概述
spring的核心容器实现了Ioc,其目 的是提供一种无侵入式的框架
BeanFactory提供了一种先进的配置机制来管理任何种类的bean。是Spring框架的基础设施面上的功能,是最本质的Spring的基础。
ApplicationContext建立在BeanFactory之上,并增加了其他功能,如国际化,获取资源,事件传递等。面向的是使用Spring框架的开发者,计划所有的场合都适用。
Bean的基础知识
在XML中定义Bean时, id:指定在benafactory中管理该bean的唯一的标识。name可用来唯一标识bean 或给bean起别名。bean共有五种作用域:分别是singleton、prototype、request、session、global和global Session。
spring中,bean的注入方式有setter注入、构造函数以及接口注入,之后一一讲解。
Beanfactory中bean生命周期实例
工程结构
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="helloworldBeanId" class="com.ssm.beans.HelloWorld">
<property name="username" value="YEN"/>
<property name="password" value="123"/>
</bean>
<bean id="beanLifeBeanId" class="com.ssm.beans.BeanLife">
<property name="username" value="C"/>
<property name="password" value="1"/>
</bean>
</beans>BeanLife.java
package com.ssm.beans;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;
/**
* DateTime: 2016/11/2 17:24
* 功能:
* 思路:
*/
public class BeanLife implements BeanFactoryAware,BeanNameAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean{
private String username;
private String password;
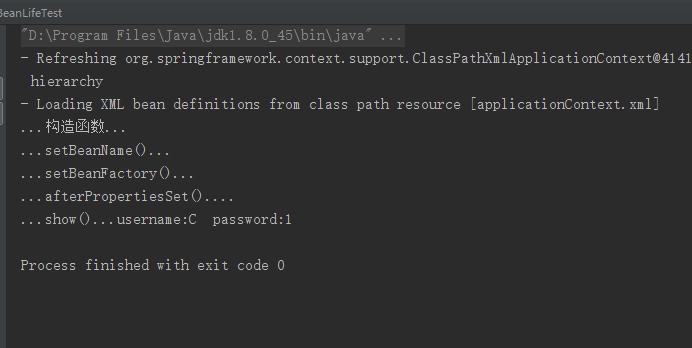
public BeanLife(){
System.out.println("...构造函数...");
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("...show()...username:"+username+" password:"+password);
}
/**
* BeanFactoryAware的setBeanFactory():
* 如果Bean类有实现org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware接口,工厂调用setBeanFactory()方法传入工厂自身。
* @param beanFactory
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("...setBeanFactory()...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("...destroy()...");
}
/**
* initializingBean的afterPropertiesSet():
* 如果Bean类已实现org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean接口,则执行他的afterProPertiesSet()方法
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("...afterPropertiesSet()....");
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
/**
* BeanNameAware的setBeanName()
* 如果Bean类有实现org.springframework.beans.BeanNameAware接口,工厂调用Bean的setBeanName()方法传递Bean的ID。
* @param s
*/
@Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("...setBeanName()...");
}
}
BeanLifeTest .java
package com.ssm.test;
import com.ssm.beans.BeanLife;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* DateTime: 2016/11/2 18:32
* 功能:
* 思路:
*/
public class BeanLifeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanFactory factory=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
BeanLife beanLife= (BeanLife) factory.getBean("beanLifeBeanId");
beanLife.show();
}
}
ApplicationContext与Beanfactory获取bean的区别
ApplicationContext,当我们去实例化applicationContext.xml,该实例中配置的bean就被实例化,优点是可以预先加载,缺点是浪费内存。
ApplicationContext有三种方式加载文件:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext->从类路径加载;FileSystemXmlApplicationContext->从文件系统加载;XmlWebApplicationContext->从web系统中加载(当tomcat启动的时候加载)
Beanfactory,当去实例化对象的时候,配置的bean不会马上被实例化,只有当使用factory.getBean(“beanName”)时才实例化,好处是节约内存,坏处是速度慢。

























 497
497

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








