JAVA训练营-5月
一、环境
1、idea安装
idea就是一个开发工具,写代码的地方
目录结构:
--- 项目(工程 project) 比如:京东
---- 模块(module) 比如:订单、购物车、秒杀等
----- 包(package) 比如:com.jd
------ 类(class) 比如:用户类、订单类、购物车类等
------- 代码(方法、属性等)
2、jdk安装(1.8)
jdk:java开发环境
jre:java运行环境
jvm(java virtual machine):java虚拟机
三个检测命令
java 查看java运行环境
javac 查看java编译环境
java -version 查看java的版本信息
(1)先安装jdk,再安装jre
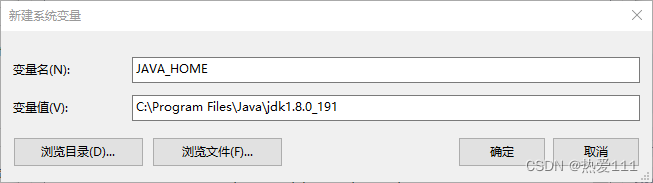
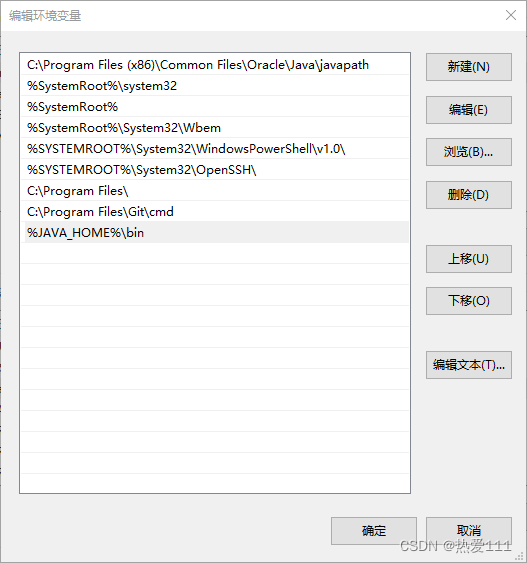
(2)配置系统环境变量JAVA_HOME和Path
package cn.tedu;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("这是我的第一个JAVA演示项目!");
}
}
二、数据类型
1、基本数据类型
(1)整型:存整数,默认是int
①byte
存储范围:[-128,127]
②short
存储范围:[-32768,32767]
③int
存储范围:[-2147483648,2147483647]
④long
(2)浮点型:存小数,默认是double
①float,需要加一个后缀F(f)
②double
(3)字符型:存单个字符(英文字母、汉字、数字[0-65535])
char
注:当存储的是一个数字时,会根据ascii码表查出对应的字符
(4)布尔型:存true或者false
boolean
package cn.tedu.datatype;
/**
* 演示基本数据类型的使用
*/
public class Test1 {
//程序运行的入口-main方法
public static void main(String[] arg) {
//整型:byte short int long
//定义变量格式:
//变量的类型 变量的名字 = 变量的值;
byte b1 = 125;//[-128,127]
short s1 = 32111;//[-32768,32767]
int i1 = 21474;//[-2147483648,2147483647]
long l1 = 10;
System.out.println(b1);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(l1);
float f1 = 8.73F;
double d1 = 8.73;
System.out.println(f1);
System.out.println(d1);
char c1 = 'X';
char c2 = '达';
char c3 = 77;
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
boolean bl1 = true;
boolean bl2 = false;
System.out.println(bl1);
System.out.println(bl2);
}
}
类型从大到小排序:double > float > long > int > short > byte
基本数据类型转换:
①强制转换(显式转换)
格式:
小类型 变量的名字 = (小类型/比小类型还小的类型)变量的值;
强制转换虽然能解决编译的问题,但是同样也带来了新的问题:精度丢失,数据可能会有问题
②自动转换(隐式转换)
package cn.tedu.datatype;
/**
* 测试基本数据类型转换
* double > float > long > int > char > short > byte
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//整型举例
byte b1 = (byte)128;//小 = 大
System.out.println(b1);
int i1 = (int)5.88;//小 = 大
int i2 = (short)5.88;//小 = 大 大 = 小
int i3 = (byte)5.88;//小 = 大 大 = 小
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(i2);
System.out.println(i3);
//自动类型转换(隐式转换)
int i4 = (byte)127;//大 = 小
}
}
2、引用类型:除基本数据类型以外的都称为引用类型
三、运算符
1、算术运算符
+:有双重含义,一种是正常的加法运算,还有一种是字符串拼接
-
*
/
++
--
%(取模,求余数)
package cn.tedu.operator;
/**
* 演示算术运算符的使用
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//+
//第一种:正常的加法运算
byte b1 = 5;
byte b2 = 10;
//低于int的类型,做运算时,会自动将运算后的结果提升成int类型
byte b3 = (byte)(b1+b2);
System.out.println(b3);
//第二种:字符串拼接
int age = 31;
System.out.println("小明的年龄是:" + age);
//-
double d1 = 15.0;
double d2 = 8.3;
System.out.println(d1-d2);//出现数据精度丢失问题
//++
//前++:先运算,再赋值
short s1 = 10;
short s3 = ++s1;
System.out.println(s3);//11
System.out.println(s1);//11
//后++:先赋值,再运算
short s4 = 10;
short s6 = s4++;
System.out.println(s6);//10
System.out.println(s4);//11
//--
//前--
byte b4 = 20;
byte b5 = --b4;
System.out.println(b5);//19
System.out.println(b4);//19
//后--
byte b6 = 20;
byte b7 = b6--;
System.out.println(b7);//20
System.out.println(b6);//19
//%
long l1 = 10;
