1. IO和NIO
2. 多线程
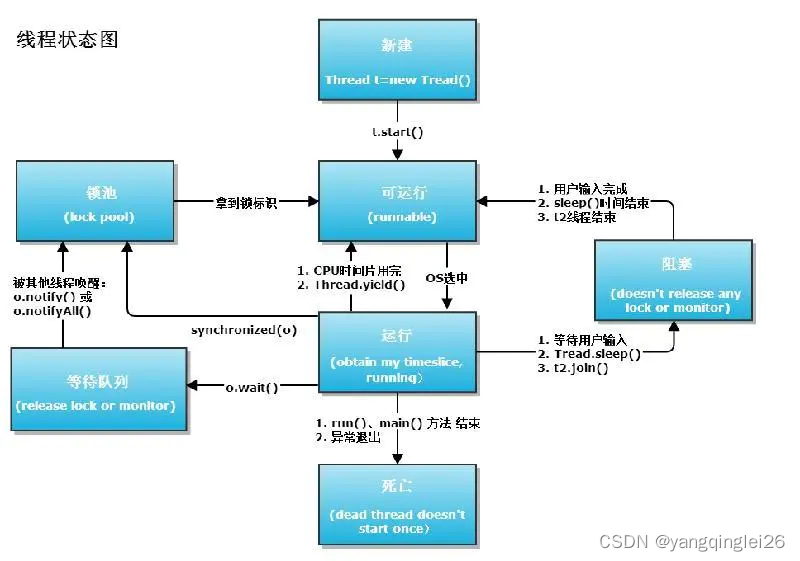
2.1. 创建线程
2.1.1. 实现Runnable接口
推进使用:方便同一个对象被多个线程使用
new Thread(Runnable 实现).start()
2.1.2. 继承Thread
2.1.3. 实现Callable接口
实现Callable接口,需要返回值类型
重写call方法,需要抛出异常
创建目标对象
创建执行服务:ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
提交执行:Future<Boolean> result1 = ser.submit(t1);
获取结果:boolean r1 = result1.get()
关闭服务:ser.shutdownNow()
2.2. 停止线程
2.2.1. 设置一个标志位
publ
2.3. 礼让线程
yield()
- 礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
- 将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态
- 让cpu重新调度,礼让不一定成功!看cpu心情
2.4. 强制执行线程
join()
2.5. 线程优先级
priority(1-10)
- 先设置优先级,再start()
2.6. 守护线程
2.7. 线程同步
-
队列+锁
-
synchronized
-
lock
2.8. 线程通信
-
生产者和消费者问题
-
synchronized
-
while 防止虚假唤醒
-
wait()、notifyall()
2.8.1. 管程法
- 缓冲池
2.8.2. 信号灯法
- 标志位
2.9. 线程池
3. 注解和反射
4. JUC
ThreadLocal Java中的ThreadLocal详解 多个 THREADLOCAL 在 THREAD 中的 THREADLOCALS 里是怎么存储的
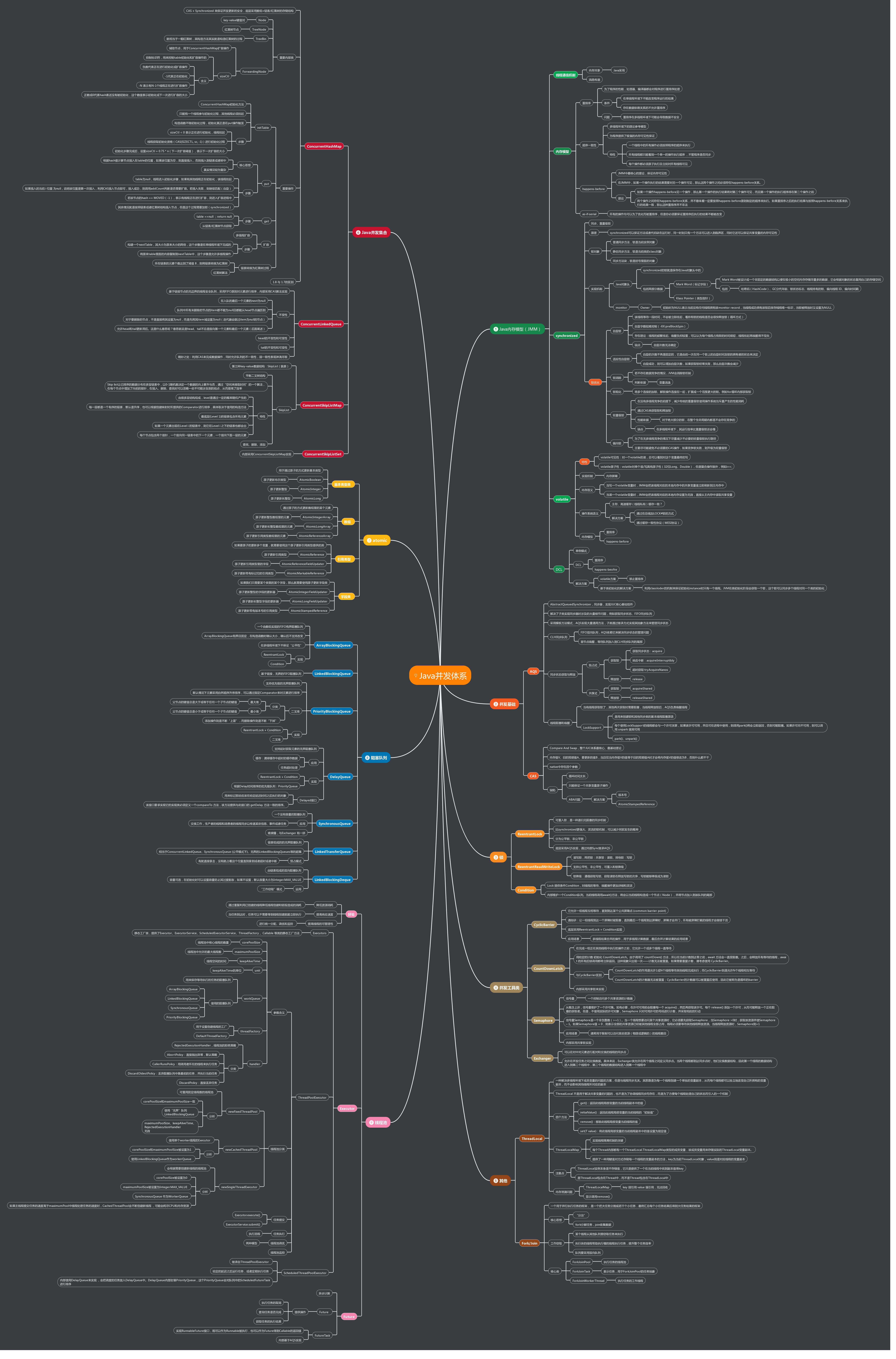
4.1. wait和sleep的区别
- 来自不同的类
wait => object sleep => Thread
- 锁的释放
wait 会释放锁,sleep 不会释放
- 使用范围
wait 在 synchronized 中使用
4.2. Lock锁
4.2.1. ReentrantLock
- 默认非公平锁
- 必须成对出现
- 示例:
public class ReentrantLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mycache mycache = new Mycache();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++){
try {
mycache.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+j,"toy"+j);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread"+i).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++){
mycache.get(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+j);
