ArrayDeque是一个双端队列,它是线程不安全的,不能插入null元素,当使用栈时比Stack要快,当使用队列时比LinkedList要快。
先初始化一个一定大小的数组,大小是2的n次方,接下来看下添加的源码。
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
//head ,和tail开始都是0,当下次再相同时,说明数组满了,需要扩展了
if (head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1),当第一次添加时head变成数组的最后一个元素,以后每次减一。
添加一个元素后的图如下
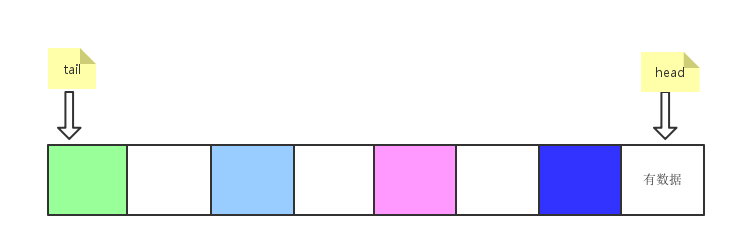
接下来看扩容的源码
private void doubleCapacity() {
assert head == tail;
int p = head;
int n = elements.length;
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
int newCapacity = n << 1;
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
elements = (E[])a;
head = 0;
tail = n;
}将老数组复制到新的数组中,
接下来看addLast
public void addLast(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[tail] = e;
//保证tail正向增长
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}pollFirst()返回第一个元素,并删除
public E pollFirst() {
int h = head;
E result = elements[h]; // Element is null if deque empty
if (result == null)
return null;
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
//将head增长一个,如果没元素就是0
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}其它的几个增删就和上面的几个方法类似,我就不再写了。
说说ArrayDeque和Stack和LindedList的对比
Stack是继承的vector里面很多方法都是同步的,所以比ArrayDeque慢,而且有很多vector的方法。LindedList作为队列在增加和删除的时候需要移动指针,需要再开辟空间。ArrayDeque很多时候不需要从扩大,这也是ArrayDeque性能较好的原因吧。

























 373
373

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