long l2 = 3;
long l3 = -2;
//大取小,求余数
long l4 = l1%l2;//1
System.out.println(l4);
//小取大,直接得到最小的那个数
long l5 = l3%l1;//-2
System.out.println(l5);//-2
}
}
2、关系运算符
>
>=
<
<=
==
!=
package cn.tedu.operator;
/**
* 测试关系运算符
*/
public class Test2 {
//psvm
public static void main(String[] args) {
//sout
int i1,i2,i3,i4,i5,i6;
boolean b1,b2,b3;
i1 = -50;
i2 = 37;
i3 = -28;
i4 = 99;
i5 = 101;
b1 = i1 >= i3;//false
System.out.println(b1);
b2 = i2 == i4;//false
System.out.println(b2);
b3 = i2 != i5;//true
System.out.println(b3);
}
}
3、逻辑运算符
&&(与):一假则假,全真则真
||(或):一真则真,全假则假
!(非):取反,如果是true,取反后的结果是false,如果是false,取反的结果是true
package cn.tedu.operator;
/**
* 测试逻辑运算符
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i1,i2,i3,i4;
i1 = 20;
i2 = -15;
i3 = 27;
i4 = 18;
//false && true
System.out.println((i1 > i3) && (i2 < i4));//false
//false && true
System.out.println((i2 > i3) || (i1 > i4));//true
//!false
System.out.println(!(i2>i3));//true
}
}
4、赋值运算符
=
+=
-=
*=
/=
%=
package cn.tedu.operator;
/**
* 测试赋值运算符
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i1, i2, i3, i4;
i1 = 10;
i2 = 2;
i3 = 3;
i4 = 20;
i1 += i2;//<=> i1=i1+i2
System.out.println(i1);//12
i4 %= i3;//<=> i4=i4%i3
System.out.println(i4);//2
}
}
5、三元(三目或条件)运算符
a>b?c表达式:d表达式;
package cn.tedu.operator;
/**
* 测试三元运算符
*/
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a,b;
a = 10;
b = 20;
int max = a > b ? a : b;
System.out.println("a、b当中的最大值:" + max);
//求c、d、e当中的最小值
int c = 21;
int d = 38;
int e = 19;
int min = c < d ? (c < e?c:e) : (d < e?d:e);
System.out.println("c、d、e当中的最小值:" + min);
}
}
四、分支结构和循环结构
1、分支结构
(1)if else
格式:
if(boolean) {
} else {
}
(2)if elseif elseif… else
if(boolean) {
} else if(boolean) {
} else if(boolean) {
} else {
}
(3)switch case
格式:
switch(byte/short/int/char/String/enum) {
case value1:
case value2:
case value3:
default:
}
①default可有可无,当没有匹配case的时候,就会执行default
②没有break的情况下,会从匹配的case开始,一直穿透(包括default),如果遇到了break,就会停止穿透
③有break的情况下,会从匹配的case开始,到break的地方停止
package cn.tedu.branch;
/**
* 测试分支结构
*
*
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//if else
/* if(boolean) {
} else {
}*/
double score = 88;
if(score>90) {
System.out.println("奖励一台ipad");
} else {
System.out.println("什么奖励都没有");
}
//if elseif elseif... else
/*if(boolean) {
} else if(boolean) {
} else if(boolean) {
} else {
}*/
double mathScore = 73;
if(mathScore>=90 && mathScore<=100) {
System.out.println("你的成绩是优秀");
} else if(mathScore >= 80) {
System.out.println("你的成绩是良");
} else if(mathScore >= 70) {
System.out.println("你的成绩是一般");
} else if(mathScore >= 60) {
System.out.println("你的成绩是及格");
} else if(mathScore >= 0){
System.out.println("你的成绩是不及格");
} else {
System.out.println("你的成绩不合法");
}
//switch case
/* switch(byte/short/int/char/String/enum) {
case value1:
case value2:
case value3:
default:
}*/
int b1 = 100;
switch (b1) {
case 20:
System.out.println("case 20");
break;
case 30:
System.out.println("case 30");
break;
case 100:
System.out.println("case 100");
break;
case 50:
System.out.println("case 50");
break;
case 40:
System.out.println("case 40");
break;
default:
System.out.println("default");
}
}
}
day01作业:
一、交换两个变量的值
编写步骤:
1. 定义类Homework6
2. 定义 main方法
3. 定义两个整数变量a,b并赋值
4. 控制台输出变量a,b互换前的值
5. 定义一个第三方变量temp
6. 利用第三方变量temp使a,b的值互换
7. 控制台输出变量a,b互换后的值
二、
编写步骤:
1. 定义类 Homework7
2. 定义 main方法
3. 定义2个int类型变量x、y,x赋值为100,y赋值为200
4. 定义新变量add,保存变量x,y的和并打印到控制台
5. 定义新变量sub,保存变量x,y的差并打印到控制台
6. 定义新变量mul,保存变量x,y的积并打印到控制台
7. 定义新变量div,保存变量x,y的商并打印到控制台
三、
编写步骤:
1. 定义类 Homework8
2. 定义 main方法
3. 定义2个double类型变量x、y,x赋值为100.8,y赋值为20.6
4. 定义新变量add,保存变量x,y的和并打印到控制台
5. 定义新变量sub,保存变量x,y的差并打印到控制台
6. 定义新变量mul,保存变量x,y的积并打印到控制台
7. 定义新变量div,保存变量x,y的商并打印到控制台
四、 强制类型转换练习
(1)先声明两个byte类型的变量b1,b2,并分别赋值为10和20,求b1和b2变量的和,并将结果保存在byte类型的变量b3中,最后输出b3变量的值
(2)先声明两个short类型的变量s1,s2,并分别赋值为1000和2000,求s1和s2变量的和,并将结果保存在short类型的变量s3中,最后输出s3变量的值
(3)先声明1个char类型的变量c1赋值为'a',再声明一个int类型的变量num赋值为5,求c1和num变量的和,并将结果将结果保存在char类型的变量letter中,最后输出letter变量的值。
(4)先声明两个int类型的变量i1,i2,并分别赋值5和2,求i1和i2的商,并将结果保存在double类型的变量result中,最后输出result变量的值。如何得到结果2.5呢?
五、
1. 定义两个int类型变量a1和a2,分别赋值10,11,判断变量是否为偶数,拼接输出结果
2. 定义两个int类型变量a3和a4,分别赋值12,13,判断变量是否为奇数,拼接输出结果
答案:
public class Day01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a, b, temp;
a = 10;
b = 20;
System.out.println("交换前:a=" + a + ",b=" + b);
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("交换后:a=" + a + ",b=" + b);
int x, y, add, sub, mul, div;
x = 100;
y = 200;
add = x + y;
sub = x - y;
mul = x * y;
div = x / y;
System.out.println("add:" + add);
System.out.println("sub:" + sub);
System.out.println("mul:" + mul);
System.out.println("div:" + div);
double x1, y1, add1, sub1, mul1, div1;
x1 = 100.8;
y1 = 20.6;
add1 = 100.8 + 20.6;
sub1 = 100.8 - 20.6;
mul1 = 100.8 * 20.6;
div1 = 100.8 / 20.6;
System.out.println("add1:" + add1);
System.out.println("sub1:" + sub1);
System.out.println("mul1:" + mul1);
System.out.println("div1:" + div1);
//ctrl + shift + F10
byte b1, b2, b3;
b1 = 10;
b2 = 20;
b3 = (byte) (b1 + b2);
System.out.println("b3 = " + b3);
short s1, s2, s3;
s1 = 1000;
s2 = 2000;
s3 = (short) (s1 + s2);
System.out.println("s3 = " + s3);
char c1, letter;
int num = 5;
c1 = 'a';//97(a) 98(b) 99(c) 100(d) 101(e) 102(f)
letter = (char) (c1 + num);
System.out.println("letter = " + letter);//f
int i1, i2;
i1 = 5;
i2 = 2;
double result = (double) i1 / (double) i2;//2.0
System.out.println("result = " + result);
int a1, a2;
a1 = 10;
a2 = 11;//判断偶数:能被2整除,判断奇数:不能被2整除
if (a1 % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("a1=" + a1 + ",它是偶数");
}
if (a2 % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("a2=" + a2 + ",它是偶数");
}
int a3, a4;
a3 = 12;
a4 = 13;
if (a3 % 2 != 0) {
System.out.println("a3=" + a3 + ",它是奇数");
}
if (a4 % 2 !=0) {
System.out.println("a4=" + a4 + ",它是奇数");
}
}
}
2、循环结构
(1)for
格式:
for(①变量定义及初始化;②判断表达式;④表达式) {
③循环体
}
(2)while
while(①判断表达式) {
②循环体
}
(3)do while
do {
①循环体
} while(②判断表达式);
package cn.tedu.loop;
