排序问题总结
简单选择排序

#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 50;
int a[MAXN], n;
void selectSort() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int k = i;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
if (a[j] < a[k]) {
k = j;
}
}
swap(a[i], a[k]);
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
selectSort();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d", a[i]);
printf(i < n - 1 ? " " : "\n");
}
return 0;
}
理解:简单排序从第一位一直进行到最后一位置=i;
j表示的是已经排序好的i的开始(最大顺序排序+最小顺序排序)的下一位进行比较好最大值或者是最小值
直接插入排序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void paixu_sort(int a[], int n)
{
int t;//表示存储选择排序的对象的临时变量;
int j;//表示的是选择遍历的对象,因为选择的都是i前面的对象,所以j选择的是i-1;
//开始
//先进行遍历,比较大小,不断的向前推进,然后交换
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)//都是从第二位进行选择的,所以开始师从1开始的
{
if (a[i] < a[i - 1])
{
t = a[i];//将需要插入的元素临时存储起来
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && t < a[j]; j--)//是从i位置之前开始就需要腾出空间了
{
a[j + 1] = a[j];//需要交换元素的前一位就开始依次的腾出空间,插入i位置的元素
}
a[j + 1] = t;
}
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
cout << a[k] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[10] = { 2,1,5,4,6,9,8,7,10,3 };
int n = 9;
paixu_sort(a, n);
return 0;
}
#include <cstdio>
const int MAXN = 50;
int a[MAXN], n;
void insertSort() {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int temp = a[i];
int j = i;
while (j - 1 >= 0 && a[j - 1] > temp) {
a[j] = a[j - 1];
j--;
}
a[j] = temp;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
insertSort();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d", a[i]);
printf(i < n - 1 ? " " : "\n");
}
return 0;
}
冒泡排序
冒泡排序本质是将两个数分别进行排序
从开始进行依次的排序,知道排序到属于他的位置
