https://ke.qq.com/course/4032547?flowToken=1042705
目录
一 uboot的命令集
启动并进入uboot,输入help,并按回车键,得到本uboot支持的命令集
=> help
? - alias for 'help'
base - print or set address offset
bdinfo - print Board Info structure
bmode - sd1|sd2|qspi1|normal|usb|sata|ecspi1:0|ecspi1:1|ecspi1:2|ecspi1:3|esdhc1|esdhc2|esdhc3|esdhc4 [noreset]
boot - boot default, i.e., run 'bootcmd'
bootd - boot default, i.e., run 'bootcmd'
bootelf - Boot from an ELF image in memory
bootm - boot application image from memory
bootp - boot image via network using BOOTP/TFTP protocol
bootvx - Boot vxWorks from an ELF image
bootz - boot Linux zImage image from memory
clocks - display clocks
cmp - memory compare
coninfo - print console devices and information
cp - memory copy
crc32 - checksum calculation
dcache - enable or disable data cache
dhcp - boot image via network using DHCP/TFTP protocol
dm - Driver model low level access
echo - echo args to console
editenv - edit environment variable
env - environment handling commands
erase - erase FLASH memory
exit - exit script
ext2load- load binary file from a Ext2 filesystem
ext2ls - list files in a directory (default /)
ext4load- load binary file from a Ext4 filesystem
ext4ls - list files in a directory (default /)
ext4size- determine a file's size
ext4write- create a file in the root directory
false - do nothing, unsuccessfully
fatinfo - print information about filesystem
fatload - load binary file from a dos filesystem
fatls - list files in a directory (default /)
fatsize - determine a file's size
fatwrite- write file into a dos filesystem
fdt - flattened device tree utility commands
flinfo - print FLASH memory information
fstype - Look up a filesystem type
fuse - Fuse sub-system
go - start application at address 'addr'
gpio - query and control gpio pins
help - print command description/usage
icache - enable or disable instruction cache
iminfo - print header information for application image
imxtract- extract a part of a multi-image
itest - return true/false on integer compare
load - load binary file from a filesystem
loadb - load binary file over serial line (kermit mode)
loads - load S-Record file over serial line
loadx - load binary file over serial line (xmodem mode)
loady - load binary file over serial line (ymodem mode)
loop - infinite loop on address range
ls - list files in a directory (default /)
md - memory display
mdio - MDIO utility commands
mii - MII utility commands
mm - memory modify (auto-incrementing address)
mmc - MMC sub system
mmcinfo - display MMC info
mtest - simple RAM read/write test
mw - memory write (fill)
nfs - boot image via network using NFS protocol
nm - memory modify (constant address)
ping - send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network host
printenv- print environment variables
protect - enable or disable FLASH write protection
reset - Perform RESET of the CPU
run - run commands in an environment variable
save - save file to a filesystem
saveenv - save environment variables to persistent storage
setenv - set environment variables
setexpr - set environment variable as the result of eval expression
sf - SPI flash sub-system
showvar - print local hushshell variables
size - determine a file's size
sleep - delay execution for some time
source - run script from memory
test - minimal test like /bin/sh
tftpboot- boot image via network using TFTP protocol
true - do nothing, successfully
version - print monitor, compiler and linker version
cmd文件夹下有很多的cmd_xxx.c文件,他们就是命令相关的具体实现。
二 help命令的原理
help命令对应的处理函数是d_help,源码如下所示:
static int do_help(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char * const argv[])
{
cmd_tbl_t *start = ll_entry_start(cmd_tbl_t, cmd);
const int len = ll_entry_count(cmd_tbl_t, cmd);
return _do_help(start, len, cmdtp, flag, argc, argv);
}
U_BOOT_CMD(
help, CONFIG_SYS_MAXARGS, 1, do_help,
"print command description/usage",
"\n"
" - print brief description of all commands\n"
"help command ...\n"
" - print detailed usage of 'command'"
);
/* This does not use the U_BOOT_CMD macro as ? can't be used in symbol names */
ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, question_mark, cmd) = {
"?", CONFIG_SYS_MAXARGS, 1, do_help,
"alias for 'help'",
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP
""
#endif /* CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP */
};
它调用了_do_help在common/command.c文件中:
int _do_help(cmd_tbl_t *cmd_start, int cmd_items, cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag,
int argc, char * const argv[])help命令就是调用这个函数实现的。
1.同理,每一个命令也对应一个执行的函数。
2.由_do_help函数参数和代码分析可知,命令是以argc 、argv形式传递给处理函数的。
3.命令集全局变量static FDC_COMMAND_STRUCT cmd; /* global command struct */
4.宏U_BOOT_CMD用户注册命令,注册内容包括命令名字、帮助信息、执行函数等。
5.ll_entry_declare宏用于创建一个help命令的别名符号'?'