/**
* 测试for循环
*
* for(①变量定义及初始化;②判断表达式;④表达式) {
* ③循环体
* }
*
* while(①判断表达式) {
* ②循环体
* }
*
* do {
* ①循环体
* } while(②判断表达式);
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ctrl + D 向下复制一行代码
//(1)控制台从1打印到10
//使用for
for(int i = 1;i < 11;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
//使用while
int j = 1;
while(j < 11) {
System.out.println(j);
j++;
}
//使用do while
int x = 1;
do {
System.out.println(x);
x++;
} while(x < 11);
}
}
package cn.tedu.loop;
/**
* 测试循环
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求:找出1-1000里面的奇数和偶数并输出
//使用for
int i = 0;
for(i =1;i < 101;i++) {
if(i%2!=0) {//奇数
System.out.println("奇数:" + i);
} else {//偶数
System.out.println("偶数:" + i);
}
}
System.out.println("---while---");
int j = 1;
while(j < 101) {
if(j%2!=0) {
System.out.println("奇数:" + j);
} else {
System.out.println("偶数:" + j);
}
j++;
}
System.out.println("---do while---");
int x = 1;
do {
if(x%2!=0) {
System.out.println("奇数:" + x);
} else {
System.out.println("偶数:" + x);
}
x++;
} while(x < 101);
}
}
package cn.tedu.loop;
/**
* 乘法口诀表
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ctrl + / 单行注释
//ctrl + shift + / 多行注释
//System.out.println(); 带ln,让下一行去换行输出
//System.out.print(); 不带ln,让下一行不换行输出
//使用for
/*for(int j = 1;j < 10;j++) {//控制行数
for(int i = 1;i < j+1;i++) {//控制每一行的个数
System.out.print(i+"*"+j+"="+i*i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}*/
//使用while
/*System.out.println("---while---");
int y = 1;
while (y < 10) {
int x = 1;
while (x < y + 1) {
System.out.print(x + "*" + y + "=" + y * x + " ");
x++;
}
System.out.println();
y++;
}*/
//使用do while
System.out.println("---do while---");
int m = 1;
do {
int k = 1;
do {
System.out.print(k+"*"+m+"="+1*k + " ");
k++;
} while(k < m+1);
System.out.println();
m++;
} while (m < 10);
}
}
package cn.tedu.loop;
/**
* 测试循环
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//案例1:输出1-100之间是3的倍数的数
//for
System.out.println("---for---");
for(int i = 1;i < 101;i++) {
if(i%3==0) {
System.out.println(i+"是3的倍数");
}
}
//while
System.out.println("---while---");
int k = 1;
while(k < 101) {
if(k%3==0) {
System.out.println(k+"是3的倍数");
}
k++;
}
//do while
System.out.println("---do while---");
int m = 1;
do {
if(m%3==0) {
System.out.println(m+"是3的倍数");
}
m++;
} while(m < 101);
//案例2:输出1-100之间以3结尾的数
//for
System.out.println("---for---");
for(int j = 1;j < 101;j++) {
if(j%10==3) {
System.out.println(j+"是以3结尾的数");
}
}
//while
System.out.println("---while---");
int k1 = 1;
while(k1 < 101) {
if(k1%10==3) {
System.out.println(k1+"是以3结尾的数");
}
k1++;
}
//do while
System.out.println("---do while---");
int m1 = 1;
do {
if(m1%10==3) {
System.out.println(m1+"是以3结尾的数");
}
m1++;
} while(m1 < 101);
}
}
package cn.tedu.loop;
/**
* 死循环
*/
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//for
/*for(;;) {
System.out.println("for的死循环");
}*/
/*for(int i = 1;i > 0;i++) {
System.out.println("for的死循环2");
}*/
//while
/*while(true) {
System.out.println("while的死循环");
