用法:
- @PropertySource 注解提供便利和声明的机制添加 PropertySource 到Spring的 Environment
- @PropertySource 和 @Value组合使用,可以将自定义属性文件中的属性变量值注入到当前类的使用@Value注解的成员变量中
- @PropertySource 和 @ConfigurationProperties组合使用,可以将属性文件与一个Java类绑定,将属性文件中的变量值注入到该Java类的成员变量中
- @EnableConfigurationProperties注解 和 @ConfigurationProperties组合使用
例子:
app.properties
name=tianming
age=18
db.name=root
db.password=admin示例一:
AppConfig1.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:/app.properties")
public class AppConfig {
@Autowired
Environment env;
}示例二:
AppConfig2.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@PropertySource(value = {"/app.properties"})
public class AppConfig2 {
@Value("${name}")
public String name;
@Value("${age}")
public Integer age;
}示例三:
AppConfig3.java
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@PropertySource(value = {"/app.properties"})
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "db")
public class AppConfig3 {
private String name;
private String password;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}示例四:
@EnableConfigurationProperties注解的作用是:使 使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解的类生效。
如果一个配置类只配置@ConfigurationProperties注解,而没有使用@Component或者实现了@Component的其他注解,那么在IOC容器中是获取不到properties 配置文件转化的bean。说白了 @EnableConfigurationProperties 相当于把使用 @ConfigurationProperties 的类进行了一次注入。
简单点说@EnableConfigurationProperties的功能类似于@Component。
application.properties
dp.name=yiguang
dp.age=13StudentConfig.class
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//@Component 使用@EnableConfigurationProperties替代
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="dp") // 根据application.properties中的配置填充字段
//@PropertySource("classpath:config.properties") 如果使用此注解和@EnableConfigurationProperties一起使用,不报错,但是填充的字段为null
public class StudentConfig {
public String name;
public int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@EnableConfigurationProperties在实际项目中的使用场景
如下,在配置类NacosConfigAutoConfiguration的头上加注解@EnableConfigurationProperties(NacosConfigProperties.class),
