题目:输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。比如输入下图中二叉搜索树,则输出转换后的排序双向链表。
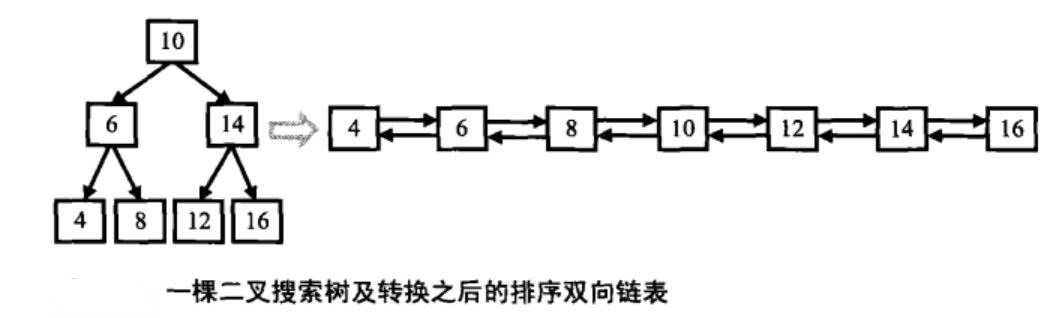
解析:在二叉搜索树中,每个结点都有两个分别指向其左、右子树的指针,左子树结点的值总是小于父结点的值,右子树结点的值总是大于父结点的值。在双向链表中,每个结点也有两个指针,它们分别指向前一个结点和后一个结点。所以这两种数据结构的结点是一致,二叉搜索树和双向链表,只是因为两个指针的指向不同而已,通过改变其指针的指向来实现是完全可能的。
为了减少指针的变换次数,并让操作更加简单,在转换成排序双向链表时,原先指向左子结点的指针调整为链表中指向前一个结点的指针,原先指向右子结点的指针调整为链表中指向下一个结点的指针。
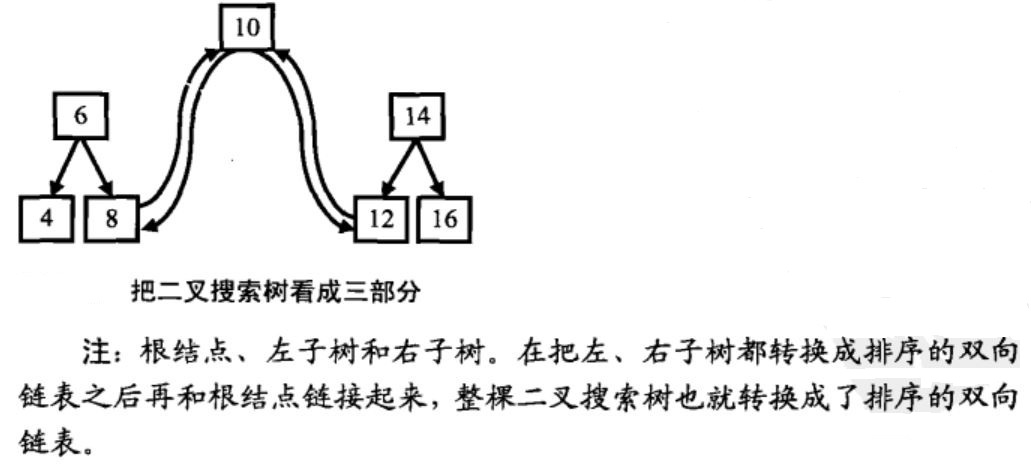
由于要求链表是有序的,可以借助二叉树中序遍历,因为中序遍历算法的特点就是从小到大访问结点。当遍历访问到根结点时,假设根结点的左侧已经处理好,只需将根结点与上次访问的最近结点(左子树中最大值结点)的指针连接好即可。进而更新当前链表的最后一个结点指针。同时中序遍历过程正好是转换成链表的过程,可采用递归方法处理。
完整代码及测试用例:
运行结果:
The Test1:
value of this node is 4
value of this node is 6
value of this node is 8
value of this node is 10
value of this node is 12
value of this node is 14
value of this node is 16
4 6 8 10 12 14 16
PrintList ends.
The Test2:
value of this node is 1
value of this node is 2
value of this node is 3
value of this node is 4
value of this node is 5
1 2 3 4 5
PrintList ends.
The Test3:
value of this node is 1
value of this node is 2
value of this node is 3
value of this node is 4
value of this node is 5
1 2 3 4 5
PrintList ends.
The Test4:
value of this node is 1
1
PrintList ends.
The Test5:
value of this node is 0
0
PrintList ends.
请按任意键继续. . .
时间复杂度与空间复杂度:
该算法首先从根要点一直向左走,找到最左边的结点,其时间复杂度为O(logN),然后对二叉排序树中的每个结点遍历一次,进行指针变换,其时间复杂度为O(N),所以总的时间复杂度为O(N)。空间复杂度,由于Convert函数进行递归调用,其函数有两个开参,而函数栈中的函数调用层数不会超过树高,所以其空间复杂度为O(logN)。