}*/
/*int num1 = 1;
while(num1 > 0) {
System.out.println("while的死循环2");
num1++;
}*/
//do while
/*do {
System.out.println("do while死循环");
} while(true);*/
int m2 = 10;
do {
System.out.println("do while死循环2");
m2++;
} while(m2 > 1);
}
}
package cn.tedu.loop;
/**
* 测试循环
*/
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//循环打印三角形
/*
*
**
***
****
*****
*/
for(int j = 1;j < 6;j++) {
for(int i = 1;i < j+1;i++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
/*
*
**
***
****
*****
*/
int z1 = 1;
while(z1 < 6) {//控制行数
int x1 = 5;
while(x1 > z1) {//空格
System.out.print(" ");
x1--;
}
int y1 = 1;
while(y1 < z1+1) {//星号
System.out.print("*");
y1++;
}
System.out.println();
z1++;
}
/*
*****
****
***
**
*
*/
int y2 = 1;
do {
int x2 = 6;
do {
System.out.print("*");
x2--;
} while(x2 > y2);
System.out.println();
y2++;
} while(y2 < 6);
/*
*****
****
***
**
*
*/
int y3 = 1;
while(y3 < 6) {//行数
//空格
int x3 = 1;
while(x3 < y3) {
System.out.print(" ");
x3++;
}
//星号
int z3 = 6;
while(z3 > y3) {
System.out.print("*");
z3--;
}
System.out.println();
y3++;
}
}
}
五、数组(Array)
1、概念
可以看作是一个容器,用来存放同一种类型的多个数据
2、创建方式
(1)静态
格式1:
数组的类型[] 数组名 = new 数组的类型[]{元素1,元素2,元素3...};
格式2:
数组的类型[] 数组名 = {元素1,元素2,元素3...};
(2)动态
格式:
数组的类型 数组名 = new 数组的类型[数组的长度];
注:
①数组的长度=数组元素的个数=数组名.length
②数组的元素获取方式:通过下标,下标范围[0,数组的长度-1];
数组的类型 变量名 = 数组名[下标];
package cn.tedu.array1;
/**
* 测试数组
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//静态
//数组的类型[] 数组名 = new 数组的类型[]{元素1,元素2,元素3...};
int[] arr1 = new int[]{1,3,5,7,9,11};
//数组的长度:6
//数组的下标:0~5
System.out.println(arr1[0]);
System.out.println(arr1[1]);
System.out.println(arr1[2]);
System.out.println(arr1[3]);
System.out.println(arr1[4]);
System.out.println(arr1[5]);
for(int i = 0;i < arr1.length;i++){
System.out.println(arr1[i]);
}
//数组的类型[] 数组名 = {元素1,元素2,元素3...};
byte[] arr2 = {2,4,6,8,10,12};
//动态
//数组的类型 数组名 = new 数组的类型[数组的长度];
double[] arr3 = new double[10];
}
}
day02作业:
一、案例:为抵抗洪水,战士连续作战89小时,编程计算共多少天零多少小时?
定义一个int类型变量hours,赋值为89
定义一个int类型变量day,用来保存89小时中天数的结果
定义一个int类型变量hour,用来保存89小时中不够一天的剩余小时数的结果
输出结果
二、今天是周2,100天以后是周几?
定义一个int类型变量week,赋值为2
修改week的值,在原值基础上加上100
修改week的值,在原值基础上模以7
输出结果,在输出结果的时候考虑特殊值,例如周日
三、求三个整数x,y,z中的最大值
定义三个int类型变量,x,y,z,随意赋值整数值
定义一个int类型变量max,先存储x与y中的最大值(使用三元运算符)
再次对max赋值,让它等于上面max与z中的最大值(使用三元运算符)
输出结果
四、计算折扣后金额
从键盘输入订单总价格totalPrice(总价格必须>=0),根据优惠政策计算打折后的总价格。
编写步骤:
判断当totalPrice >=500 ,discount赋值为0.8
判断当totalPrice >=400 且<500时,discount赋值为0.85
判断当totalPrice >=300 且<400时,discount赋值为0.9
判断当totalPrice >=200 且<300时,discount赋值为0.95
判断当totalPrice >=0 且<200时,不打折,即discount赋值为1
判断当totalPrice<0时,显示输入有误
输出结果
五、 计算今天是星期几
定义变量week赋值为上一年12月31日的星期值(可以通过查询日历获取),定义变量year、month、day,分别赋值今天日期年、月、日值。计算今天是星期几。
六、5个一行输出1-100之间的偶数
输出1-100偶数,每5个一行,一行中的每个数字之间使用逗号分隔
七、计算这一天是这一年的第几天
案例需求:从键盘分别输入年、月、日,使用循环for+if实现,判断这一天是当年的第几天
答案:
package cn.tedu.homework;
import java.util.Random;
public class Day02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 一、案例:为抵抗洪水,战士连续作战89小时,编程计算共多少天零多少小时?
