本文将讲解生成连通图的最小生成树中的克鲁斯卡尔算法及其Java实现。
上篇博客中已经讲解了什么是最小生成树以及找连通图的最小生成树中一种经典的普里姆算法的原理和实现。有兴趣的可以浏览 http://blog.csdn.net/yz930618/article/details/77930364
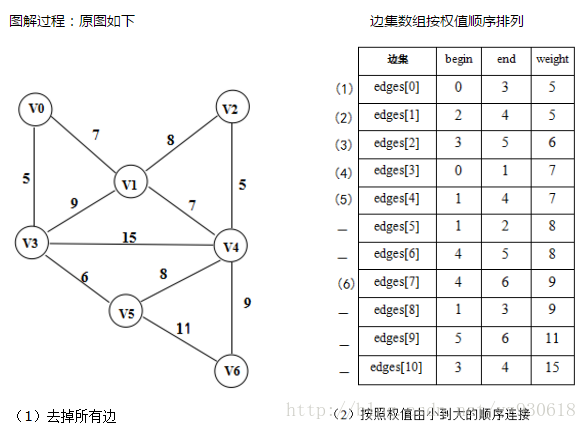
克鲁斯卡尔算法原理
为使生成树上边的权值之和达到最小,则应使生成树中每一条边的权值尽可能的小。普里姆算法是以某顶点为起点,逐步找各顶点上最小权值的边来构建最小生成树。而克鲁斯卡尔算法始终选择当前可用(所选的边不能构成回路)的最小权值边来构建生成树。
克鲁斯卡尔算法步骤如下:
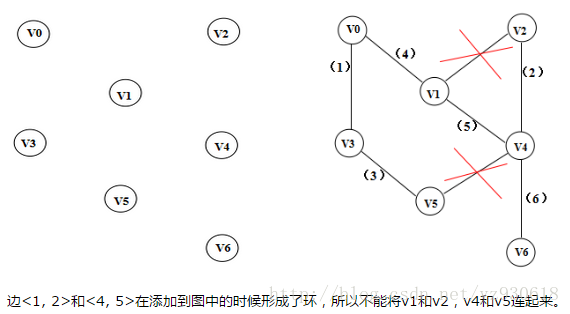
- 将图中的所有边都去掉。
- 将边按权值从小到大的顺序添加到图中,保证添加的过程中不会形成环
- 重复上一步直到连接所有顶点,此时就生成了最小生成树。
克鲁斯卡尔算法图解如下:
克鲁斯卡尔算法实现
下面是利用Java实现的克鲁斯卡尔算法。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 最小生成树:克鲁斯卡尔算法
*/
public class MinSpanTree {
int[][] arc; // 邻接矩阵
int MAXVEX; // 顶点个数
List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>(); // 边集数组
int[] parent; // 用于判断边与边是否形成回路
public MinSpanTree(){
createArc(9); //生成邻接矩阵
createEdge(9); //生成边集数组
createParent(9); //生成parent数组
}
//生成parent数组
private void createParent(int i) {
parent = new int[MAXVEX];
}
// 生成边集数组
private void createEdge(int i) {
Edge v0 = new Edge(4,7,7);
Edge v1 = new Edge(2,8,8);
Edge v2 = new Edge(0,1,10);
Edge v3 = new Edge(0,5,11);
Edge v4 = new Edge(1,8,12);
Edge v5 = new Edge(3,7,16);
Edge v6 = new Edge(1,6,16);
Edge v7 = new Edge(5,6,17);
Edge v8 = new Edge(1,2,18);
Edge v9 = new Edge(6,7,19);
Edge v10 = new Edge(3,4,20);
Edge v11 = new Edge(3,8,21);
Edge v12 = new Edge(2,3,22);
Edge v13 = new Edge(3,6,24);
Edge v14 = new Edge(4,5,26);
this.edges.add(v0);
this.edges.add(v1);
this.edges.add(v2);
this.edges.add(v3);
this.edges.add(v4);
this.edges.add(v5);
this.edges.add(v6);
this.edges.add(v7);
this.edges.add(v8);
this.edges.add(v9);
this.edges.add(v10);
this.edges.add(v11);
this.edges.add(v12);
this.edges.add(v13);
this.edges.add(v14);
}
// 生成邻接矩阵
private void createArc(int index) {
MAXVEX = index;
arc = new int[index][index];
this.arc[0] = new int[]{ 0, 10,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 11,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX};
this.arc[1] = new int[]{ 10, 0, 18,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 16,MAXVEX, 12};
this.arc[2] = new int[]{MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 0, 22,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 8};
this.arc[3] = new int[]{MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 22, 0, 20,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 16, 21};
this.arc[4] = new int[]{MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 20, 0, 26,MAXVEX, 7,MAXVEX};
this.arc[5] = new int[]{ 11,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 26, 0, 17,MAXVEX,MAXVEX};
this.arc[6] = new int[]{MAXVEX, 16,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 17, 0, 19,MAXVEX};
this.arc[7] = new int[]{MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 16, 7,MAXVEX, 19, 0,MAXVEX};
this.arc[8] = new int[]{MAXVEX, 12, 8, 21,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX,MAXVEX, 0};
}
/**
* 克鲁斯卡尔实现最小生成树
*/
public void kruskal(){
int i,n,m;
int count = 0;
for(i = 0;i < this.edges.size();i++){//遍历每一条边
int begin = this.edges.get(i).getBegin();
int end = this.edges.get(i).getEnd();
n = this.find(begin);
m = this.find(end);
if(n != m) {//如果n不等于m,则说明没有形成回路
count++;
parent[n] = m; //将此边的尾结点放入parent数组中,数组的下标表示头结点。parent[n] = m表示此顶点已经在生成树中
System.out.println(" 第 "+count+" 条边为 : ( "+this.edges.get(i).getBegin()+" , "+ this.edges.get(i).getEnd() +" ) = "+this.edges.get(i).getWeight()+" ");
}
}
}
//查找连接顶点的尾部下标
public int find(int f){
while(this.parent[f] > 0){
f = this.parent[f];
}
return f;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MinSpanTree kruskal = new MinSpanTree();
kruskal.kruskal();
}
}边的实体类:
public class Edge {
private int begin; // 边的起点
private int end; // 边的终点
int weight; // 边的权重
public Edge(int begin, int end, int weight) {
this.begin = begin;
this.end = end;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getBegin() {
return begin;
}
public void setBegin(int begin) {
this.begin = begin;
}
public int getEnd() {
return end;
}
public void setEnd(int end) {
this.end = end;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
}运行结果如下























 1224
1224

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








