0 Preface/Foreword
0.1 摘要:
The Hands-Free Profile (HFP) specification defines a set of functions such that a Mobile Phone can be used in conjunction with a Hands-Free device (e.g., installed in the car or represented by a wearable device such as a headset), with a Bluetooth Link providing a wireless means for both remote control of the Mobile Phone by the Hands-Free device and voice connections between the Mobile Phone and the Hands-Free device.
Compliance with this specification assures interoperability between a Bluetooth enabled Hands-Free device and any Bluetooth equipped Mobile Phone supporting this profile.
HFP版本信息:
- V1.7.0, 18 Sept 2014, adopted by the Bluetooth SIG BoD
- V1.7.1, 15 Dec 2014, adopted by the Bluetooth SIG BoD
- V1.7.2, 2019-01-21, adopted by the Bluetooth SIG Board of Directors
- V1.8, 2020-04-14, adopted by the Bluetooth SIG Board of Directors
0.2 Acronym & abbreviation
- HF: Hands-Free unit
- AG: Audio Gateway
- SCO: Synchronous Connection Oriented
- eSCO: enhanced Synchronous Connection Oriented
- RFU: RFU is equivalent to Reserved for Future Use
- PDU: Protocol Data Unit
- OSI: Open System Interconnection,开发系统互联。一般值OSI reference model,开放系统互联七层参考模型
- ISO: International Organization for Standardization,国际标准化组织
0.3 Role
- AG (Audio Gateway), it means Cellular Phone
- HF (Hands-Free), it means Hands-Free unit
0.4 types of diagram
fundamental types as below:
- system block diagram
- functional block diagram
1 介绍
1.1 Scope
This document defines the protocols and procedures that shall be used by devices implementing the Hands-Free Profile. The most common examples are in-car Hands-Free units used together with cellular phones, or wearable wireless headsets.
The profile defines how two devices supporting the Hands-Free Profile shall interact with each other on a point-to-point basis.
An implementation of the Hands-Free Profile typically enables a headset, or an embedded hands-free unit to connect, wirelesssly, to a cellular phone for the purpose of acting as the cellular phone's audio input and output mechanism and allowing typical telephony functions to be performed without access to the actual phone.
1.2 Profile dependencies
The Bluetooth profile structure and dependencies of the profile are depicted. A profile is dependent upon another profile if it re-uses parts of that profile, by explicitly referencing it. Dependency is illustrated in below figure.
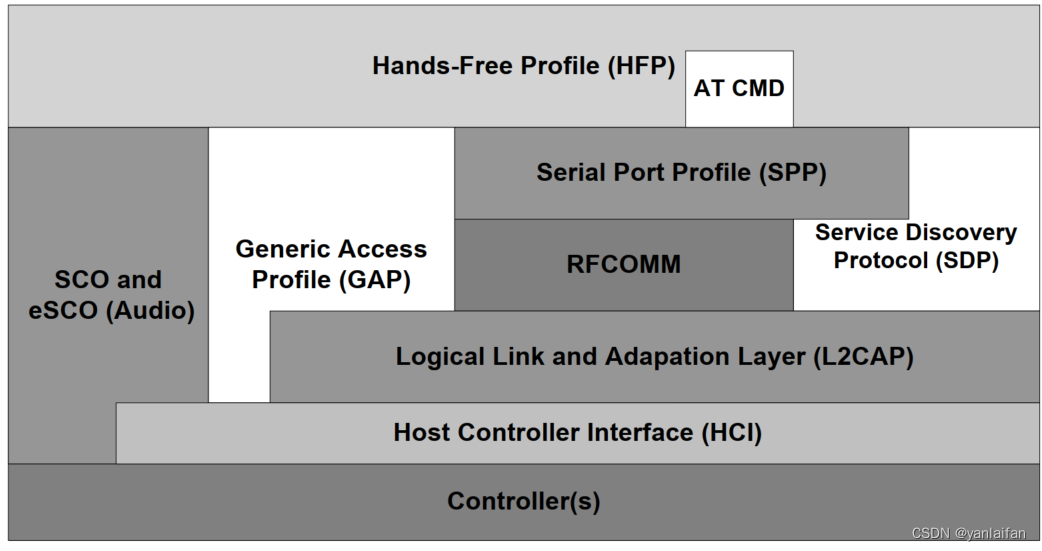
As indicated in above figure, the Hands-Free Profile is dependent upon both the Serial Port Profile (SPP) and the Generic Access Profile (GAP).