*
* 定义一个int类型变量hours,赋值为89
* 定义一个int类型变量day,用来保存89小时中天数的结果
* 定义一个int类型变量hour,用来保存89小时中不够一天的剩余小时数的结果
* 输出结果
*/
int hours, day, hour;
hours = 89;
day = hours / 24;
hour = hours % 24;
System.out.println("day:" + day);
System.out.println("hour:" + hour);
day = 0;
hour = 0;
while (hours >= 24) {
hours -= 24;
day++;
}
hour = hours;//剩余小时数
System.out.println("day: " + day);
System.out.println("hour " + hour);
/**
* 二、今天是周2,100天以后是周几?
*
* 定义一个int类型变量week,赋值为2
* 修改week的值,在原值基础上加上100
* 修改week的值,在原值基础上模以7
* 输出结果,在输出结果的时候考虑特殊值,例如周日
*/
int week = 2;
week += 12;
week %= 7;
if (week == 0) {
week = 7;
}
System.out.println("week: " + week);
/**
* 三、求三个整数x,y,z中的最大值
*
* 定义三个int类型变量,x,y,z,随意赋值整数值
* 定义一个int类型变量max,先存储x与y中的最大值(使用三元运算符)
* 再次对max赋值,让它等于上面max与z中的最大值(使用三元运算符)
* 输出结果
*/
int x, y, z, max;
//如何产生一个随机值
//(1)
Math.random();
//(2)
new Random().nextInt(10);
x = new Random().nextInt(100);
y = new Random().nextInt(100);
z = new Random().nextInt(100);
System.out.println("x:" + x + ",y:" + y + ",z:" + z);
max = (x > y ? (x > z) ? x : z : (y > z) ? y : z);
System.out.println("max:" + max);
/**
* 四、计算折扣后金额
* 从键盘输入订单总价格totalPrice(总价格必须>=0),根据优惠政策计算打折后的总价格。
* 编写步骤:
*
* 判断当totalPrice >=500 ,discount赋值为0.8
* 判断当totalPrice >=400 且<500时,discount赋值为0.85
* 判断当totalPrice >=300 且<400时,discount赋值为0.9
* 判断当totalPrice >=200 且<300时,discount赋值为0.95
* 判断当totalPrice >=0 且<200时,不打折,即discount赋值为1
* 判断当totalPrice<0时,显示输入有误
* 输出结果
*/
int totalPrice = 300;
double discount = 0.0;
if (totalPrice >= 500) {
discount = 0.8;
totalPrice *= discount;
} else if (totalPrice >= 400) {
discount = 0.85;
totalPrice *= discount;
} else if (totalPrice >= 300) {
discount = 0.9;
totalPrice *= discount;
} else if (totalPrice >= 200) {
discount = 0.95;
totalPrice *= discount;
} else if (totalPrice >= 0) {
discount = 1;
totalPrice *= discount;
} else if (totalPrice < 0) {
System.out.println("输入有误!");
}
System.out.println("totalPrice:" + totalPrice);
/**
* 五、 计算今天是星期几
*
* 定义变量week赋值为上一年12月31日的星期值(可以通过查询日历获取),
* 定义变量year、month、day,分别赋值今天日期年、月、日值。计算今天是星期几。
*/
int week1 = 6;
int year1, month1, day1,week2;
year1 = 2023;
month1 = 5;
day1 = 24;
int days = 0;//天数
month1--;
while (month1 > 0) {
switch (month1) {
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
days += 31;
break;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
days += 30;
break;
case 2://2020 2100 2000
if ((year1 % 4 == 0 && year1 % 100 != 0) || (year1 % 400 == 0)) {//能被4整除,但不能被100整除,或者能被400整除
days += 29;
} else {
days += 28;
}
break;
}
month1--;
}
days+=day1;
System.out.println("今天是今年的第"+days+"天");
days+=6;
week2=days%=7;
System.out.println("今天是星期"+week2);
/**
* 六、5个一行输出1-100之间的偶数
* 输出1-100偶数,每5个一行,一行中的每个数字之间使用逗号分隔
*/
for(int i = 1;i < 101;i++) {
if(i%2==0) {
if(i%5==0) {
System.out.print(i);
System.out.println();
} else {
System.out.print(i+",");
}
}
}
/**
* 七、计算这一天是这一年的第几天
* 案例需求:从键盘分别输入年、月、日,使用循环for+if实现,判断这一天是当年的第几天
*/
int year3 = 2023;
int month3 = 5;
int day3 = 24;
for (month3-=1;month3 > 0;month3--) {
if(month3==1 || month3==3 || month3==5 || month3==7 || month3==8 || month3==10 || month3==12) {
day3+=31;
} else if(month3==4 || month3==6 || month3==9 || month3==11) {
day3=+30;
} else {
if((year3%4==0 && year3%100!=0) || year3%400==0) {
day3+=29;
} else {
day3+=28;
}
}
}
System.out.println("今天是今年的第 " + day3 + " 天");
}
}
2、数组的赋值和遍历