}
},"thread"+i).start();
}
}
static class Mycache{
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void put(String key,String value) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"开始写入");
map.put(key,value);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"退出写入");
lock.unlock();
}
public String get(String key){
lock.lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"开始读取");
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"退出读取");
lock.unlock();
return value;
}
}
}
执行结果:
thread0:开始写入
thread0:退出写入
thread1:开始写入
thread1:退出写入
thread1:开始写入
thread1:退出写入
thread2:开始写入
thread2:退出写入
thread0:开始读取
thread0:toy0
thread0:退出读取
thread0:开始读取
thread0:null
thread0:退出读取
thread1:开始读取
thread1:toy0
thread1:退出读取
thread1:开始读取
thread1:toy1
thread1:退出读取
thread2:开始读取
thread2:toy0
thread2:退出读取
thread2:开始读取
thread2:null
thread2:退出读取
thread0:开始写入
thread0:退出写入
thread2:开始写入
thread2:退出写入
4.2.2. synchronized 和 lock 的区别
| 序号 | synchronized | lock |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 内置的java关键字 | java接口 |
| 2 | 无法获取锁的状态 | 可以获取锁的状态 |
| 3 | 会自动释放锁 | 手动释放锁 |
| 4 | 线程阻塞时,其它线程会一直等待 | 可以主动尝试获取锁 |
| 5 | 非公平锁,不可以中断 | 可以自定义 |
| 6 | 适合锁少量的同步代码 | 适合锁大量的同步代码 |
4.2.3. Condition
await() 、signal()
4.2.4. 八锁现象
synchronized 锁的对象
- 方法的调用者
- class类模板(static)
4.3. 集合相关
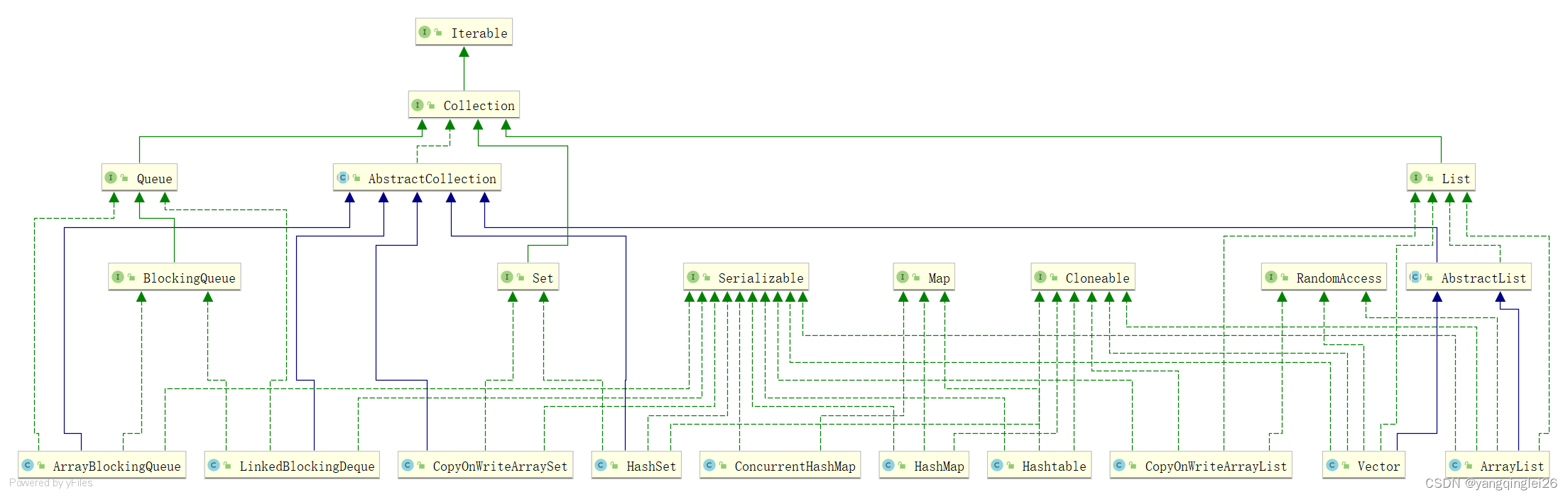
4.3.1. ArrayList
并发下 ArrayList 会抛出 ConcurrentModificationExecptin ,解决办法:
- new Vector()
// Vector.class
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
-
Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList())
