双链表与单链表的区别就在于:单链表中一个节点只包含指向下一个节点的指针;但是双链表中,一个节点既包含指向下一个节点的指针,又包含指向上一个节点的指针。
双链表的具体实现与文件结构都与单链表相似,只是在插入、删除元素的实现上有细微的差别。
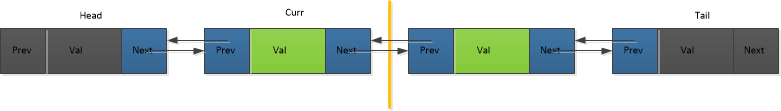
双链表的结构形式:
需要注意的是,在双链表中,curr仍然是指当前位置的前一个位置。
在单链表中,表头head不包含具体的元素,但是tail是包含具体元素值的;在双链表中,head和tail都不包含具体元素。
文件结构:
其中,Public.h、Tools.h、Tools.cpp为提供辅助功能的文件:Public.h包含常用的头文件,Tools.h和Tools.cpp实现了异常机制Assert();
List.h中实现线性表的抽象类模板,不包含数据成员,成员函数都是虚函数(当然构造函数除外);
Doubly_Linked_List.h和Doubly_Linked_List_Def.h实现单链表的模板类定义,其继承自List.h中的线性表模板;
main.cpp为主函数,实现单链表的调用和测试。
List.h的内容不再展示。
Doubly_Linked_List.h:将整张双链表定义为一个类(模板)
/********************************************************/
// 用模板实现单向链表(Doubly Linked List)的定义
// 继承基类线性表template<class dataType> class List
/********************************************************/
#pragma once
#include "List.h"
// 1,定义节点类模板
template<class E>
class Doubly_Node
{
public:
E element; //本结点存储的元素值
Doubly_Node* next;//指向下一结点的指针
Doubly_Node* prev;//指向上一结点的指针
Doubly_Node(const E& elemval, Doubly_Node* nextval = NULL, Doubly_Node* prevval = NULL) :
element(elemval), next(nextval), prev(prevval) {}
Doubly_Node(Doubly_Node* nextval = NULL, Doubly_Node* prevval = NULL) :
next(nextval), prev(prevval) {}
};
// 2,定义链表类模板
template<class E>
class Doubly_LList : public List<E>
{
private:
Doubly_Node<E>* head; //表头,head结点内并不存储真是的元素
Doubly_Node<E>* tail;
Doubly_Node<E>* curr; //实际上curr->next才是真正的当前位置
int cnt; //链表中当前存储的元素个数
void init(); //初始化
void remove_all(); //清空
public:
Doubly_LList();
~Doubly_LList();
void print() const;
void clear();
void insert(const E& it); //在当前位置插入元素
void append(const E& it); //在链表末尾追加
E remove(); //删除当前的元素并返回其值
void moveToStart(); //将当前位置设为链表开始
void moveToEnd(); //将当前位置设为链表结束的前一个位置
void prev(); //将当前位置左移一位
void next(); //将当前位置右移一位
int length() const; //返回当前链表存储的元素个数
int currPos() const; //返回当前位置
void moveToPos(int pos); //将当前位置设为指定位置
const E& getValue() const;//返回当前位置的元素值
};Doubly_Linked_List_Def.h:实现Doubly_Linked_List.h中的成员函数定义
/********************************************************/
// 用模板实现单向链表(Doubly Linked List)的定义
// 继承基类线性表 template<class dataType> class List
// 本头文件实现 Doubly_LList<class E>的成员函数
/********************************************************/
#pragma once
#include "Doubly_Linked_List.h"
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::init()
{
//所有指针指向新开的空间
head = curr = new Doubly_Node<E>;
tail = new Doubly_Node<E>;
head->next = tail;
tail->prev = head;
cnt = 0;
}
//删除所有结点
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::remove_all()
{
while (head != NULL)
{
curr = head;
//请注意,下面两句的顺序不能颠倒,不然curr删除后就相当于head删除了,就不能再获取head->next了
head = head->next;
delete curr;
}
}
//构造函数
template<class E>
Doubly_LList<E>:: Doubly_LList()
{
//构造时只开辟首尾节点的空间
init();
}
//析构函数
template<class E>
Doubly_LList<E>::~ Doubly_LList()
{
remove_all();
}
//打印所有元素
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::print() const
{
Doubly_Node<E>* temp = head->next; //head中不存储数据,head->next中才有数据
while (tail != temp)
{
//此处暗示类型E必须定义了“<<”操作,否则报错
cout << temp->element << endl;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
//清空链表
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::clear()
{
remove_all();
