一、栈的定义
栈(stack)是限定仅在表尾进行插入或者删除的线性表。对于栈来说,表尾端称为栈顶(top),表头端称为栈低(bottom)。不含元素的空表称为空栈。因为栈限定在表尾进行插入或者删除,所以栈又被称为后进先出的线性表。
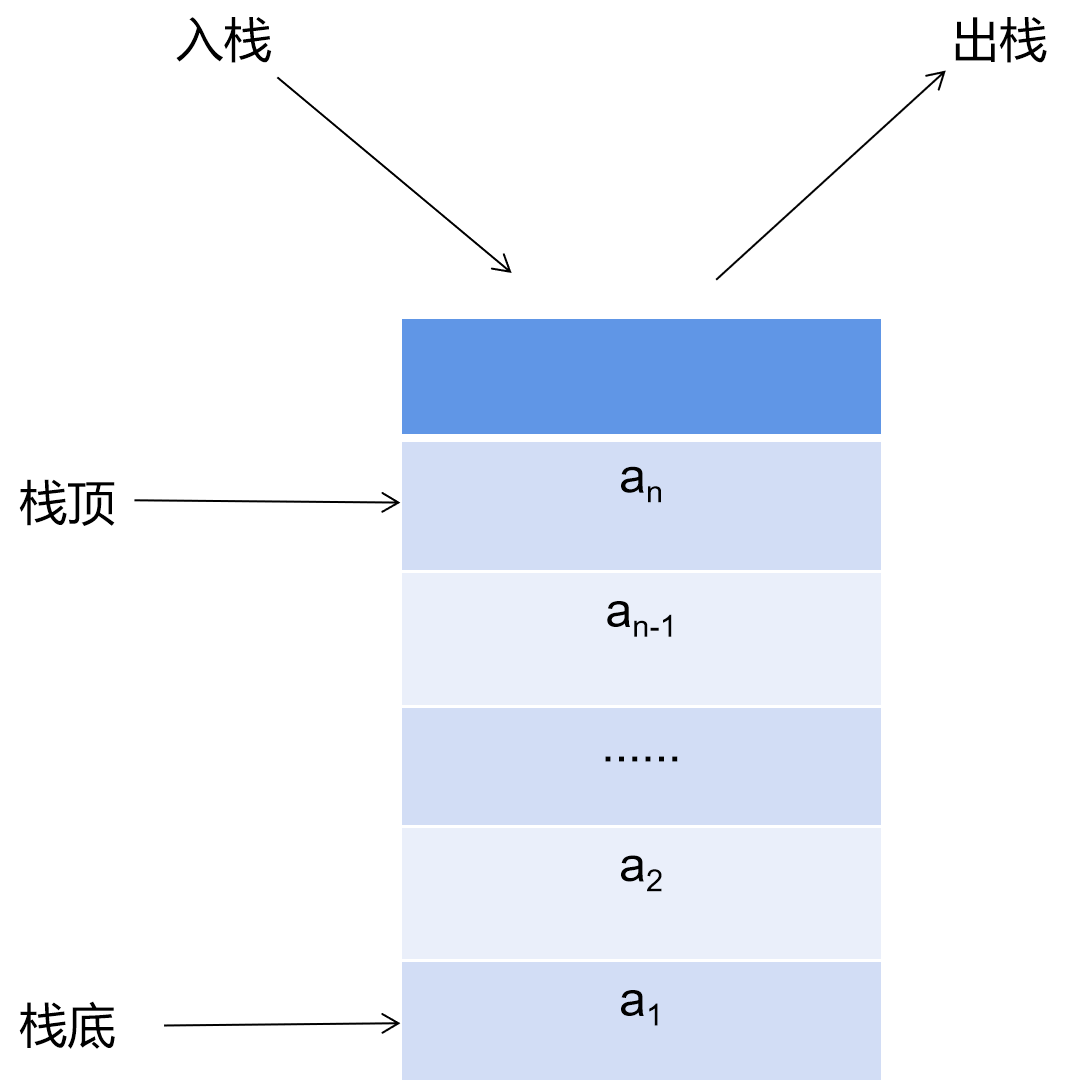
二、栈的基本操作
1.栈的结构体
typedef struct CharStack
{
int top;
int data[STACK_MAX_SIZE];
} *CharStackPtr;2.初始化
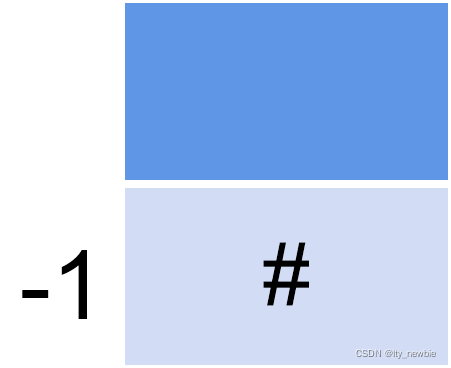
CharStackPtr charStackInit()
{
CharStackPtr resultPtr = (CharStackPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct CharStack));
resultPtr->top = -1;
return resultPtr;
}
3.打印
void outputStack(CharStackPtr paraStack)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= paraStack->top; i ++)
{
printf("%c ", paraStack->data[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
}
4.压栈
void push(CharStackPtr paraStackPtr, int paraValue)
{
// 空间检查(是否栈满)
if (paraStackPtr->top >= STACK_MAX_SIZE - 1)
{
printf("堆栈已满,无法添加.\r\n");
return;
}
// 顶部更新.
paraStackPtr->top ++;
// 入栈.
paraStackPtr->data[paraStackPtr->top] = paraValue;
}
5.弹栈
char pop(CharStackPtr paraStackPtr)
{