void paixu_sort(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++)//这是从左边到右边进行的,升序排序,将左边的排序到右边合适的位置
{
if (a[j] > a[j + 1])
{
int t = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = t;
}
}
}
}
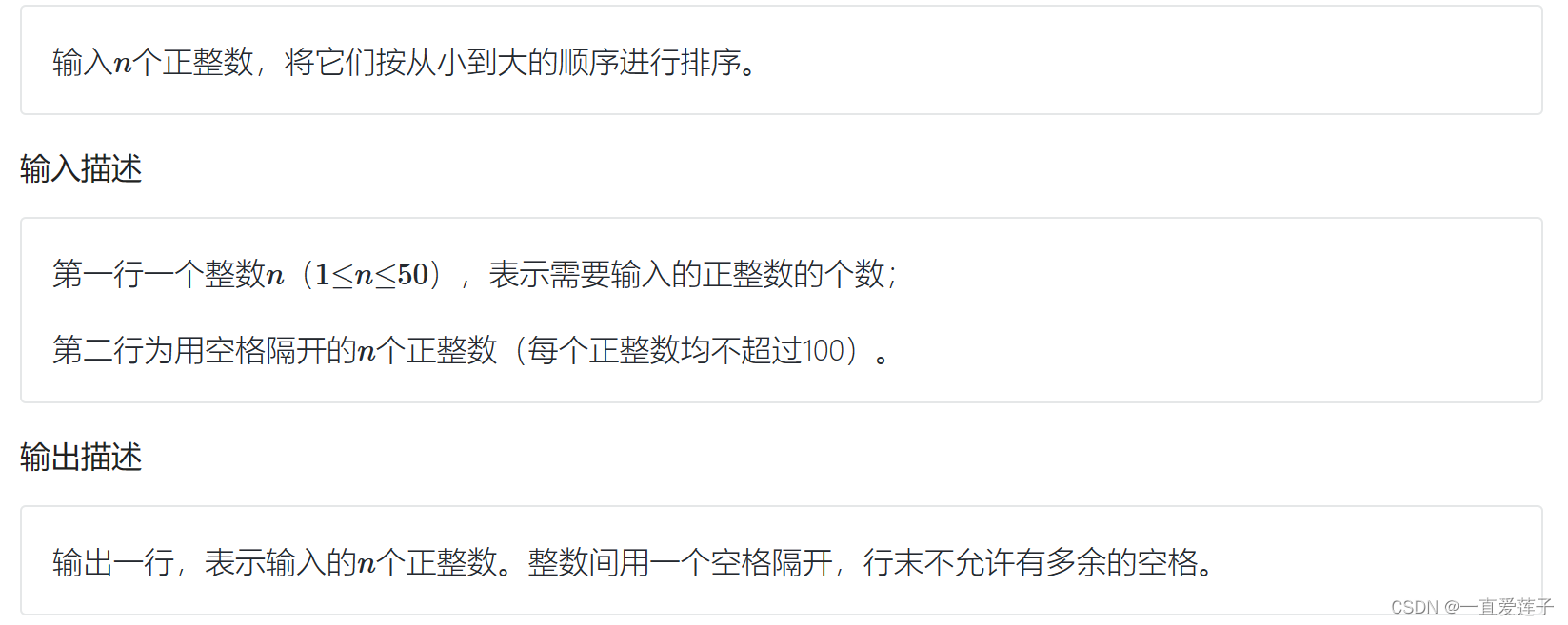
整数升序排序

利用c++函数sort函数
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 50;
int a[MAXN], n;
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
sort(a, a + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d", a[i]);
printf(i < n - 1 ? " " : "\n");
}
return 0;
}
整数降序排序 #整数降序排序
利用的是c++函数sort加一个函数进行降序
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1001;
bool cmp(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
int main()
{
int n;
int a[N] = { 0 };
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n, cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d", a[i]);
printf(i != n - 1 ? " " : "\n");
}
}
字符串升序排序