package cn.tedu.array1;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 测试数组的赋值和遍历
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义long类型数组arr1,长度是5
long[] larr1 = new long[5];
//遍历:for
System.out.println("larr1赋值前的遍历结果:");
for(int i = 0;i < larr1.length;i++) {
System.out.print(larr1[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//do while给larr1赋随机值 范围[0,101)
int z = 0;
do {
larr1[z] = new Random().nextInt(101);
z++;
} while(z < larr1.length);
//遍历:while
System.out.println("larr1赋值后的遍历结果:");
int x = 0;
while(x < larr1.length) {
System.out.print(larr1[x] + " ");
x++;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
package cn.tedu.array1;
import com.sun.scenario.effect.impl.sw.sse.SSEBlend_SRC_OUTPeer;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 验证码
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、生成四位数验证码(包含数字、字母)
char[] cArr1 = new char[4];
//数字[48,57] 大写英文字母[65,90] 小写英文字母[97,122]
int x = 0;
do {
if(x>3) {
break;
}
int random = new Random().nextInt(123);//[0,123) [0,122]
if((random > 47 && random < 58) || (random > 64 && random < 91)
|| (random > 96 && random < 123)) {
cArr1[x] = (char)random;
x++;
}
} while(true);
//遍历:while
System.out.println("验证码:");
int y = 0;
while(y < cArr1.length) {
System.out.print(cArr1[y] + " ");
y++;
}
System.out.println();
//2、根据用户键盘输入的验证码进行比较,结果正确进入该系统,否则提示进入系统失败
System.out.print("请输入验证码:");
String input = new Scanner(System.in).next();//从键盘输入一段字符串
// System.out.println(input);
//获取字符串中的字符
// System.out.println(input.charAt(0));
// System.out.println(input.charAt(1));
// System.out.println(input.charAt(2));
// System.out.println(input.charAt(3));
int temp = 0;
for(int j = 0;j < cArr1.length;j++) {
if(cArr1[j] == input.charAt(j)) {
temp++;
}
}
if(temp==4) {
System.out.println("欢迎进入本系统!");
} else {
System.out.println("验证码有误!");
}
}
}
六、方法
1、静态方法
格式:
访问权限修饰符 static 返回值类型 方法名(方法的形参) {
方法体
}
①访问权限修饰符:public > protectd > default > private
public(公开):所有类均可访问
protected(受保护的):
default(缺省的,默认的):
private(私有的):只能在本类中访问
②static(静态):static中只能调用static的资源,不能调用非static的资源;非static中既能调用static资源,也能调用非static资源
③返回值类型:void/基本数据类型/引用类型
④return关键字:一般用于结束方法,也可以返回一个值
②String[] args:形式参数,简称形参,方法的形参可以有也可以无,可以是基本数据类型,也可以是引用类型,而main方法的形参就是一个String类型的数组
⑥方法传入的实际参数简称为实参
package cn.tedu.method;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 静态方法
*
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//调用m1方法
m1();
//调用m3方法,得到m3方法的返回值
int returnM3 = m3();
System.out.println("m3方法的返回值:" + returnM3 + "---");
System.out.println("m3方法的返回值:" + m3() + "~~~");
//调用m4方法,并且输出返回值
byte returnM4 = m4();
System.out.println("m4方法的返回值:" + returnM4);
//调用m5方法,传入定义好A、B两个实际参数(实参),输出m5方法的返回值
int A,B;
A = 18;
B = 28;
int m5Return = m5(A,B);
System.out.println("m5方法的返回值:" + m5Return);
int k = 1;
int v = 100;
int[] C1 = new int[50];
int[] D1 = new int[50];
int[] newArr2 = m6(k,v,C1,D1);
System.out.println("奇数数组:" + Arrays.toString(newArr2));
}
//void,无需返回值
public static void m1() {
System.out.println("调用了m1方法");
}
//有返回值,返回值类型是int
public static int m3() {
return 10;
}
//有返回值,返回值类型是byte
public static byte m4() {
byte a = 10;
byte b = 20;
return (byte)(a+b);
}
//有返回值,返回值类型是int
public static int m5(int num1,int num2) {
int num3 = num1 + num2;
return num3;
}
//有返回值,返回值的类型是一个数组
public static int[] m6(int n1,int n2,int[] arr1,int[] arr2) {