// 空间检查(判断空栈).
if (paraStackPtr->top < 0)
{
printf("堆栈为空,无法弹出.\r\n");
return '\0';
}
// 顶部更新.
paraStackPtr->top --;
return paraStackPtr->data[paraStackPtr->top + 1];
}
6.功能测试
void pushPopTest()
{
printf("栈的进出开始测试:\r\n");
// 初始化
CharStackPtr tempStack = charStackInit();
printf("初始化后的栈: ");
outputStack(tempStack);
// 压栈
for (char ch = 'a'; ch < 'n'; ch ++)
{
printf("添加 %c.\r\n", ch);
push(tempStack, ch);
outputStack(tempStack);
}//Of for i
// 弹栈
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
char ch = pop(tempStack);
printf("删除 %c.\r\n", ch);
outputStack(tempStack);
}
printf("测试结束\r\n");
}测试结果
栈的进出开始测试:
初始化后的栈:
添加 a.
a
添加 b.
a b
添加 c.
a b c
添加 d.
a b c d
添加 e.
a b c d e
添加 f.
a b c d e f
添加 g.
a b c d e f g
添加 h.
a b c d e f g h
添加 i.
a b c d e f g h i
添加 j.
a b c d e f g h i j
添加 k.
堆栈已满,无法添加.
a b c d e f g h i j
添加 l.
堆栈已满,无法添加.
a b c d e f g h i j
添加 m.
堆栈已满,无法添加.
a b c d e f g h i j
删除 j.
a b c d e f g h i
删除 i.
a b c d e f g h
删除 h.
a b c d e f g
删除 g.