-
new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>() 读写分离
// CopyOnWriteArrayList.class
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
newElements[len] = e;
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
4.3.2. HashSet
- 底层
// HashSet.class
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
- 并发下 HashSet 会抛出 ConcurrentModificationExecptin ,解决办法:
- Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet ())
- new CopyOnWriteArraySet()
4.3.3. HashMap
并发下 HashMap 会抛出 ConcurrentModificationExecptin ,解决办法:
- Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap ())
- new ConcurrentHashMap()
4.4. Callable
- 调用
new Thread(new FutureTask(new Callable() {
public Object call() throws Exception {
return null;
}
})).start();
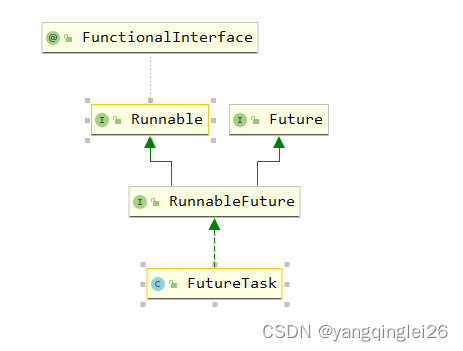
public class CallableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask task = new FutureTask(new Callable() {
public String call() throws InterruptedException {
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("A1")){
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
return Thread.currentThread().getName() +" do working";
}
});
new Thread(task,"A1").start();
// task.get 会阻塞线程
String status = (String) task.get();
System.out.println(status);
// call 只会被执行一次
new Thread(task,"A2").start();
status = (String) task.get();
System.out.println(status);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
结果为:
A1 do working
A1 do working
main
4.5. CountDownLatch(倒计时弹簧锁)
