1 Octave 中的for 和 while
for i<10,
i = i + 1;
end;
这样是错误的,这里的for 应该换成while。
2 Octave 中的std和mean
函数std(x),算出x的标准偏差。x可以是一行的matrix或者一个多行matrix,如果只有一行,那么就是算一行的标准偏差,如果有多行,就是算每一列的标准偏差。
std(x,a)也是x的标准偏差,但是a可以=0或者1.如果是0和前面没有区别,如果是1就是最后除以n,而不是n-1.(你参考计算标准偏差的公式,一般都用除以n-1的公式。)
std (x, a, b) 这里a表示是要用n还是n-1,如果是a是0就是除以n-1,如果是1就是除以n,b这里是维数,比如说
1 2 3 4;
4 5 6 1;
如果b是1,就是按照列分,如果b是2就是按照行分,如果是三维的矩阵,b=3就按照第三维来分数据
M = mean(A),如果A只有一行或者一列数据,那么计算结果为这一行或这一列的平均值,如果A是一个矩阵,那么这里默认按照列来计算平均值
M = mean(A,dim),dim=1 表示按照列计算,dim=2表示按照行计算
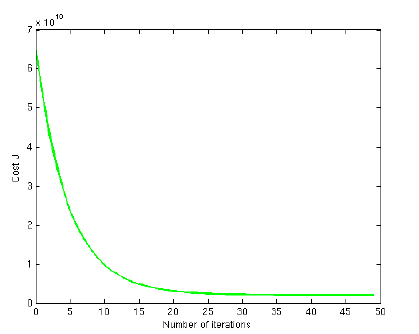
Linear regression with one variable
ex1data1.txt 下面是部分数据,第一列是城市人口数量,第二列是在此城市开分店的利润
6.1101,17.592
5.5277,9.1302
8.5186,13.662
7.0032,11.854
5.8598,6.8233
8.3829,11.886
7.4764,4.3483主程序
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 1: Linear Regression
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% linear exercise. You will need to complete the following functions
% in this exericse:
%
% warmUpExercise.m
% plotData.m
% gradientDescent.m
% computeCost.m
% gradientDescentMulti.m
% computeCostMulti.m
% featureNormalize.m
% normalEqn.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
% x refers to the population size in 10,000s
% y refers to the profit in $10,000s
%
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% ==================== Part 1: Basic Function ====================
% Complete warmUpExercise.m
fprintf('Running warmUpExercise ... \n');
fprintf('5x5 Identity Matrix: \n');
warmUpExercise()
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ======================= Part 2: Plotting =======================
fprintf('Plotting Data ...\n')
data = load('ex1data1.txt');
X = data(:, 1); y = data(:, 2);
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% Plot Data
% Note: You have to complete the code in plotData.m
plotData(X, y);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% =================== Part 3: Gradient descent ===================
fprintf('Running Gradient Descent ...\n')
X = [ones(m, 1), data(:,1)]; % Add a column of ones to x
theta = zeros(2, 1); % initialize fitting parameters
% Some gradient descent settings
iterations = 1500;
alpha = 0.01;
% compute and display initial cost
computeCost(X, y, theta)
% run gradient descent
theta = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, iterations);
% print theta to screen
fprintf('Theta found by gradient descent: ');
fprintf('%f %f \n', theta(1), theta(2));
% Plot the linear fit
hold on; % keep previous plot visible
plot(X(:,2), X*theta, '-')
legend('Training data', 'Linear regression')
hold off % don't overlay any more plots on this figure
% Predict values for population sizes of 35,000 and 70,000
predict1 = [1, 3.5] *theta;
fprintf('For population = 35,000, we predict a profit of %f\n',...
predict1*10000);
predict2 = [1, 7] * theta;
fprintf('For population = 70,000, we predict a profit of %f\n',...