三 创建一个自定义uboot命令
我先自己添加一个命令,然后再分析它的执行流程,其实我只想让它工作,不想知道它是如何工作的。
操作步骤如下,进入uboot源码的cmd文件夹,复制help.c为一个新的文件hello.c,修改内容如下所示:
写一个命令文件hello.c
#ifdef debug
#undef debug
#endif
#define debug(format,...) printf("%s,%s,line=%d:"format"\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__,##__VA_ARGS__)
static int do_hello(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char * const argv[])
{
int i = 0;
debug("argc = %d",argc);
debug("cmdtp->name = %s",cmdtp->name);
for(i = 0;i < argc;i++){
debug("argv[%d] = %s",i,argv[i]);
}
return 0;
}
U_BOOT_CMD(
hello, CONFIG_SYS_MAXARGS, 1, do_hello,
"print hello world/usage",
"\n"
" - print hello world for test\n"
"hello command ...\n"
" - print a valueable message for lkmao"
);
/* This does not use the U_BOOT_CMD macro as ? can't be used in symbol names */
ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, hello_mark, cmd) = {
"h", CONFIG_SYS_MAXARGS, 1, do_hello,
"alias for 'help'",
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP
""
#endif /* CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP */
};
配置文件到Makefile中
然后修改Makefile文件,使它能够被编译和执行
在cmd目录的Makefile文件中添加如下内容
obj-y += hello.o编译并测试结果
添加完毕,重新编译uboot,下载并启动,然后使用help命令测试
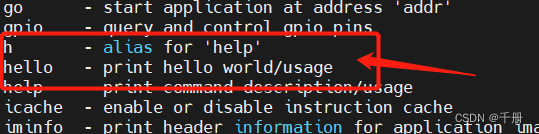
看,这里不仅创建了一个hello命令,还创建了一个hello命令的别名h,测试一下这两个命令
=> help hello
hello - print hello world/usage
Usage:
hello
- print hello world for test
hello command ...
- print a valueable message for lkmao=> help h
h - alias for 'help'
Usage:
h
完美输出了帮助信息
=> hello
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=19:argc = 1
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=20:cmdtp->name = hello
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=22:argv[0] = hello
完美执行了自定义的hello命令,且它的传参原理和c语言main相同。
使用h别名
=> h
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=19:argc = 1
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=20:cmdtp->name = h
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=22:argv[0] = h
完美执行了自定义的hello命令的别名h,且它的传参原理和c语言main相同。
传递参数a b c,如下所示,参数完美的传递给了hello命令。
=> hello a b c
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=19:argc = 4
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=20:cmdtp->name = hello
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=22:argv[0] = hello
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=22:argv[1] = a
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=22:argv[2] = b
cmd/hello.c,do_hello,line=22:argv[3] = c
自此自建命令,测试完毕,结果完美。
cmd_tbl_s 结构体
U_BOOT_CMD宏本质上就是在构造一个cmd_tbl_s 结构体。
struct cmd_tbl_s {
char *name; /* Command Name 名字 */
int maxargs; /* maximum number of arguments 命令最多接收参数个数 */
int repeatable; /* autorepeat allowed? 按回车键时,是否重复执行,直接按回车执行上一条命令*/
/* Implementation function 命令对应的函数指针*/
int (*cmd)(struct cmd_tbl_s *, int, int, char * const []);
char *usage; /* Usage message (short) 命令的短帮助信息,简单描述,函数的使用方法*/
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP
char *help; /* Help message (long) 命令的长帮助信息,细节的帮助信息*/
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_AUTO_COMPLETE
/* do auto completion on the arguments 指向自动补全的函数*/
int (*complete)(int argc, char * const argv[], char last_char, int maxv, char *cmdv[]);
#endif
};
下面的可以不用看了。
四 命令交互
位置:Main.c (common)
函数:void main_loop(void)
/* We come here after U-Boot is initialised and ready to process commands */
void main_loop(void)
{
const char *s;
bootstage_mark_name(BOOTSTAGE_ID_MAIN_LOOP, "main_loop");
#ifndef CONFIG_SYS_GENERIC_BOARD
puts("Warning: Your board does not use generic board. Please read\n");
puts("doc/README.generic-board and take action. Boards not\n");
puts("upgraded by the late 2014 may break or be removed.\n");
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLE
setenv("ver", version_string); /* set version variable */