public class CountDownLatchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (CountDownLatchTest.class) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
":" +"进入等待" +
(latch.getCount() == 0 ?"": latch.getCount()));
latch.countDown();
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" +"结束等待" );
},"cousumer"+i).start();
}
}
}
- 执行结果:
cousumer0:进入等待5
cousumer4:进入等待4
cousumer5:进入等待3
cousumer3:进入等待2
cousumer2:进入等待1
cousumer2:结束等待
cousumer4:结束等待
cousumer1:进入等待
cousumer3:结束等待
cousumer0:结束等待
cousumer5:结束等待
cousumer1:结束等待
cousumer8:进入等待
cousumer8:结束等待
cousumer6:进入等待
cousumer6:结束等待
cousumer9:进入等待
cousumer9:结束等待
cousumer7:进入等待
cousumer7:结束等待
4.6. CyclicBarrier(循环阻塞)
public class CyclicBarrierTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 3;
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(num);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (CountDownLatchTest.class) {
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() +
":" + "进入等待" +
cyclicBarrier.getNumberWaiting()
);
}
try {
// 计数 + 等待
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" +"结束等待" );
},"cousumer"+i).start();
}
}
}
- 执行结果
cousumer0:进入等待0
cousumer1:进入等待1
cousumer3:进入等待2
cousumer3:结束等待
cousumer2:进入等待0
cousumer1:结束等待
cousumer0:结束等待
cousumer4:进入等待1
cousumer5:进入等待2
cousumer6:进入等待0
cousumer4:结束等待
cousumer2:结束等待
cousumer5:结束等待
cousumer7:进入等待1
cousumer8:进入等待2
cousumer8:结束等待
cousumer6:结束等待
cousumer7:结束等待
4.7. Semaphore(信号量)
public class SemaphoreTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + "开始任务");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + "执行结束" );