predict2*10000);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
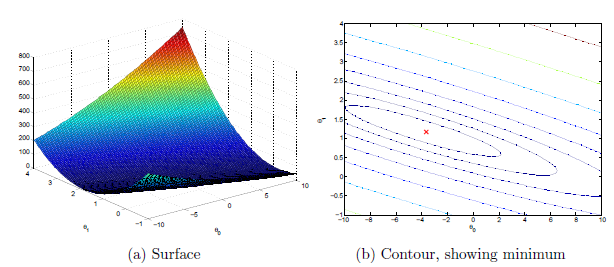
%% ============= Part 4: Visualizing J(theta_0, theta_1) =============
fprintf('Visualizing J(theta_0, theta_1) ...\n')
% Grid over which we will calculate J
theta0_vals = linspace(-10, 10, 100);
theta1_vals = linspace(-1, 4, 100);
% initialize J_vals to a matrix of 0's
J_vals = zeros(length(theta0_vals), length(theta1_vals));
% Fill out J_vals
for i = 1:length(theta0_vals)
for j = 1:length(theta1_vals)
t = [theta0_vals(i); theta1_vals(j)];
J_vals(i,j) = computeCost(X, y, t);
end
end
% Because of the way meshgrids work in the surf command, we need to
% transpose J_vals before calling surf, or else the axes will be flipped
J_vals = J_vals';
% Surface plot
figure;
surf(theta0_vals, theta1_vals, J_vals)
xlabel('\theta_0'); ylabel('\theta_1');
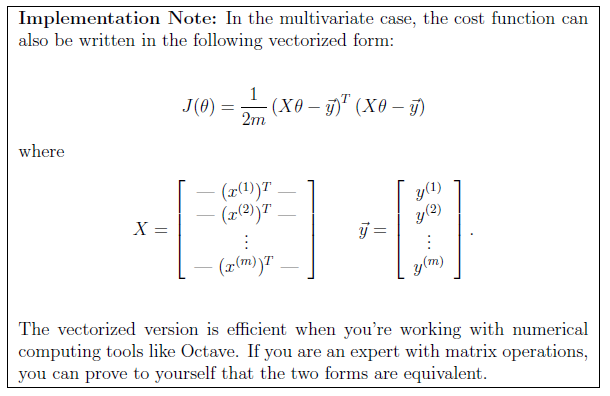
% Contour plot
figure;
% Plot J_vals as 15 contours spaced logarithmically between 0.01 and 100
contour(theta0_vals, theta1_vals, J_vals, logspace(-2, 3, 20))
xlabel('\theta_0'); ylabel('\theta_1');
hold on;
plot(theta(1), theta(2), 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 2);
1 ploting data
function plotData(x, y)
%PLOTDATA Plots the data points x and y into a new figure
% PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points and gives the figure axes labels of
% population and profit.
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Plot the training data into a figure using the
% "figure" and "plot" commands. Set the axes labels using
% the "xlabel" and "ylabel" commands. Assume the
% population and revenue data have been passed in
% as the x and y arguments of this function.
%
% Hint: You can use the 'rx' option with plot to have the markers
% appear as red crosses. Furthermore, you can make the
% markers larger by using plot(..., 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10);
figure; % open a new figure window
plot(x, y, 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10);
ylabel('Profit in $10,000s');
xlabel('Population of City in 10,000s');
% ============================================================
end
2 Gradient Descent
cost function
function J = computeCost(X, y, theta)
%COMPUTECOST Compute cost for linear regression
% J = COMPUTECOST(X, y, theta) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for linear regression to fit the data points in X and y
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta
% You should set J to the cost.
J = sum((X * theta - y).^2)/(2*m);
% =========================================================================
end
Gradient Descent
function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters)
%GRADIENTDESCENT Performs gradient descent to learn theta
% theta = GRADIENTDESENT(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) updates theta by
% taking num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1);
for iter = 1:num_iters
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Perform a single gradient step on the parameter vector
% theta.
%
% Hint: While debugging, it can be useful to print out the values
% of the cost function (computeCost) and gradient here.
