1,Linux系统的线程非常特别,他对线程与进程并不特别区分。对Linux而言,线程是一种特殊的进程。
2,在Linux系统中,调用fork()创建进程,该系统调用通过复制一个现有进程来创建一个全新的进程,调用fork()的进程称为父进程,新生的进程称为子进程,在调用结束时,在返回点这个位置上,父进程恢复执行,子进程开始执行,fork()系统调用从内核返回两次:一次回到父进程,一次回到新生的子进程。
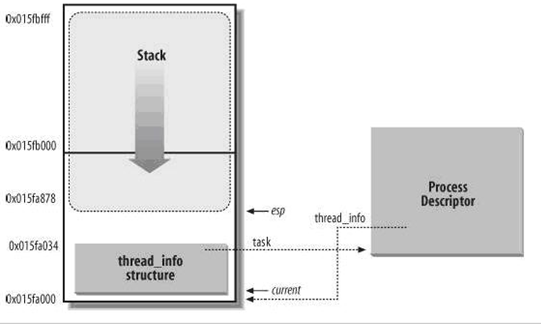
3,在OSE系统(ENEA公司出品,该公司成立于1968年,总部位于瑞典斯得哥尔摩,与爱立信共同成长)中,PCB与进程栈在内存中是相邻的,PCB在低地址处,进程栈(从高向低地址增长)在紧接着PCB的高地址存放(PCB+栈:在systemPool中分配)。而在Linux系统中并不直接存储PCB,取代PCB的是一个小的结构体:struct thread_info, 这个结构中并没有直接包含与进程相关的字段,而是通过task字段指向具体某个进程描述符(struct task_struct),这是因为现在用slab分配器动态生成task_struct(通过预先分配或重复使用task_struct,优点是进程创建迅速),所以只需在栈定(栈的低地址处)创建一个struct thread_info结构体,并指向task_struct。通过下图可知内核的栈(真正的栈)顶指针存储在esp寄存器中。
\include\asm-x86_64:
struct thread_info {
struct task_struct *task; /* main task structure */
struct exec_domain *exec_domain; /* execution domain */
__u32 flags; /* low level flags */
__u32 status; /* thread synchronous flags */
__u32 cpu; /* current CPU */
int preempt_count;
mm_segment_t addr_limit;
struct restart_block restart_block;
};<em><span style="font-family:FangSong_GB2312;font-size:14px;">/**
* 内核栈与thread_info 是个联合体, 在\include\linux\sched.h中定义
*/
union thread_union {
struct thread_info thread_info;
unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
};</span></em>如在i386处理器中:
#ifdef CONFIG_4KSTACKS
#define THREAD_SIZE (4096)
#else
#define THREAD_SIZE (8192)
#endif
即内核stack数组大小为2048,如果THREAD_SIZE = 8192。
由于thread_union是联合体,我们可知stack[0]的地址与thread_info地址相同,也就是说每个thread的thread_info保存在进程内核栈的最低端(这与OSE系统不一样,OSE系统的PCB与栈是分开的,PCB并不占用栈的空间)
4,内核访问进程需要获取进程的task_struct,通过current宏可以得到当前正在运行的进程的进程描述符,硬件体系结构不同,该宏的实现也不同,有的硬件体系结构可以用专门的寄存器存放指向task_struct的指针,但像x86,其寄存器并不富裕,只能通过栈尾端的thread_info结构,计算偏移得到task_struct。对于i386(32位 x86)的current_thread_info定义如下:
<span style="font-size:14px;"><em>\include\asm-i386\thread_info.h
static inline struct thread_info *current_thread_info(void)
{
struct thread_info *ti;
__asm__("andl %%esp,%0; ":"=r" (ti) : "0" (~(THREAD_SIZE - 1)));
return ti;
}</em></span>上述代码,如果THREAD_SIZE=8192,则~(THREAD_SIZE - 1)=0xE000,即低13位为0,这样esp寄存器的LSB 13bit被清零,得到了内核堆栈thread_info结构的地址。
current_thread_info()->task就得到了进程task_struct。
通过current宏可以直接得到task_struck:
<span style="font-size:14px;">#ifndef _I386_CURRENT_H \include\asm-i386
#define _I386_CURRENT_H
#include <linux/thread_info.h>
struct task_struct;
static inline struct task_struct * get_current(void)
{
return current_thread_info()->task;
}
#define current get_current()
#endif /* !(_I386_CURRENT_H) */</span><span style="font-size: 18px;">
</span>5,OSE系统怎么得到current_process?
<span style="font-size:14px;">PROCESS current_process(void)
{
D_DIV( debug_printf("current_process *\n"); );
return odo_sys.current->pid;
}
</span>





















 3198
3198

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