字符串也是可以直接用sort函数的
考生排序 一

还是利用函数sort进行排列
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1001;
struct student
{
int score;
string name;
}stu[N];
bool cmp(student a, student b)
{
if (a.score != b.score)
{
return a.score < b.score;
}
else
return a.name < b.name;
}
int main()
{
int i, j;
int n;
cin >> n;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> stu[i].name >> stu[i].score;
}
sort(stu, stu + n, cmp);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << stu[i].name << " " << stu[i].score << endl;
}
return 0;
}
考生排序二
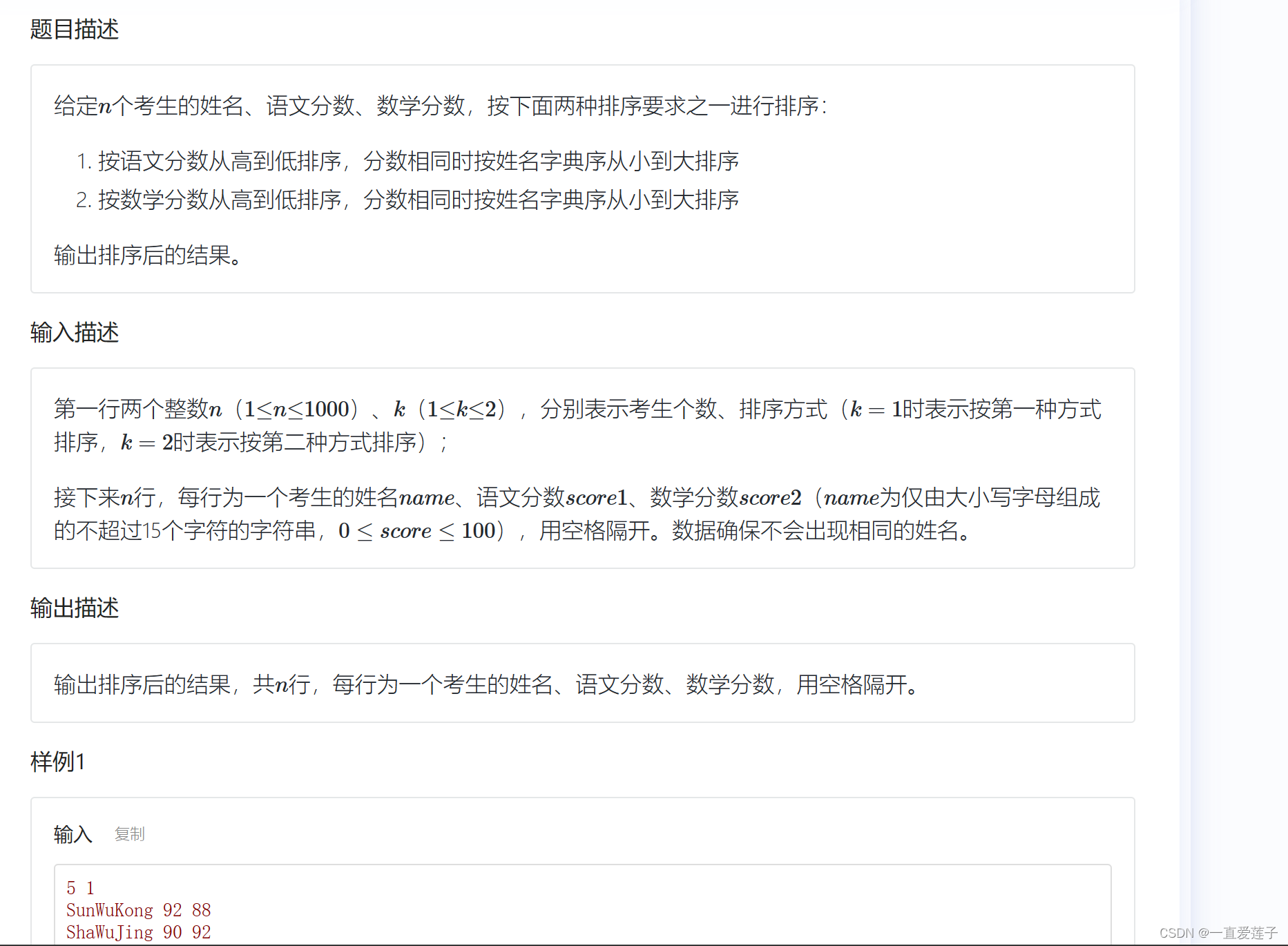
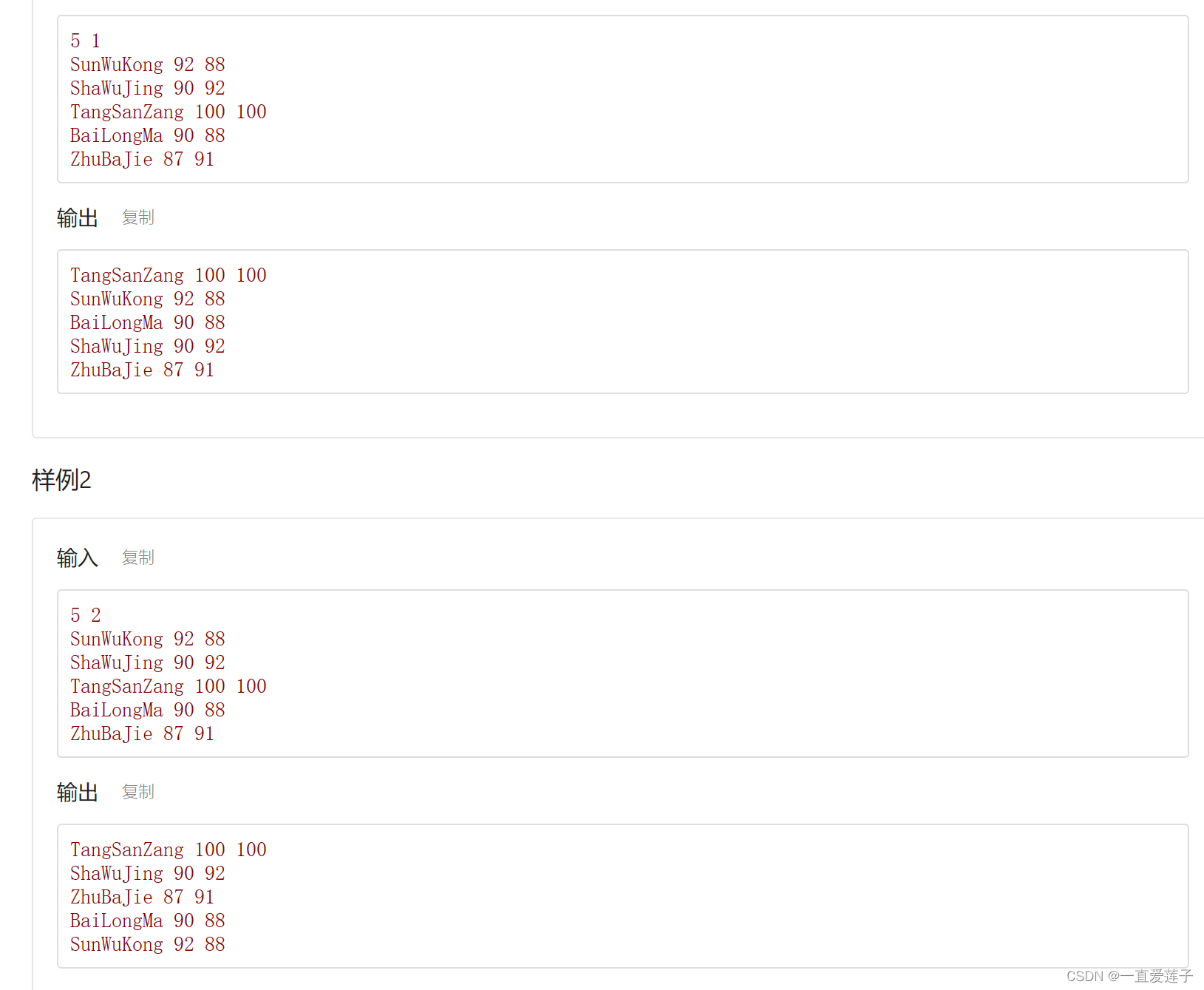
对于这类型题目其实很简单,就是选择按照哪一种方式解决句行了,选择一就用方法,选择二就用方法二,然后就是如果语文成绩只要不相同就用语文成绩的多少进行排序
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1000;
struct Student {
string name;
int chinese, math;
} stu[MAXN];
bool cmpChinese(Student a, Student b) {