%
% ============================================================
% Save the cost J in every iteration
theta = theta - alpha * (X' * (X * theta - y)) / m;
J_history(iter) = computeCost(X, y, theta);
end
end
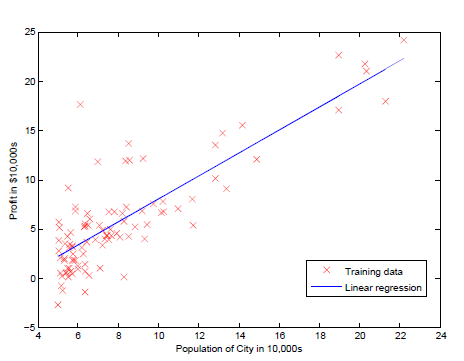
总结:
1 一开始计算cost function的时候忘记1/2m的系数了,导致计算结果是一个很大的值
2 最后一步中画surf的方法可以借鉴
3 一个很好的习惯就是计算grandient descent的时候,跟踪J(theta)的变化,来分析cost function随着迭代的收敛情况,来决定选择合适的alpha学习速率。
4 学习X = [ones(m, 1), data(:,1)]; % Add a column of ones to x, 其中为feature增加一列1的方法
Linear regression with multiple variables
1 dataset 第一列是房屋的面积,第二列是房屋中包含的卧室的数量,第三列是目标结果,在这里是价格
2104,3,399900
1600,3,329900
2400,3,369000
1416,2,232000
3000,4,539900
1985,4,299900
1534,3,314900
1427,3,198999
很容易发现,第一列和第二列数据的量级相差很大,不利于梯度下降的收敛,这里对数据进行规约,采取的方法是
(sample - mean)/ standard divation, 另外一种方案是(sample - mean)/ (max - min),这里采取第一种
使用的函数分别为mean和std计算平均值和标准差
function [X_norm, mu, sigma] = featureNormalize(X)
%FEATURENORMALIZE Normalizes the features in X
% FEATURENORMALIZE(X) returns a normalized version of X where
% the mean value of each feature is 0 and the standard deviation
% is 1. This is often a good preprocessing step to do when
% working with learning algorithms.
% You need to set these values correctly
X_norm = X;
mu = zeros(1, size(X, 2));
sigma = zeros(1, size(X, 2));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: First, for each feature dimension, compute the mean
% of the feature and subtract it from the dataset,
% storing the mean value in mu. Next, compute the
% standard deviation of each feature and divide
% each feature by it's standard deviation, storing
% the standard deviation in sigma.
%
% Note that X is a matrix where each column is a
% feature and each row is an example. You need
% to perform the normalization separately for
% each feature.
%
% Hint: You might find the 'mean' and 'std' functions useful.
%
mu = mean(X,1);
sigma = std(X);
i = 1;
le = size(X, 2);
while i <= le,
X_norm(:,i) = (X(:,i) - mu(1,i))/sigma(1,i);
i = i + 1;
end;
% ============================================================
end
这里计算得到的mean和std应该保存下来,当需要对新数据进行预测的时候,使用这里计算得到的mean和std来进行数据规约,然后根据theta的值进行预测和估算
2 Gradient Descent
这里和上面的代码保持一致,但是有另外的方法计算,稍微一点不同作为参考
3 Selecting Learning Rate
We recommend trying values of the learning rate on a log-scale, at multiplicative steps of about 3 times the previous value (i.e., 0.3, 0.1, 0.03, 0.01 and so on).
把J(theta)在每次迭代的变化情况画出来后可以得到下面的图片,由此可以看出来学习速率alpha是可以工作的,可以尝试把alpha调大,本来alpha默认是0.03后来我将它调成1之后,J(theta)快速的收敛到了最小值。
总结: 当把数据做了标准化之后,得到theta,在进行预测新的数据的时候,要再次把新数据进行规约,然后计算
Normal Equation
这里非常简单的套用公式即可
function [theta] = normalEqn(X, y)
%NORMALEQN Computes the closed-form solution to linear regression
% NORMALEQN(X,y) computes the closed-form solution to linear
% regression using the normal equations.
theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the code to compute the closed form solution
% to linear regression and put the result in theta.
%
% ---------------------- Sample Solution ----------------------
theta = pinv(X'*X)*X'*y;
% -------------------------------------------------------------
% ============================================================
end在这里normal equation可以一次计算就得到最优结果,经过比较发现normal equation和gradient descent计算的结果不一样,其实原因是因为上面的gradient descent做过的数据规约的处理,所以会得到不一样的theta,但是两种方法预测的新数据时是可以得到相同的结果。
%% Machine Learning Online Class
% Exercise 1: Linear regression with multiple variables
%
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% linear regression exercise.
