流
分类:
- 输入流-----输出流
- 字节流-----比特流
- 节点流-----处理流

字符流:处理文本文件(txt .java.c.cpp)
字节流:处理非文本文件(.jpg.mp3.\doc.ppt)
字节流的后缀为Stream 字符流不是
buffer:缓冲
读字符流
在不考虑异常的情况下读取一个文件中的数据(便于学习,代码短)
- File类实例化一个对象
- FlidReader实例化一个对象参数为 1 中的对象
- 读入数据
- 关闭资源
@Test
public void test7() throws IOException {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(file);
int read ;//读一个字符
while( (read = fileReader.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)read);
}
fileReader.close();
}
chars表明每次目标读取的字符个数
len 表示实际读取字符个数
char[] chars = new char[8];
int len ;
while ((len = fr.read(chars))!= -1){
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.print(chars[i]);
}

String的一个构造器将char[]转为string可以避免上面代码中的for循环
@Test
public void test7() throws IOException {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
char[] chars = new char[8];
int len ;
while ((len = fr.read(chars))!= -1){
// for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// System.out.print(chars[i]);
String s = new String(chars, 0, len);
System.out.print(s);
}
fr.close();
}
读字节流
@Test
public void test8() throws IOException {
//造文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//造流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//读
byte[] b = new byte[6];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(b))!=-1){
String s = new String(b, 0, len);
System.out.print(s);
}
}
写字符流
在不考虑异常的情况下写入数据至文件中
- File类实例化一个对象
- FlidRite实例化一个对象参数为 1 中的对象
- 写入数据
- 关闭资源
文件不存在时创建文件
文件存在时,对文件进行覆盖
File file = new File("hello.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
fw.write("123");
fw.close();
若添加true参数,则不是覆盖而是追加存储,默认为false
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file,true);
读写的应用(文件复制)(字符流):
File file = new File("hello.txt");
File file1 = new File("hello_1.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file1,true);
char[] c = new char[5];
int i;
while((i=fr.read(c))!= -1){
fw.write(c,0,i);
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
读写的应用(图片复制)(字节流):
@Test
public void test8() throws IOException {
//造文件
File file = new File("timg.jpg");
File file1 = new File("t.jpg");
//造流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);
//复制
byte[] b = new byte[10];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(b))!=-1){
fos.write(b,0,len);
}
fis.close();
}
缓冲流复制图片
@Test
public void test10() throws IOException {
//造文件
File file1 = new File("timg.jpg");
File file2 = new File("t1.jpg");
//造流节点流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
//造缓冲流 参数为节点流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//复制数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[10];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer))!=-1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//b关闭 f自动关闭
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
缓冲流复制文本
在read方法处 采用readLine替换 读取一整行 ,记得在write时手动换行
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedTest {
/**
* 使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter实现文本文件的复制
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
//创建文件和相应的流
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("dbcp.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("dbcp1.txt")));
//读写操作
//方式一:使用char[]数组
// char[] cbuf = new char[1024];
// int len;
// while((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1){
// bw.write(cbuf,0,len);
// // bw.flush();
// }
//方式二:使用String
String data;
while((data = br.readLine()) != null){
//方法一:
// bw.write(data + "\n");//data中不包含换行符
//方法二:
bw.write(data);//data中不包含换行符
bw.newLine();//提供换行的操作
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
转换流
字节流与字符流之间的转换
InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流 : 字节(byte[ ])in ---->字符(char[ ])in
OutputStreamWriter: 将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流:字符(char [ ])out---->字节(byte[ ])out
字符 ----->字节:编码:类似:txt—>md5
字节 ----->字符:解码:类似:md5—>txt
通过转换流实现utf8---->gbk的转换
@Test
public void test11() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("hello.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("hello_gbk.txt");
//
//参数为一个字符流输出,第二个参数为字符集,没写按系统默认字符集
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf8");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "gbk");
char[] buffer = new char[10];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(buffer))!= -1){
osw.write(buffer,0,len);
}
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
常见的编码表:
- ASCII:美国标准信息交换码。
-
用一个字节的7位可以表示。 - ISO8859-1:拉丁码表。欧洲码表
-
用一个字节的8位表示。 - GB2312:中国的中文编码表。最多两个字节编码所有字符
- GBK:中国的中文编码表升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号。最多两个字节编码
- Unicode:国际标准码,融合了目前人类使用的所有字符。为每个字符分配唯一的字符码。所有的文字都用两个字节来表示。
- UTF-8:变长的编码方式,可用1-4个字节来表示一个字符。
对象流
对象流:对象的传输处理流
序列化:java对象写入到数据源中:可序列化的对象: 内存------>文件,java对象---->二进制流
反序列化:从数据源中读取java对象 :可序列化的对象: 文件---->内存,二进制流----->java对象
序列化:
@Test
public void test12() throws IOException{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("hello.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(new String("天!"));
oos.flush();
}
反序列化:
@Test
public void test13() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("hello.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
Object o = ois.readObject();
String str = (String)o;
System.out.println(str);
}
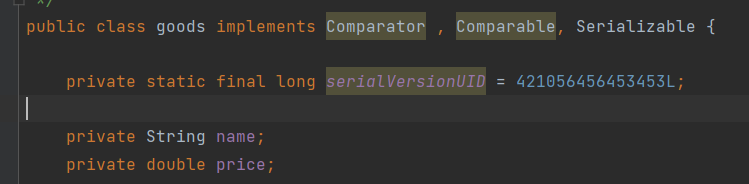
自定义类的 序列化:
- 需要自定义类继承 Serializable接口
- 在类中添加 private static final long serialVersionUID = 421056456453453L; 静态常量 数字可以自己定
- 类的所有属性也必须可以序列化(内部类也必须完成1,2步骤)
- transient 、static 无法序列化
@Test
public void test12() throws IOException{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("hello.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
goods g1 = new goods("面包", 5);
oos.writeObject(g1);
oos.flush();
}
反序列化:接受类必须与传输类相同
@Test
public void test13() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("hello.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
Object o = ois.readObject();
goods g = (goods)o;
System.out.println(g);
}





















 5429
5429











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