if (a.chinese != b.chinese) {
return a.chinese > b.chinese;
} else {
return a.name < b.name;
}
}
bool cmpMath(Student a, Student b) {
if (a.math != b.math) {
return a.math > b.math;
} else {
return a.name < b.name;
}
}
int main() {
int n, choice;
cin >> n >> choice;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> stu[i].name >> stu[i].chinese >> stu[i].math;
}
if (choice == 1) {
sort(stu, stu + n, cmpChinese);
} else {
sort(stu, stu + n, cmpMath);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << stu[i].name << " " << stu[i].chinese << " " << stu[i].math << endl;
}
return 0;
}
计算排名
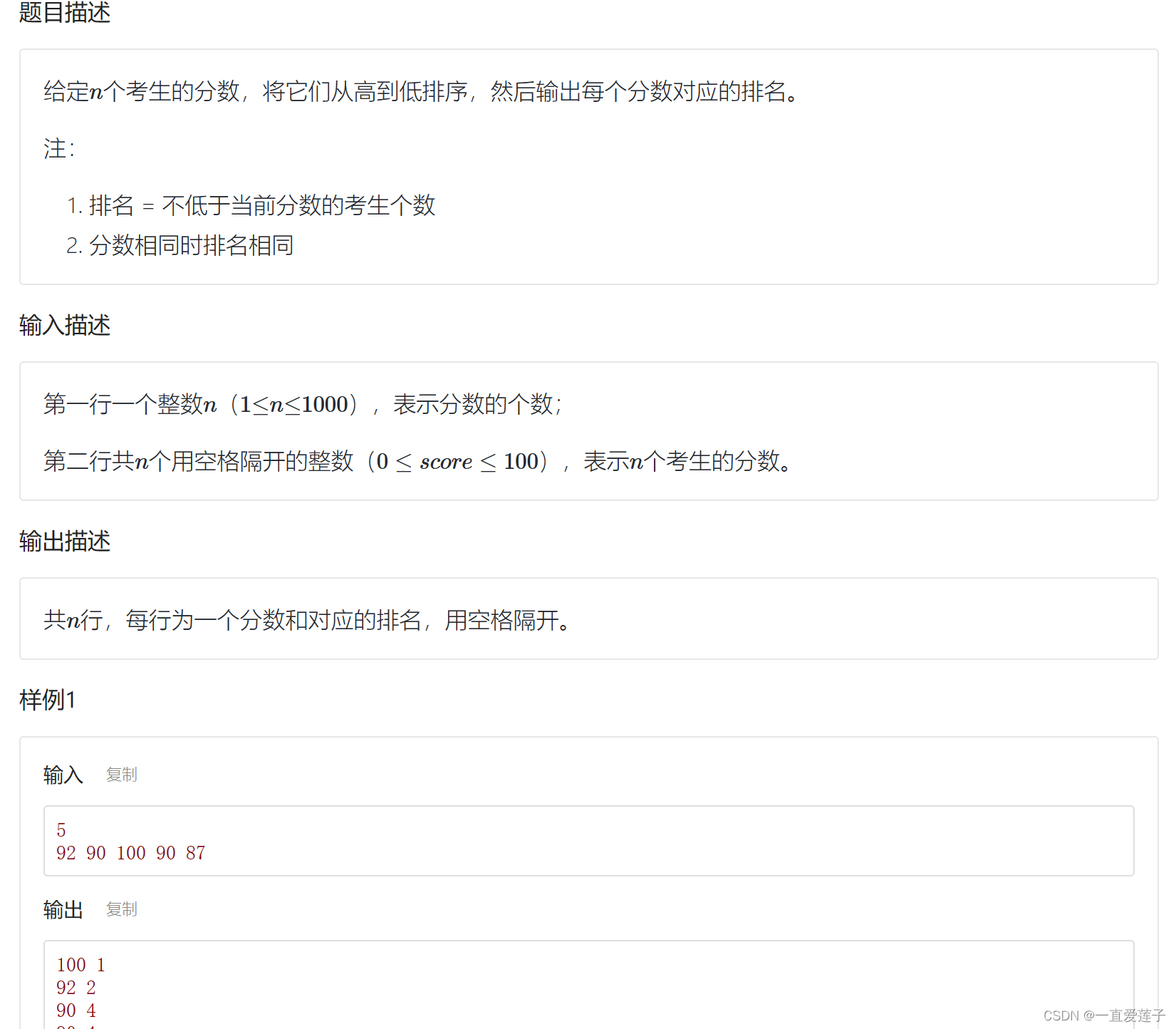
思路:设置一个数k用来记录重复数字的个数,然后就输出最后i个数然后加一(这个是真的细节)
0,1,2,3,4,5下标
1,2,3,4,5,6,正常
1,3,3,4,5,6 其中2号和三号重复
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1001;
bool cmp(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