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
semaphore.release();
}
},"cousumer"+i).start();
}
}
}
执行结果:
cousumer1:开始任务
cousumer2:开始任务
cousumer0:开始任务
cousumer0:执行结束
cousumer1:执行结束
cousumer2:执行结束
cousumer4:开始任务
cousumer5:开始任务
cousumer3:开始任务
cousumer4:执行结束
cousumer3:执行结束
cousumer6:开始任务
cousumer5:执行结束
cousumer7:开始任务
cousumer8:开始任务
cousumer8:执行结束
cousumer7:执行结束
cousumer6:执行结束
cousumer9:开始任务
cousumer9:执行结束
- 只有获取到Semaphore才会开始工作
4.8. ReadWriteLock
public class ReadWriteLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mycache mycache = new Mycache();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++){
try {
mycache.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+j,"toy"+j);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread"+i).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++){
try {
mycache.get(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+j);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread"+i).start();
}
}
static class Mycache{
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public void put(String key,String value) throws InterruptedException {
lock.writeLock().lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"开始写入");
map.put(key,value);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"退出写入");
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
public String get(String key) throws InterruptedException {
lock.readLock().lock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"开始读取");
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+"退出读取");
lock.readLock().unlock();
return value;
}
}
}
执行结果:
thread0:开始写入
thread0:退出写入
thread0:开始写入
thread0:退出写入
thread2:开始写入
thread2:退出写入
thread2:开始写入
thread2:退出写入
thread1:开始写入
thread1:退出写入
thread1:开始写入
thread1:退出写入
thread0:开始读取
thread0:toy0
thread0:退出读取
thread0:开始读取
thread2:开始读取
thread2:toy0
thread2:退出读取
thread0:toy1
thread0:退出读取
thread1:开始读取
thread1:toy0
thread1:退出读取
thread2:开始读取
thread2:toy1
thread2:退出读取
thread1:开始读取
thread1:toy1
thread1:退出读取
- 所有写线程结束,才会进入读线程。读线程读取时,并没有锁定代码块。
4.9. BlockingQueue
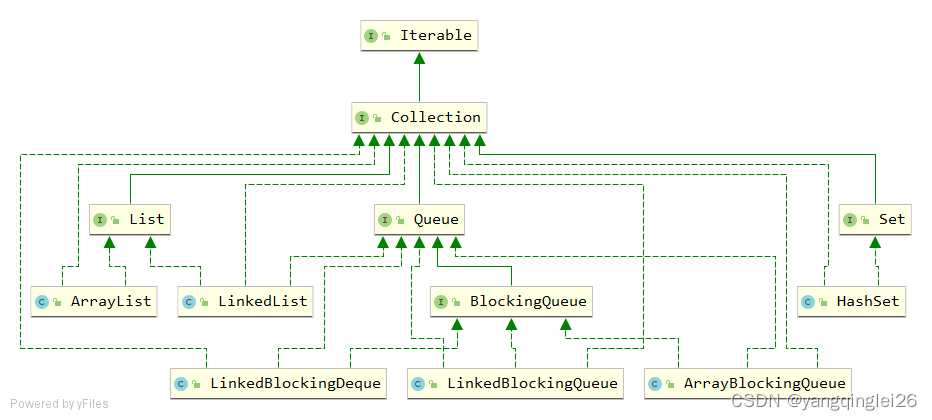
4.9.1. ArrayBlockingQueue
| 抛出异常 | 特殊值 | 阻塞 | 超时 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 插入 | add(e) | offer(e) | put(e) | offer(e, time, unit) |
| 移除 | remove() | poll() | take() | poll(time, unit) |
| 检查 | element() | peek() | 不可用 | 不可用 |
4.9.2. SynchronousQueue
4.10. Executors
4.10.1. 三种创建方式(不采用)
4.10.2. ThreadPoolExecutor 七大参数
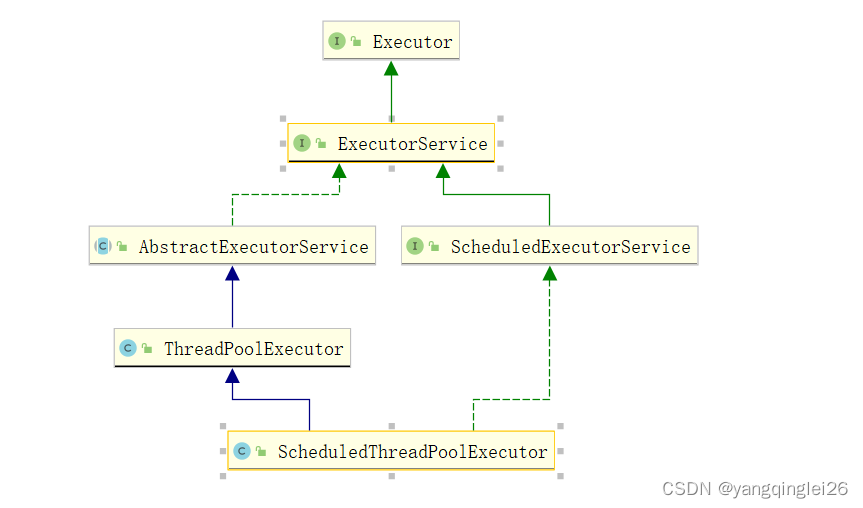
/**
* Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial
* parameters.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor
* creates a new thread
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br>
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}<br>
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue}
* or {@code threadFactory} or {@code handler} is null
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
}
- cpu密集型
- IO密集型
4.11. 四大函数式接口
4.12. Stream 流式计算
4.13. ForkJoin
4.14. 异步回调
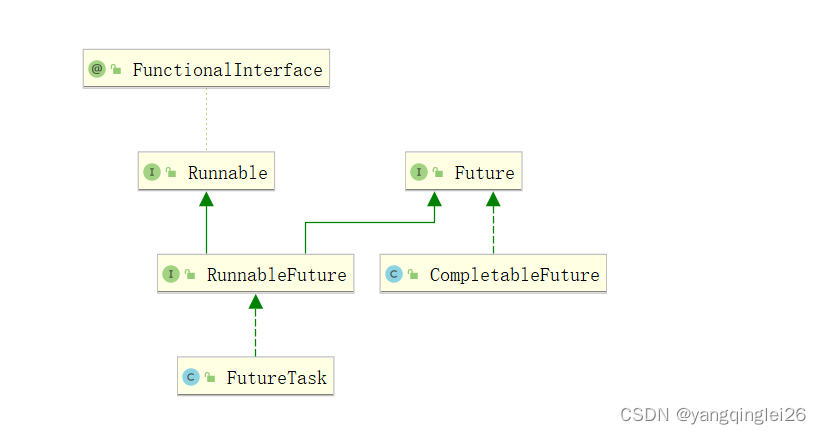
4.15. JMM
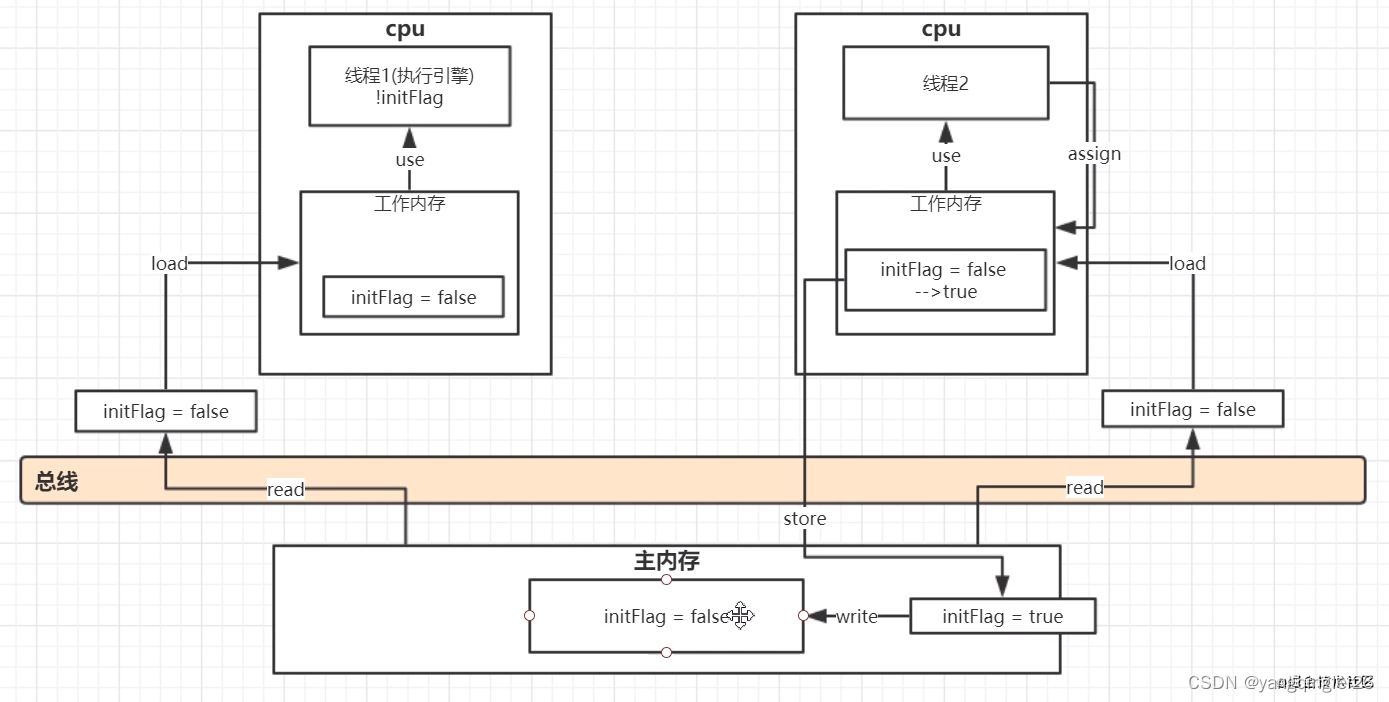
内存屏障(Memory Barrier)又称内存栅栏,是一个CPU指令,它的作用有两个:
- 保证特定操作的顺序
- 保证某些变量的内存可见性(利用该特性实现volatile的内存可见性)
4.16. volatile
volatile 是java虚拟机提供的轻量级的同步机制
- 保证可见性
- 不保证原子性
- 原子类
- 禁止指令重排
4.17. 单例模式
- DCL懒汉式
- 枚举
4.18. CAS
- ABA 问题
- AtomicInteger
- AtomicStampedReference
4.19. 各种锁
4.19.1. 公平锁、非公平锁
4.19.2. 可重入锁
4.19.3. 自旋锁
4.19.4. 死锁
- 死锁排查
程序员面试宝典4.27版
5. JVM
/**
* @Description: 字面量测试
* @Author: yql
* @Date: 2021/6/8 18:43
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class LiteralTest {
public static String s = "Hello";
public static int anInt = 25;
public int bnInt = 30;
public Integer cnInt = 50;
public static final int dnInt = 70;
int m = 100;
static {
anInt = 90;
}
}
# 查看编译后类信息
javap -verbose LiteralTest.class
6. Java8
6.1. 函数式接口
- 定义:任何接口,如果只包含唯一一个抽象方法,那么它就是函数式接口
- 可以用lamada表达式代替匿名内部类来实现
6.1.1 Predicates
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate<T> {
boolean test(T t);
}
6.1.2 Functions
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
R apply(T t);
}
6.1.3 Suppliers
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {
T get();
}
6.1.4 Consumers
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {
void accept(T t);
}








 这篇文章详细介绍了Java中的IO和NIO,多线程的创建、停止、礼让、优先级和守护线程,以及线程同步、通信、线程池、注解和反射、JUC并发工具(如ReentrantLock、Condition、CountDownLatch等)、Java8的函数式编程特性、日期时间API等。还涉及了JVM内存管理和并发编程最佳实践。
这篇文章详细介绍了Java中的IO和NIO,多线程的创建、停止、礼让、优先级和守护线程,以及线程同步、通信、线程池、注解和反射、JUC并发工具(如ReentrantLock、Condition、CountDownLatch等)、Java8的函数式编程特性、日期时间API等。还涉及了JVM内存管理和并发编程最佳实践。














 11万+
11万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