int index1 = 0;//偶数数组下标
int index2 = 0;//奇数数组下标
for (int j = n1;j <= n2;j++) {
if(j%2==0) {
arr1[index1] = j;
index1++;
} else {
arr2[index2] = j;
index2++;
}
}
//打印偶数数组
//System.out.println("偶数数组:" + arr1);//[I@1b6d3586 地址值
System.out.println("偶数数组:" + Arrays.toString(arr1));
//返回奇数数组
return arr2;
}
}
2、构造方法
作用:用于构建对象(创建类的实例)
格式:
访问权限修饰符 方法名(方法的形参) {
方法体
}
①方法名要和类名保持一致
②构造方法没有void,也没有返回值
③构造方法分为两种:无参构造(默认就有)、含参构造(自己声明)
无参构造隐式存在,但是如果一个类中声明了含参构造(1个或者多个),默认的无参构造会被覆盖,如果想要使用无参构造,需要显式声明
package cn.tedu.method;
/**
* 测试构造方法
*/
public class Student {
//定义类的一些属性
int stuNumber = 1001;//学号
int age = 23;//年龄
char address = '沪';//籍贯,住址
double mathScore = 88;//数学成绩
double englishScore = 90;//英语成绩
//无参构造
public Student() {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("调用了Student的无参构造....");
}
//含参构造
public Student(int number,int sage,char ass,double engScore) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("调用了含参构造...");
System.out.println("number:" + number);//学号
System.out.println("sage:" + sage);//年龄
System.out.println("ass:" + ass);//籍贯,住址
System.out.println("engScore:" + engScore);//英语成绩
}
//含参构造
public Student(int number1,double mScore) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("调用了含参构造...");
System.out.println("number1:" + number1);
System.out.println("mScore:" + mScore);
}
//含参构造
public Student(int number2,int sage2,char ass2,double mScore2,double eScore2) {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("调用了含参构造...");
System.out.println("number2:" + number2);
System.out.println("sage2:" + sage2);
System.out.println("ass2:" + ass2);
System.out.println("mScore:" + mScore2);
System.out.println("eScore:" + eScore2);
}
}
package cn.tedu.method;
public class TestStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建学生类对象
//创建对象格式:对象的类型 对象名字 = new 对象的类型(实参);
//调用Student的无参构造
Student student = new Student();
//调用Student的含参构造
Student student1 = new Student(1002,28,'苏',88);
//调用Student的含参构造
Student student2 = new Student(1003,93);
//调用Student的含参构造
Student student3 = new Student(1004,23,'皖',64,78);
}
}
3、普通方法
格式:
访问权限修饰符 void/基本数据类型/引用类型 方法名(方法的形参) {
方法体
}
需要对象名.方法的方式去调用
package cn.tedu.method;
/**
* 测试普通方法
*/
public class Teacher {
//普通方法:void m1()
public void m1() {
System.out.println("执行了m1方法...");
}
//普通方法:int m2(int m,int n)
public int m2(int a,int b) {
System.out.println("执行了m2方法...");
return a + b;
}
//普通方法m3:int[] m3(int l1,int m1,int[] arr)
public int[] m3(int n1,int n2,int[] arr1) {
return m4(n1,n2,arr1);
}
//普通方法m4:int[] m4(int k,int v,int[] arr3)
public int[] m4(int m1,int m2,int[] arr2) {
//找出m1到m2之间以3结尾的数,放到arr2数组,最后进行返回
int index = 0;
for(int a = m1; a < m2; a++) {
if(a%10==3) {
arr2[index] = a;
index++;
}
}
return arr2;
}
}
package cn.tedu.method;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 测试Teacher中普通方法
*/
public class TestTeacher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher();
//调用m1方法
teacher1.m1();
//调用m2方法,输出m2方法的返回值
int k = 10;
int y = 20;
int m2Return = teacher1.m2(k,y);
System.out.println("m2方法返回值:" + m2Return);
//调用m3方法,输出m3方法的返回值
int c = 1;
int d = 100;
int[] arr1 = new int[10];
int[] newArr1 = teacher1.m3(c,d,arr1);
System.out.println("m3方法返回值:" + Arrays.toString(newArr1));
}
}





















 317
317











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