#endif /* CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLE */
cli_init();
run_preboot_environment_command();
#if defined(CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP)
update_tftp(0UL, NULL, NULL);
#endif /* CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP */
s = bootdelay_process();
if (cli_process_fdt(&s))
cli_secure_boot_cmd(s);
autoboot_command(s);
cli_loop();
}
void cli_loop(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_HUSH_PARSER
parse_file_outer();
/* This point is never reached */
for (;;);
#else
cli_simple_loop();
#endif /*CONFIG_SYS_HUSH_PARSER*/
}这个函数有句注释/* This point is never reached */,有点不可思议。继续向前分析。
五 命令是存放在哪里的
1.存储段简介
由前面的分析可知,每个命令对应一个cmd_tbl_t结构体。命令不是存放在数组和链表中,而是存放在程序段中,链接时,链接到代码区的用户自定义的段中。定义在u-boot.lds中,在该链接脚本中定义了命令集段的开始地址和结束地址,uboot启动时,该代码段被加载到内存中,然后就可以通过find_cmd函数找到了。
2.宏实现
common/command.h文件中。
#ifdef CONFIG_AUTO_COMPLETE
# define _CMD_COMPLETE(x) x,
#else
# define _CMD_COMPLETE(x)
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP
# define _CMD_HELP(x) x,
#else
# define _CMD_HELP(x)
#endif
#define U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, \
_usage, _help, _comp) \
{ #_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, \
_CMD_HELP(_help) _CMD_COMPLETE(_comp) }
#define U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help) \
U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, \
_usage, _help, NULL)
#define U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help, _comp) \
ll_entry_declare(cmd_tbl_t, _name, cmd) = \
U_BOOT_CMD_MKENT_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, \
_usage, _help, _comp);
#define U_BOOT_CMD(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help) \
U_BOOT_CMD_COMPLETE(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help, NULL)先看几个简单的,
1.如果CONFIG_AUTO_COMPLETE是未定义的的,则_CMD_COMPLETE是空的,就是不支持自动补全
2. 如果CONFIG_SYS_LONGHELP是未定义的,则_CMD_HELP(x)是空的,就不支持长help功能。
3.这里还没有看到段属性信息,但是这里调用了宏ll_entry_declare,估计段属性就在ll_entry_declare宏里
ll_entry_declare宏的定义如下所示
#define ll_entry_declare(_type, _name, _list) \
_type _u_boot_list_2_##_list##_2_##_name __aligned(4) \
__attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_"#_list"_2_"#_name)))这里section括号里面的就是段属性啦。
3.段存储
在uboot文件夹根目录搜索
grep -irn u_boot_list_2_
下面只截取了部分结果。
/*略*/
u-boot.sym:1853:87844640 g O .u_boot_list 0000001c _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_mmc
u-boot.sym:1873:87844940 g O .u_boot_list 00000008 _u_boot_list_2_env_clbk_2_baudrate
u-boot.sym:1891:87844250 g O .u_boot_list 0000001c _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_ext2load
u-boot.sym:1897:878444f0 g O .u_boot_list 0000001c _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_itest
u-boot.sym:1906:87844678 g O .u_boot_list 0000001c _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_mtest
u-boot.sym:1916:878445d0 g O .u_boot_list 0000001c _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_md
u-boot.sym:1921:87844138 g O .u_boot_list 0000001c _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_cp
u-boot.sym:1924:878447ac g O .u_boot_list 0000001c _u_boot_list_2_cmd_2_saveenv
/*略*/搜索到的信息就是命令存储的段信息啦。
六 查找一个命令
find_cmd位于 commmon/command.c中
cmd_tbl_t *find_cmd(const char *cmd)
{
cmd_tbl_t *start = ll_entry_start(cmd_tbl_t, cmd);
const int len = ll_entry_count(cmd_tbl_t, cmd);
return find_cmd_tbl(cmd, start, len);
}看下两个宏ll_entry_start和ll_entry_end
/**
* ll_entry_start() - Point to first entry of linker-generated array
* @_type: Data type of the entry
* @_list: Name of the list in which this entry is placed
*
* This function returns (_type *) pointer to the very first entry of a
* linker-generated array placed into subsection of .u_boot_list section
* specified by _list argument.