a b c d e f
测试结束
三、括号匹配
借助栈
bool bracketMatching(char* paraString, int paraLength)
{
// 通过在底部压入“#”来初始化堆栈
CharStackPtr tempStack = charStackInit();
push(tempStack, '#');
char tempChar, tempPopedChar;
// 处理字符串
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
tempChar = paraString[i];
switch (tempChar) {
case '(':
case '[':
case '{':
push(tempStack, tempChar);
break;
case ')':
tempPopedChar = pop(tempStack);
if (tempPopedChar != '(') {
return false;
}
break;
case ']':
tempPopedChar = pop(tempStack);
if (tempPopedChar != '[') {
return false;
} break;
case '}':
tempPopedChar = pop(tempStack);
if (tempPopedChar != '{') {
return false;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
tempPopedChar = pop(tempStack);
if (tempPopedChar != '#')
{
return true;
}
return true;
}功能测试
void bracketMatchingTest()
{
printf("括号匹配测试开始:\r\n");
char* tempExpression = "{6+3-[1+2*(6-2)]}/2";
bool tempMatch = bracketMatching(tempExpression, 17);
printf("'%s'是否括号匹配? %d \r\n", tempExpression, tempMatch);
tempExpression = "[1+2*8)(]";
tempMatch = bracketMatching(tempExpression, 6);
printf("'%s'是否括号匹配? %d \r\n", tempExpression, tempMatch);
tempExpression = "({[]})";
tempMatch = bracketMatching(tempExpression, 8);
printf("'%s'是否括号匹配? %d \r\n", tempExpression, tempMatch);
tempExpression = "()()[]";
tempMatch = bracketMatching(tempExpression, 6);
printf("'%s'是否括号匹配? %d \r\n", tempExpression, tempMatch);
tempExpression = "{]()";
tempMatch = bracketMatching(tempExpression, 2);
printf("'%s'是否括号匹配? %d \r\n", tempExpression, tempMatch);
printf("测试结束\r\n");
}测试结果
括号匹配测试开始:
'{6+3-[1+2*(6-2)]}/2'是否括号匹配? 1
'[1+2*8)(]'是否括号匹配? 1
'({[]})'是否括号匹配? 1
'()()[]'是否括号匹配? 1
'{]()'是否括号匹配? 0
测试结束
四、表达式求值
//属实是难到了,C++还有很多不理解的地方,主要还是在观摩学习,以下为学长代码,只用了两个栈便实现了表达式求值的功能。
1.#include <cstring>:可以使用很多实用的字符串函数;
2.#include<algorithm>:algorithm意为"算法",是C++的标准模版库(STL)中最重要的头文件之一,提供了大量基于迭代器的非成员模版函数;
3.#include < stack > include < stack >为C++ STL栈stack的 头文件 ,是STL中实现的一个后进先出的容器:
stack<int>num//声明一个对象
str.size()//返回栈中元素个数于X
num.pop()//移除栈顶元素
num.push(x)//将X置于栈顶
op.top()//返回栈顶元素
4.unordered_map是一种关联容器,存储基于键值和映射组成的元素,即key-value。允许基于键快速查找元素。unordered_map中,键值唯一标识元素,映射的值是一个与该对象关联的内容的对象
5.auto是一个C/C++语言存储类型,仅在语句块内部使用,初始化可为任何表达式,其特点是当执行流程进入该语句块的时候初始化可为任何表达式。
//202031061018 刘知鑫
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
stack<int> num;
stack<char> op;
void eval()
{
auto b = num.top();
num.pop();
auto a = num.top();
num.pop();
auto c = op.top();
op.pop();
int x;
if (c == '+') x = a + b;
else if (c == '-') x = a - b;
else if (c == '*') x = a * b;
else x = a / b;
num.push(x);
}
int main()
{
unordered_map<char, int> pr{{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}};
string str;
cin >> str;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i ++ )
{
auto c = str[i];
if (isdigit(c))
{
int x = 0, j = i;
while (j < str.size() && isdigit(str[j]))
x = x * 10 + str[j ++ ] - '0';
i = j - 1;
num.push(x);
}
else if (c == '(') op.push(c);
else if (c == ')')
{
while (op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop();
}
else
{
while (op.size() && op.top() != '(' && pr[op.top()] >= pr[c]) eval();
op.push(c);
}
}
while (op.size()) eval();
cout << num.top() << endl;
return 0;
}





















 1040
1040











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