int main()
{
int a[N];
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n,cmp);
int k = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (i+1<n&&a[i] == a[i + 1])//条件是两个数都要存在才行
{
k++;//记录重复元素多少个
}
else
{
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++)//输出最后重复元素的下标+1
{
printf("%d%d", a[i], i + 1);
}
}
k = 1;//表示的重新记录重复元素
}
}
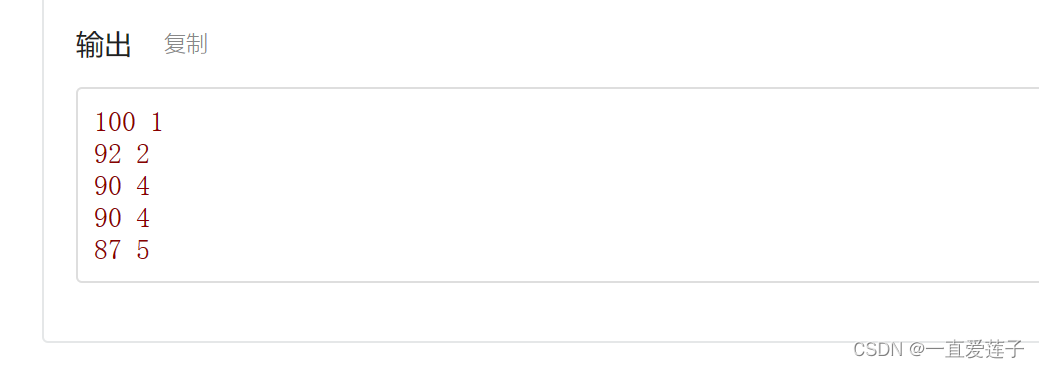
考场排名
考场的相关题目************8
无敌超级的题型,关于考场n个然后依次的进行对于每一个考场进行输出个体的内容
然后对于每一个考场进行排序,然后对于总体的数据都需要进行排序,然定义下标
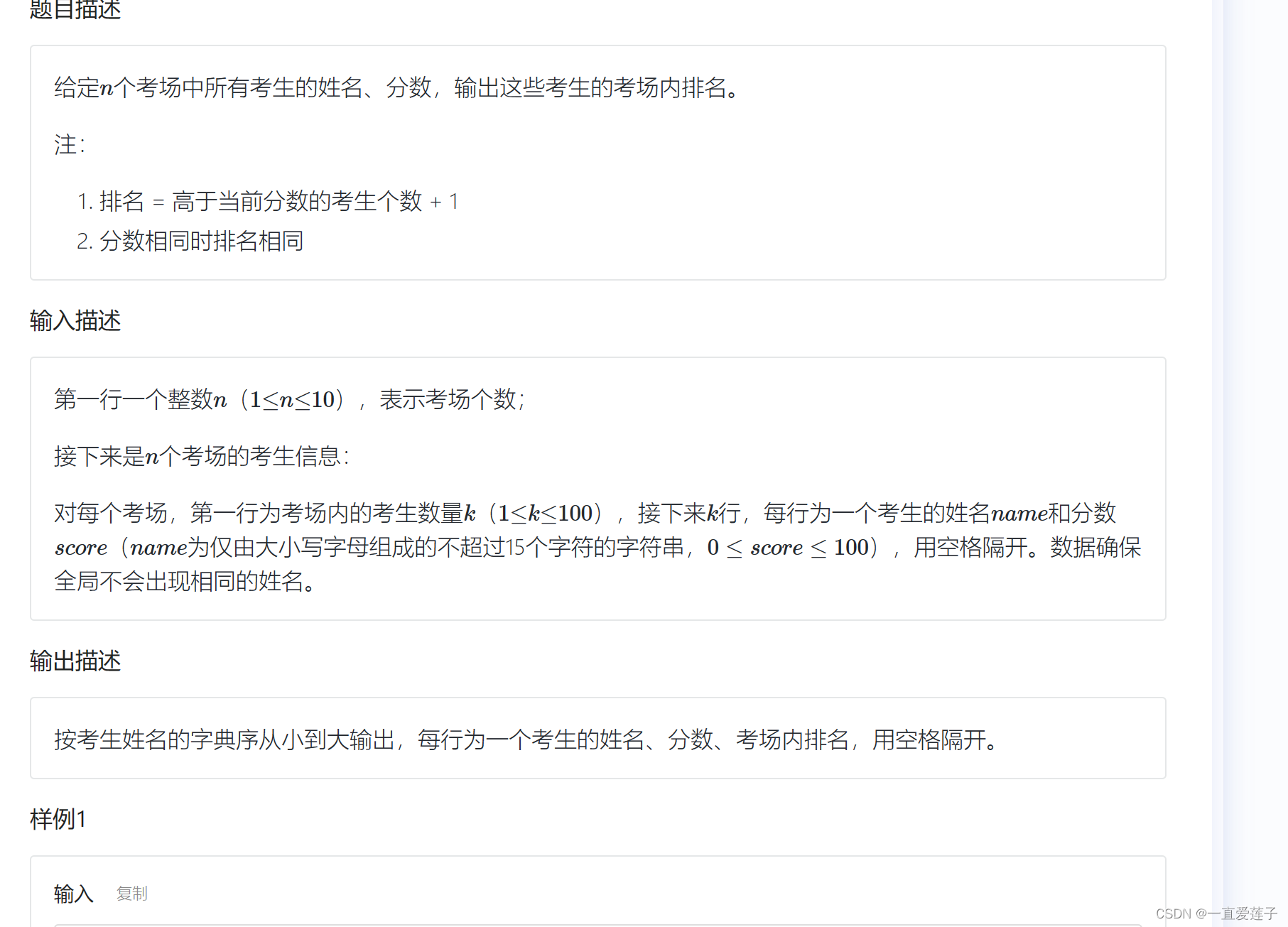
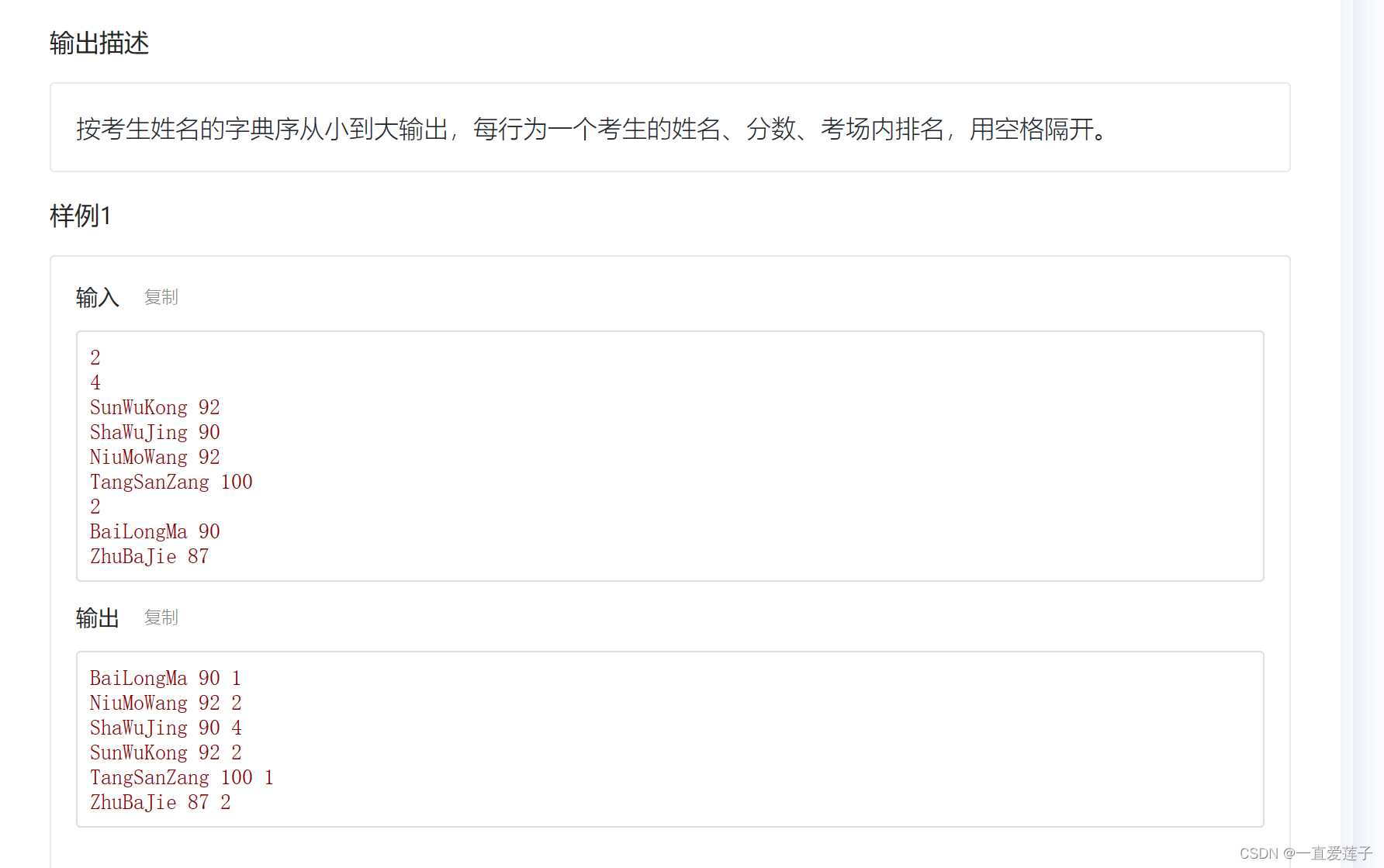
给定
个考场中所有考生的姓名、分数,输出这些考生的考场内排名。
注:
排名 = 高于当前分数的考生个数 + 1
分数相同时排名相同
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1000;
struct Student {
string name;
int score, rank;
} stu[MAXN];
bool cmpScore(Student a, Student b) {
return a.score > b.score;
}
bool cmpName(Student a, Student b) {
return a.name < b.name;
}
int main() {
int n, stuCount = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int k;
scanf("%d", &k);//每一个班级里面有多少人
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
cin >> stu[stuCount + j].name >> stu[stuCount + j].score;
}
sort(stu + stuCount, stu + stuCount + k, cmpScore);
stu[stuCount].rank = 1;
for (int j = stuCount + 1; j < stuCount + k; j++) {//只要相同的情况,就是跟第一个相同的进行输出
if (stu[j].score == stu[j - 1].score) {
stu[j].rank = stu[j - 1].rank;
}
else {
stu[j].rank = j - stuCount + 1;
}
}
stuCount += k;
}
sort(stu, stu + stuCount, cmpName);
for (int i = 0; i < stuCount; i++) {
cout << stu[i].name << " " << stu[i].score << " " << stu[i].rank << endl;
}
return 0;
}

























 661
661











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