解析:在二叉搜索树中,每个结点都有两个分别指向其左、右子树的指针,左子树结点的值总是小于父结点的值,右子树结点的值总是大于父结点的值。在双向链表中,每个结点也有两个指针,它们分别指向前一个结点和后一个结点。所以这两种数据结构的结点是一致,二叉搜索树和双向链表,只是因为两个指针的指向不同而已,通过改变其指针的指向来实现是完全可能的。
为了减少指针的变换次数,并让操作更加简单,在转换成排序双向链表时,原先指向左子结点的指针调整为链表中指向前一个结点的指针,原先指向右子结点的指针调整为链表中指向下一个结点的指针。
由于要求链表是有序的,可以借助二叉树中序遍历,因为中序遍历算法的特点就是从小到大访问结点。当遍历访问到根结点时,假设根结点的左侧已经处理好,只需将根结点与上次访问的最近结点(左子树中最大值结点)的指针连接好即可。进而更新当前链表的最后一个结点指针。同时中序遍历过程正好是转换成链表的过程,可采用递归方法处理。

完整代码及测试用例:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//二叉树结点定义
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int Value;
BinaryTreeNode* Left;
BinaryTreeNode* Right;
};
//创建二叉树结点
BinaryTreeNode* CreateBinaryTreeNode(int value)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = new BinaryTreeNode();
pNode->Value = value;
pNode->Left = NULL;
pNode->Right = NULL;
return pNode;
}
//连接树结点
void ConnectTreeNodes(BinaryTreeNode* pParent, BinaryTreeNode* pLeft, BinaryTreeNode* pRight)
{
if (pParent != NULL)
{
pParent->Left = pLeft;
pParent->Right = pRight;
}
}
//中序遍历
void InOrderPrintTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
if (pRoot != NULL)
{
//遍历左边
if (pRoot->Left != NULL)
{
InOrderPrintTree(pRoot->Left);
}
//根
cout << "value of this node is " << pRoot->Value << endl;
//遍历右边
if (pRoot->Right != NULL)
{
InOrderPrintTree(pRoot->Right);
}
}
else
{
cout << "this node is null." << endl;
}
}
//转换排序二叉树为双向链表
void Convert(BinaryTreeNode* pNode, BinaryTreeNode** pLastNodeLnList)
{
if (pNode == NULL)
{
return;
}
BinaryTreeNode* pCurrent = pNode;
//左子树转换,遍历到左子树的叶子结点
if (pCurrent->Left != NULL)
{
Convert(pCurrent->Left, pLastNodeLnList);
}
pCurrent->Left = *pLastNodeLnList;
if ((*pLastNodeLnList) != NULL)
{
(*pLastNodeLnList)->Right = pCurrent;
}
*pLastNodeLnList = pCurrent;
//右子树转换
if (pCurrent->Right != NULL)
{
Convert(pCurrent->Right, pLastNodeLnList);
}
}
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* Convert(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
//指向双向链表的尾结点
BinaryTreeNode* pLastNodeInList = NULL;
//转换排序二叉树为双向链表
Convert(pRoot, &pLastNodeInList);
//求双向链表的头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = pLastNodeInList;
while (pHeadOfList!=NULL&&pHeadOfList->Left!=NULL)
{
pHeadOfList = pHeadOfList->Left;
}
return pHeadOfList;
}
//打印双向链表
void PrintList(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = pRoot;
while (pNode!=NULL)
{
cout << pNode->Value << " ";
pNode = pNode->Right;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "PrintList ends." << endl << endl;
}
// ====================测试代码====================
void Test1()
{
// 10
// / \
// 6 14
// /\ / \
// 4 8 12 16
cout << "The Test1:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode16 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(16);
//连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, pNode16);
//中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode10);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode10);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList);
}
void Test2()
{
// 5
// /
// 4
// /
// 3
// /
// 2
// /
// 1
cout << "The Test2:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1);
//连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode4,NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, pNode3, NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, pNode2, NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, pNode1, NULL);
//中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode5);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode5);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList);
}
void Test3()
{
// 1
// \
// 2
// \
// 3
// \
// 4
// \
// 5
cout << "The Test3:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
//连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, NULL, pNode2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, NULL, pNode3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, NULL, pNode4);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, NULL, pNode5);
//中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode1);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode1);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList);
}
void Test4()
{
// 树中只有1个结点
cout << "The Test4:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1);
//连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, NULL, NULL);
//中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode1);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode1);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList);
}
void Test5()
{
// 树中没有结点
cout << "The Test5:" << endl;
//创建树结点
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(NULL);
//连接树结点
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, NULL, NULL);
//中序遍历
InOrderPrintTree(pNode1);
//获取双向链表头结点
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pNode1);
//输出链表
PrintList(pHeadOfList);
}
void main()
{
Test1();
Test2();
Test3();
Test4();
Test5();
system("pause");
}
运行结果:
The Test1:
value of this node is 4
value of this node is 6
value of this node is 8
value of this node is 10
value of this node is 12
value of this node is 14
value of this node is 16
4 6 8 10 12 14 16
PrintList ends.
The Test2:
value of this node is 1
value of this node is 2
value of this node is 3
value of this node is 4
value of this node is 5
1 2 3 4 5
PrintList ends.
The Test3:
value of this node is 1
value of this node is 2
value of this node is 3
value of this node is 4
value of this node is 5
1 2 3 4 5
PrintList ends.
The Test4:
value of this node is 1
1
PrintList ends.
The Test5:
value of this node is 0
0
PrintList ends.
请按任意键继续. . .
时间复杂度与空间复杂度:
该算法首先从根要点一直向左走,找到最左边的结点,其时间复杂度为O(logN),然后对二叉排序树中的每个结点遍历一次,进行指针变换,其时间复杂度为O(N),所以总的时间复杂度为O(N)。空间复杂度,由于Convert函数进行递归调用,其函数有两个开参,而函数栈中的函数调用层数不会超过树高,所以其空间复杂度为O(logN)。






















 523
523

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