*
* Since this macro defines an array start symbol, its leftmost index
* must be 2 and its rightmost index must be 1.
*
* Example:
* struct my_sub_cmd *msc = ll_entry_start(struct my_sub_cmd, cmd_sub);
*/
#define ll_entry_start(_type, _list) \
({ \
static char start[0] __aligned(4) __attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_"#_list"_1"))); \
(_type *)&start; \
})
/**
* ll_entry_end() - Point after last entry of linker-generated array
* @_type: Data type of the entry
* @_list: Name of the list in which this entry is placed
* (with underscores instead of dots)
*
* This function returns (_type *) pointer after the very last entry of
* a linker-generated array placed into subsection of .u_boot_list
* section specified by _list argument.
*
* Since this macro defines an array end symbol, its leftmost index
* must be 2 and its rightmost index must be 3.
*
* Example:
* struct my_sub_cmd *msc = ll_entry_end(struct my_sub_cmd, cmd_sub);
*/
#define ll_entry_end(_type, _list) \
({ \
static char end[0] __aligned(4) __attribute__((unused, \
section(".u_boot_list_2_"#_list"_3"))); \
(_type *)&end; \
})宏ll_entry_count()用于返回命令数量
/**
* ll_entry_count() - Return the number of elements in linker-generated array
* @_type: Data type of the entry
* @_list: Name of the list of which the number of elements is computed
*
* This function returns the number of elements of a linker-generated array
* placed into subsection of .u_boot_list section specified by _list
* argument. The result is of an unsigned int type.
*
* Example:
* int i;
* const unsigned int count = ll_entry_count(struct my_sub_cmd, cmd_sub);
* struct my_sub_cmd *msc = ll_entry_start(struct my_sub_cmd, cmd_sub);
* for (i = 0; i < count; i++, msc++)
* printf("Entry %i, x=%i y=%i\n", i, msc->x, msc->y);
*/
#define ll_entry_count(_type, _list) \
({ \
_type *start = ll_entry_start(_type, _list); \
_type *end = ll_entry_end(_type, _list); \
unsigned int _ll_result = end - start; \
_ll_result; \
})它最终就是在以u_boot_list_2_xxx命名的段中查找命令的,并返回该命令对应的cmd_tbl_t结构体
七 运行一个命令
Cli.c (common)文件
run_command函数用于运行一个命令,它最终调用的就是cmd_tbl_t结构体的函数指针cmd
int (*cmd)(struct cmd_tbl_s *, int, int, char * const []);/*
* Run a command using the selected parser.
*
* @param cmd Command to run
* @param flag Execution flags (CMD_FLAG_...)
* @return 0 on success, or != 0 on error.
*/
int run_command(const char *cmd, int flag)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_SYS_HUSH_PARSER
/*
* cli_run_command can return 0 or 1 for success, so clean up
* its result.
*/
if (cli_simple_run_command(cmd, flag) == -1)
return 1;
return 0;
#else
int hush_flags = FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON | FLAG_EXIT_FROM_LOOP;
if (flag & CMD_FLAG_ENV)
hush_flags |= FLAG_CONT_ON_NEWLINE;
return parse_string_outer(cmd, hush_flags);
#endif
}






















 1421
1421

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