%
% You will need to complete the following functions in this
% exericse:
%
% warmUpExercise.m
% plotData.m
% gradientDescent.m
% computeCost.m
% gradientDescentMulti.m
% computeCostMulti.m
% featureNormalize.m
% normalEqn.m
%
% For this part of the exercise, you will need to change some
% parts of the code below for various experiments (e.g., changing
% learning rates).
%
%% Initialization
%% ================ Part 1: Feature Normalization ================
%% Clear and Close Figures
clear ; close all; clc
fprintf('Loading data ...\n');
%% Load Data
data = load('ex1data2.txt');
X = data(:, 1:2);
y = data(:, 3);
m = length(y);
% Print out some data points
fprintf('First 10 examples from the dataset: \n');
fprintf(' x = [%.0f %.0f], y = %.0f \n', [X(1:10,:) y(1:10,:)]');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
% Scale features and set them to zero mean
fprintf('Normalizing Features ...\n');
[X mu sigma] = featureNormalize(X);
% Add intercept term to X
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
%% ================ Part 2: Gradient Descent ================
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: We have provided you with the following starter
% code that runs gradient descent with a particular
% learning rate (alpha).
%
% Your task is to first make sure that your functions -
% computeCost and gradientDescent already work with
% this starter code and support multiple variables.
%
% After that, try running gradient descent with
% different values of alpha and see which one gives
% you the best result.
%
% Finally, you should complete the code at the end
% to predict the price of a 1650 sq-ft, 3 br house.
%
% Hint: By using the 'hold on' command, you can plot multiple
% graphs on the same figure.
%
% Hint: At prediction, make sure you do the same feature normalization.
%
fprintf('Running gradient descent ...\n');
% Choose some alpha value
alpha = 0.01;
num_iters = 400;
% Init Theta and Run Gradient Descent
theta = zeros(3, 1);
[theta, J_history] = gradientDescentMulti(X, y, theta, 1, num_iters);
% Plot the convergence graph
figure;
plot(1:50, J_history(1:50), '-b', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('Number of iterations');
ylabel('Cost J');
% Display gradient descent's result
fprintf('Theta computed from gradient descent: \n');
fprintf(' %f \n', theta);
fprintf('\n');
% Estimate the price of a 1650 sq-ft, 3 br house
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Recall that the first column of X is all-ones. Thus, it does
% not need to be normalized.
price = ([1 ([1650 3].-mu)./sigma])*theta; % You should change this
% ============================================================
fprintf(['Predicted price of a 1650 sq-ft, 3 br house ' ...
'(using gradient descent):\n $%f\n'], price);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ================ Part 3: Normal Equations ================
fprintf('Solving with normal equations...\n');
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: The following code computes the closed form
% solution for linear regression using the normal
% equations. You should complete the code in
% normalEqn.m
%
% After doing so, you should complete this code
% to predict the price of a 1650 sq-ft, 3 br house.
%
%% Load Data
data = csvread('ex1data2.txt');
X = data(:, 1:2);
y = data(:, 3);
m = length(y);
% Add intercept term to X
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% Calculate the parameters from the normal equation
theta = normalEqn(X, y);
% Display normal equation's result
fprintf('Theta computed from the normal equations: \n');
fprintf(' %f \n', theta);
fprintf('\n');
% Estimate the price of a 1650 sq-ft, 3 br house
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
price = [1 1650 3] * theta; % You should change this
% ============================================================
fprintf(['Predicted price of a 1650 sq-ft, 3 br house ' ...
'(using normal equations):\n $%f\n'], price);







 本文深入探讨了机器学习与数据科学的基础概念、关键算法与实践应用,包括线性回归、逻辑回归、决策树、随机森林、支持向量机、神经网络等有监督学习方法,以及聚类算法、主成分分析等无监督学习方法。同时,文章介绍了如何利用这些技术解决实际问题,并通过代码示例展示了解决方案。
本文深入探讨了机器学习与数据科学的基础概念、关键算法与实践应用,包括线性回归、逻辑回归、决策树、随机森林、支持向量机、神经网络等有监督学习方法,以及聚类算法、主成分分析等无监督学习方法。同时,文章介绍了如何利用这些技术解决实际问题,并通过代码示例展示了解决方案。
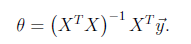

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