init(); //删除之后,还要留着表头、表尾
}
//当前位置插入元素
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::insert(const E& it)
{
//Doubly_Node<E> *temp = NULL;
//temp = new Doubly_Node<E>(it, curr->next, curr);
//curr->next->prev = temp; //下面两句的顺序有讲究
//curr->next = temp;
// 下面一句等于上面4句
curr->next = curr->next->prev = new Doubly_Node<E>(it, curr->next, curr);
cnt++;
}
//链表末尾追加元素
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::append(const E& it)
{
//Doubly_Node<E> *temp = new Doubly_Node<E>(it, tail, tail->prev);
//tail->prev->next = temp;//下面两句的顺序有讲究
//tail->prev = temp;
tail->prev = tail->prev->next = new Doubly_Node<E>(it, tail, tail->prev);
cnt++;
}
//删除当前元素并返回其值
template<class E>
E Doubly_LList<E>::remove()
{
Assert(curr != tail, "当前位置无效,无法删除");
Doubly_Node<E>* temp = curr->next;
if (temp == tail)
{
return NULL;
}
E it = temp->element;
curr->next = temp->next; //即便是temp为tail的时候,这句依然成立
temp->next->prev = curr;
delete temp;
cnt--;
return it;
}
//将head设为当前位置
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::moveToStart()
{
curr = head;
}
//将tail设为当前位置
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::moveToEnd()
{
curr = tail->prev;
}
//将当前位置左移一位,如果已在最前,无改变
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::prev()
{
if (curr == head)
{
return;
}
curr = curr->prev;
}
//将当前位置右移一位,如果已在最后,无改变
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::next()
{
if (curr == tail)
{
return;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
//返回链表长度,即
template<class E>
int Doubly_LList<E>::length() const
{
return cnt;
}
//返回当前位置
template<class E>
int Doubly_LList<E>::currPos() const
{
Doubly_Node<E>* temp = head;
int pos = 0;
while (temp != curr)
{
pos++;
temp = temp->next;
}
return pos;
}
//将当前位置设为指定位置
template<class E>
void Doubly_LList<E>::moveToPos(int pos)
{
Assert((pos >= 0) && (pos <= cnt), "设定位置越界");
curr = head;
for (int i = 0; i != pos; i++)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
}
//返回当前位置的元素值
template<class E>
const E& Doubly_LList<E>::getValue() const
{
Assert(curr != tail, "无值可取");
return curr->next->element;
}main.c 主函数,测试构造的双链表是否可用
/********************************************************/
// 主函数
// 用于测试编写的各函数与数据结构
/********************************************************/
#include "Public.h"
#include "Tools.h"
#include "SeqStack.h"
#include "SeqStack_Vector.h"
#include "SeqStack_VT_Def.h"
#include "postfix.h"
#include "ArrayBasedList_Def.h"
#include "Single_Linked_List_Def.h"
#include "Doubly_Linked_List_Def.h"
int main()
{
/********************************************************/
// 5,《数据结构与算法分析》Clifford 4.1.5 双链表
/********************************************************/
Doubly_LList<int> iDLList;
iDLList.insert(1);
iDLList.insert(2);
iDLList.insert(3);
iDLList.insert(4);
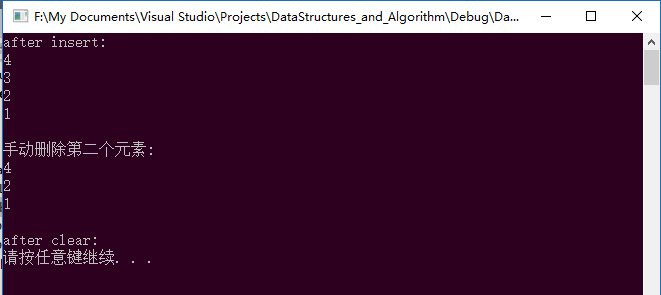
cout << "after insert:" << endl;
iDLList.print();
cout << "\n手动删除第二个元素:" << endl;
iDLList.moveToPos(1);
iDLList.remove();
iDLList.print();
iDLList.clear();
cout << "\nafter clear:" << endl;
iDLList.print();
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:























 229
229

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