而在NacosConfigProperties配置类本身并没有实现了@Component相关的注解,也就是说运行项目时,不会直接把NacosConfigProperties配置类注入到Spring 容器中,而是在执行NacosConfigAutoConfiguration这个配置类时才会去把NacosConfigProperties类注入到spring
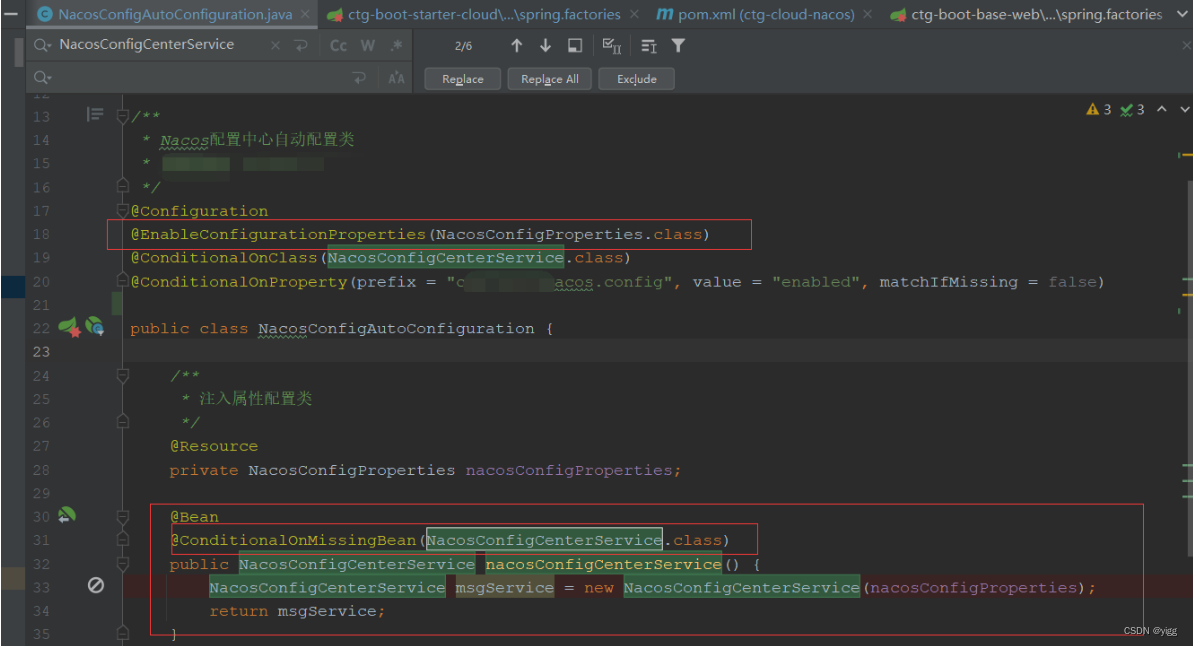
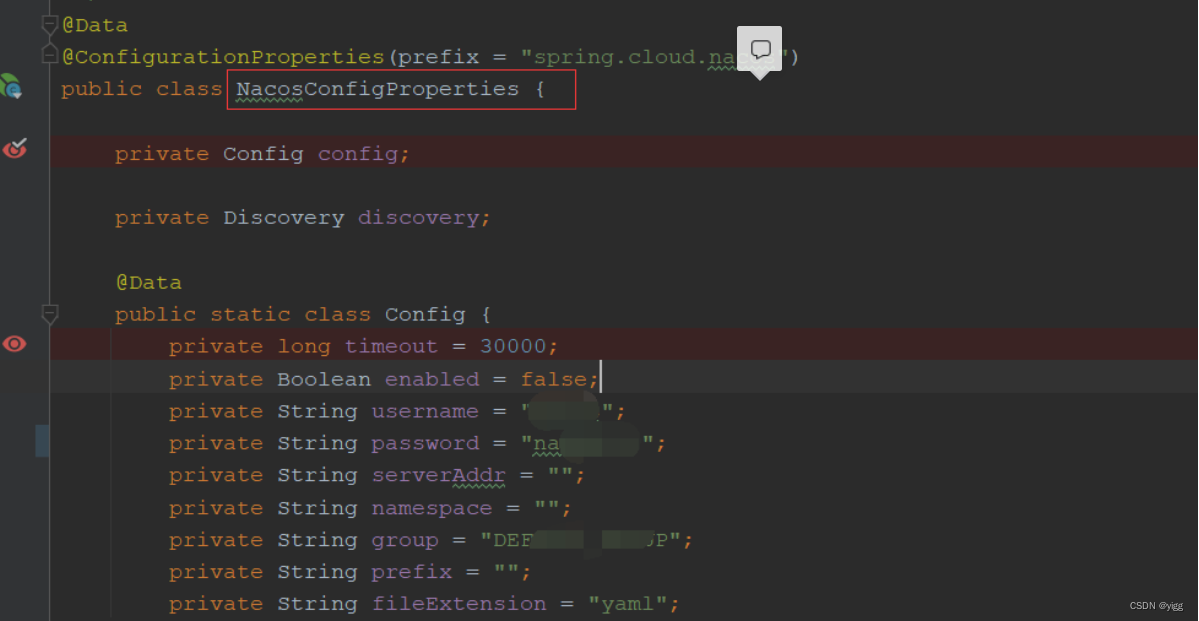
如下,NacosConfigProperties类本身并没有@Component相关注解:
例:
Application.class
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
import org.springframework.boot.web.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;
import springboot111.springboot.config.StudentConfig;
@SpringBootApplication
@ServletComponentScan
@EnableConfigurationProperties(StudentConfig.class) // 注意此处
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Application.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}结果:
HelloController.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import springboot111.springboot.config.AppConfig;
import springboot111.springboot.config.AppConfig2;
import springboot111.springboot.config.AppConfig3;
import springboot111.springboot.config.StudentConfig;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
Environment env;
@Autowired
AppConfig2 appConfig2;
@Autowired
AppConfig3 appConfig3;
@Autowired
StudentConfig studentConfig;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println(env.getProperty("name")); // tianming
return "Hello Spring Boot!";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2() {
System.out.println(appConfig2.name); // tianming
System.out.println(appConfig2.age); // 18
return "Hello Spring Boot!";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello3")
public String hello3() {
System.out.println(appConfig3.getName()); // root
System.out.println(appConfig3.getPassword()); // admin
return "Hello Spring Boot!";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello4")
public String hello() {
System.out.println(studentConfig.name); // yiguang
return "Hello Spring Boot!";
}
}





















 291
291











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