1.3 Requirement Status Symbols
The symbols as below:
- "M" for mandatory to support
- "O" for optional to support
- "X" for excluded (used for capabilities that may be supported by the device, but the Hands-Free Profile shall not use these capabilities)
- "C" for conditional to support
- "N/A" for not applicable (in the given context this capability is not defined)
Some capabilites or features (identified as "X"), mandated according to the relevant Bluetooth specifications, are excluded with respect to this profile because they might degrade the operation of devices in the particular use case. Therefore, features or capabilites labelled "X" shall never be activated while operating in a use case where they are labelled as such.
1.4 Naming convention
- LMP link:a link over Link Manager Protocol (LMP)
- RFCOMM connection:it means the presence of a virtual serial port (SPP: Serial Port Protocol).
- Service Level Connection
- Service Level Connection initialization
- Service Level Connection establishment
- Synchronous Connection: a SCO or eSCO logical link intended for supporting a full duplex Audio Connection
- Audio Connection
- Codec Connection
- Wide Band Speech Connection
- mSBC
- incoming call, a call connection in the direction "Phone Network=>AG", such that it is initiated by the Network to which the AG is attached.
- outgoing call, a call connection in the direction "AG=>Phone Network", such that it is initiated by the AG towards the Network to which it is attached.
- legacy device
1.5 Signaling diagram conventions

1.6 Language
1.6.1 Language conventions
The Bluetooth SIG has established the following conventions for use of the words shall, must, will, should, may, can, is, and note in the development of specifications.
- shall, is required to --used to define requirements
- must, is used to express: a natural consequence of a previously stated mandatory requirement. OR an indisputable statement of fact (one that is always true regardless of the circumstances)
- will, it is true that -- only used in statements of fact
- should, is recommended that -- used to indicate that among several possibilities on is recommended as particularly suitable, but not required
- may, is permitted to -- used to allow options
- can, is able to --used to relate statements in a casual manner.
- is, is defined as -- used to further explain elements that are previously required or allowed
- note, used to indicate text that is included for informational purposes only and is not required in order to implement the specification. Each note is clearly designated as a "Note" and set off in a separate paragraph.
1.6.2 Reserved for Future Use
Where a field in a packet, Protocol Data Unit (PDU), or other data structure is described as "Reserved for Future Use" (irrespective of whether in uppercase or lowercase), the device creating the structure should set its value to zero unless otherwise specified.
Where a filed, parameter, or other variable object can take a range of values, and some values are described as "Reserved for Future Use", a device sending the object should not set the object to those values.
1.6.3 Prohibited
When a filed value is an enumeration, unassigned values can be marked as "Prohibited".
2 协议概览
2.1 Protocol Stack
Please see the protocols and entities used in this profile as following figure.
