
}public class Black_kerneled_rice extends Food{
public Black_kerneled_rice(){
this.description = "black kerneled rice";
}
}public abstract class Comdiment extends Food{
public abstract String getDescription();
}public class Salt extends Comdiment{
public Salt(Food food){
this.food = food;
}
public String getDescription() {
return this.food.getDescription() + " ,salt";
}
private Food food;
}public class Soy_sauce extends Comdiment{
public Soy_sauce(Food food){
this.food = food;
}
public String getDescription() {
return this.food.getDescription() + " ,soy sauce";
}
private Food food;
}public class Chicken_essence extends Comdiment{
public Chicken_essence(Food food){
this.food = food;
}
public String getDescription() {
return this.food.getDescription() + " ,chicken essence";
}
private Food food;
}public static void main(String[] args){
/*
* 白米油炒饭 加酱油、盐、鸡精
*/
Food food = new Rice();
food = new Salt(food);
food = new Soy_sauce(food);
food = new Chicken_essence(food);
System.out.println(food.getDescription());
/*
* 黑米炒饭 加盐、双份鸡精
*/
food = new Black_kerneled_rice();
food = new Salt(food);
food = new Chicken_essence(food);
food = new Chicken_essence(food);
System.out.println(food.getDescription());
}
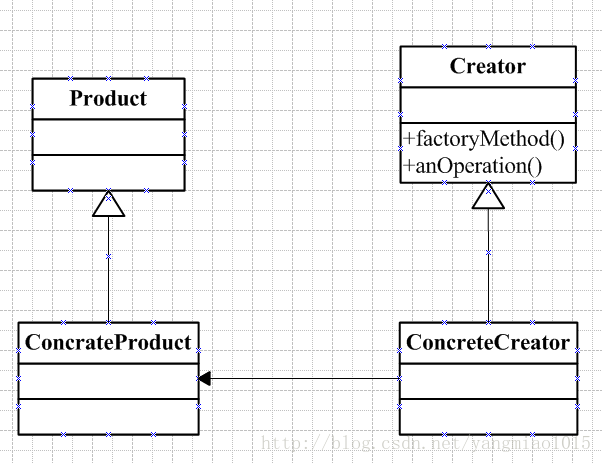
3.工厂方法模式
工厂方法模式:定义一个创建对象的接口,但由子类决定要是梨花的类是哪一个。工厂方法让实例化推迟到子类。
具体用一个蛋糕店来演示:
抽象类Cake:
public abstract class Cake {
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public abstract void prepare(); // 准备工作
public abstract void bake(); // 烘烤
public abstract void decorate(); // 添加饰品
public abstract void box(); // 装箱
protected String name;
}public abstract class CakeFactory {
public Cake createCake(String name) {
this.cake = this.makeCake(name);
cake.prepare();
cake.bake();
cake.decorate();
cake.box();
return cake;
}
public abstract Cake makeCake(String name);
private Cake cake;
}鸡蛋蛋糕、水果蛋糕:
public class EggCake extends Cake {
public EggCake(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void prepare() {
System.out.println("准备面粉,奶油,鸡蛋,甜精");
System.out.println("将面粉和鸡蛋、甜精一起搅拌");
System.out.println("搅拌后做成蛋糕的形状");
}
public void bake() {
System.out.println("将做好的蛋糕原型放入烤箱烘烤,烤好后就出炉了");
}
public void decorate() {
System.out.println("将烤好后的蛋糕添加奶油、巧克力");
}
public void box() {
System.out.println("将加好奶油的蛋糕装入蛋糕盒");
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
}public class FruitCake extends Cake {
public FruitCake(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void prepare() {
System.out.println("准备面粉,奶油,甜精");
System.out.println("将面粉和甜精一起搅拌");
System.out.println("搅拌后做成蛋糕的形状");
}
public void bake() {
System.out.println("将做好的蛋糕原型放入烤箱烘烤,烤好后就出炉了");
}
public void decorate() {
System.out.println("将烤好后的蛋糕添加奶油、巧克力和水果片");
}
public void box() {
System.out.println("将加好奶油的蛋糕装入蛋糕盒");
}
}鸡蛋蛋糕工厂、水果蛋糕工厂:
public class EggCakeFactory extends CakeFactory {
public Cake makeCake(String name) {
return new EggCake(name);
}
}public class FruitCakeFactory extends CakeFactory {
public Cake makeCake(String name) {
return new FruitCake(name);
}
}测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
CakeFactory cakeFactory = new FruitCakeFactory();
Cake cake = cakeFactory.createCake("草莓蛋糕");
System.out.println(cake.getName());
cakeFactory = new EggCakeFactory();
cake = cakeFactory.createCake("蛋黄蛋糕");
System.out.println(cake.getName());
}4.抽象工厂模式
抽象工厂模式:提供一个借口,用于创建相关或依赖对象的家族,而不要明确制定具体类。
还是用蛋糕店的例子来演示:
抽象类Cake:
public abstract class Cake {
protected String name;
protected String cream;
protected String chocolate;
protected String condiments;
public abstract void prepare();
public void bake(){
System.out.println("将蛋糕放进烤箱烘烤");
}
public void decorate(){
System.out.println("将" + condiments + "添加到蛋糕上");
}
public void box(){
System.out.println("将蛋糕装入包装箱中");
}
public void makeCake(){
this.prepare();
this.bake();
this.decorate();
this.box();
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
}抽象类CakeStore:
public abstract class CakeStore {
public abstract Cake createCake(String name);
}抽象原料工厂:
public abstract class IngredientFactory {
public abstract String createCream();
public abstract String createChocolate();
public abstract String createCondiments();
}
public class StrawberryCake extends Cake{
public StrawberryCake(IngredientFactory ingredientFactory){
this.ingredientFactory = ingredientFactory;
}
public void prepare() {
this.cream = this.ingredientFactory.createCream();
this.chocolate = this.ingredientFactory.createChocolate();
this.condiments = this.ingredientFactory.createCondiments();
}
private IngredientFactory ingredientFactory = null;
}抽象原料工厂的实现类CreamIngredientFactory:
public class CreamIngredientFactory extends IngredientFactory{
public String createCream() {
return "酸奶冰淇淋";
}
public String createChocolate() {
return "黑巧克力";
}
public String createCondiments() {
return "草莓片、苹果片、西瓜片、蓝莓片、猕猴桃片";
}
}
public class XXCakeStore extends CakeStore{
public Cake createCake(String name) {
IngredientFactory ingredientFactory = new CreamIngredientFactory();
Cake cake = null;
if("草莓蛋糕".equals(name)){
cake = new StrawberryCake(ingredientFactory);
cake.makeCake();
cake.setName("草莓奶油蛋糕");
return cake;
}else{
//......
}
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cake cake = new XXCakeStore().createCake("草莓蛋糕");
if(cake != null){
System.out.println(cake.getName());
}
}
























 497
497

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