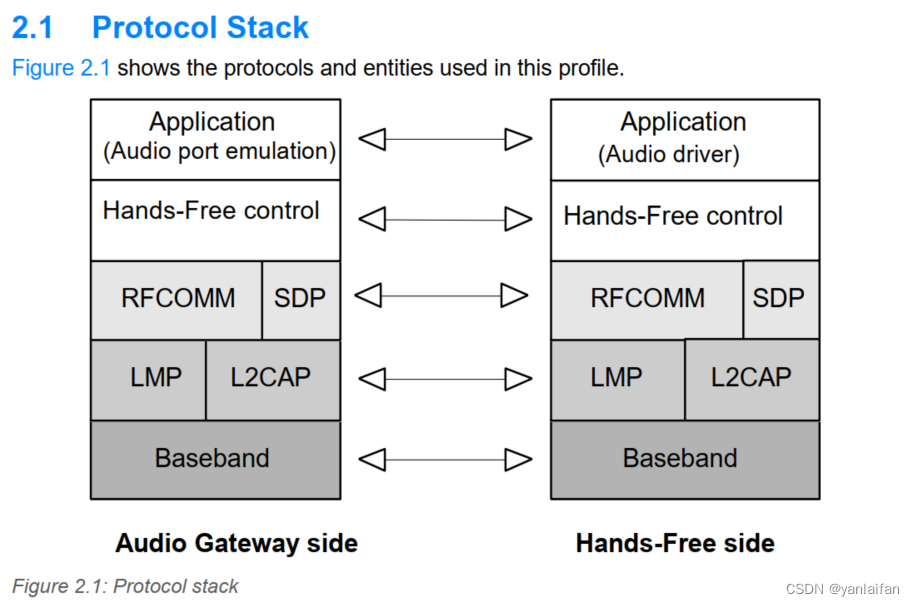
The Baseband, LMP (Link Management Protocol), and L2CAP are the OSI layer 1 and layer 2 Bluetooth protocols.
- Physical Layer: Baseband
- Data Link Layer: LMP, L2CAP
RFCOMM is the Bluetooth serial port emulation entity.
SDP is the Bluetooth Discovery Protocol.
Hands-Free control is the entity responsible for Hands-Free unit specific control signaling; this signaling is AT command based.
The audio port emulation layer shown in above figure is the entity emulating the audio port on the Audio Gateway, and the audio driver is the driver software in the Hands-Free unit.
For the shaded protocols/entities, the Serial Port Protocol is used as the base standard.
3 应用层
4 Hands-Free控制互操作需求
5 串口协议
6 通用访问协议
7 入门通读
7.1 基本信息
HFP协议定义了:
- 实现HFP的设备应该使用的协议和
- 实现步骤
- HFP是点对点的通讯交互
OSI协议层级关系:
SDP: Service Discovery Protocol
SCO: Synchronous Connection Oriented
eSCO: enhanced Synchronous Connection Oriented,增强型
- Audio Port emulation(AG) & Audio driver (HF),相当于应用层。
- HFP协议,放在TCP/IP模型中,相当于网络层。
- SPP/RFCOMM/SDP & SCO/eSCO,相当于传输层;
- L2CAP,相当于链路层;
- HCI/Controller,相当于物理层;
电话支持行为:
- Accept call
- Reject call
- Terminate call.
通话类型:
- incoming,来电
- outgoing,去电
通话支持的算法:
EC: Echo Cancellation
NR: Noise Reduction
SBC类型:
- SBC: Sub-band codec,子带编码,蓝牙规范强制要求的编解码方式,支持采样率有:16Kbps/32Kbps/44.1Kbsp/48Kbps
- mSBC: Media streaming over Bluetooth Classic SBC. V4.0引入的codec 编解码方式,为了适配蓝牙数据包。
HFP中角色:
- AG:负责音频的输入
- HF:远程音频的输入和输出。HF还可以远程控制AG。
7.2 信令交互
SLC:Service Level Connection,服务级连接
Setup包含:
- codec connection setup,AG端通过“AT+BCS”选择编码,AT+BAC告诉支持的编码,比如说SBC/mSBC
- SLC setup
- SCO setup
7.2.1 In-band ringing(AG/HF铃声同步)
如果HF支持,那么AG需要建立SCO,AG将Ring传给HP;
如果HF不支持,只需要AG告诉HF,HF会自动响铃,铃声由HF决定。
7.2.2 VRA (Voice Recognision Activation)
HF端&AG端触发流程:
- AT + BVRA = 1,HF端触发启用,AG端应主动拉起SCO/eSCO语音链路。(分两种情况:a 手机端不建立SCO,使用内部的MIC; b. 主动建立SCO,用外部MIC,即HF MIC)
- AG端初始化:+BVRA:1

























 384
384

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








