操作BLOB类型字段
MySQL BLOB类型
在MySQL中,BLOB是一个二进制大型对象,是一个可以存储大量数据的容器。之前我们讲了PreparedStatement与Statement的区别,其实这里也算一点,就是插入BLOB类型的数据必须使用PreparedStatement,因为BLOB类型的数据无法使用字符串拼接写的。MySQL中的四种BLOB类型如下:

插入BLOB类型示例
现在有如下表,需向其中插入一组数据(’张国荣‘,18,对应图片)。对于大数据的插入操作,我们可以使用IO流操作进行传输。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class PreparedStatementBlob {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection c = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
FileInputStream is = null;
try {
c = MyUnit.getConnection();
String sql = " insert into star(name,age,photo) values(?,?,?)";
ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, "张国荣");
ps.setObject(2, 18);
is = new FileInputStream(new File("lib/gege.jpeg"));
ps.setBlob(3, is);
ps.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
MyUnit.closeResource(c, ps);
}
}
}
查询BLOB类型示例
对刚才插入到star数据库中的图片下载到本地。
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
public class PreparedStatementBlob2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection c = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
InputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
c = MyUnit.getConnection();
String sql = " select photo from star where name = ?";
ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,"张国荣");
resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
while(resultSet.next()){
Blob blob = resultSet.getBlob(1);
is = blob.getBinaryStream();
fos = new FileOutputStream("lib/zhangguorong.jpeg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(is != null)
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(fos != null)
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
MyUnit.closeResource(c,ps,resultSet);
}
}
}
注:虽然在数据库中我们用了MediumBlob类型,大小为16M,但是如果我们存入大于1M的数据时,就会出现异常,这个时候需要在mysql的安装目录下找到my.int文件,加配置参数:max_allowed_packet=16M,然后重启mysql服务。
批量插入
实现方式一:
对于批量插入操作,我们也可以使用Statement,但是很容易想到的是使用它就会存在每次插入都要经过语法检查、语义检查,执行sql语句,然后一条一条执行,那么在大量数据插入的时候就会暴露出效率非常低,所以我们还是直接使用PreparedStatement来实现。
题目:对下图的表进行20000条数据插入。
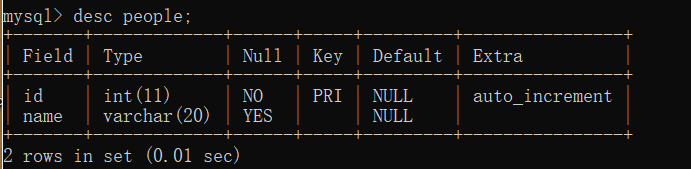
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class BigInsert1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection c = MyUnit.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into people(name) values(?)";
PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0;i < 20000;i++){
ps.setString(1,"name_"+i);
ps.execute();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-begin);
MyUnit.closeResource(c,ps);
}
}
执行结果:

实现方式二:
对于上一种方式,虽然速度也不算慢,但是我们还是可以再提高的。当我们使用IO流的时候,为了调高效率,我们使用到了缓存,那么这里也同样如此。JDBC的批量处理语句包括下面三个方法:
- addBatch(String):添加需要批量处理的SQL语句或是参数;
- executeBatch():执行批量处理语句
- clearBatch():清空缓存的数据
注:mysql服务器默认是关闭批处理的,我们需要通过一个参数让mysql开启批处理的支持。在配置url后面,我们需要加rewriteBatchedStatements=true,如果之前就有参数,那就用"&“来连接,如果没有,直接在数据库名后面加则需要用”?"来连接。
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class BigInsert2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection c = MyUnit.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into people(name) values(?)";
PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 1;i <= 1000000;i++){
ps.setString(1,"name_"+i);
ps.addBatch();
if(i % 500 == 0){
ps.executeBatch();
ps.clearBatch();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - begin);
MyUnit.closeResource(c,ps);
}
}
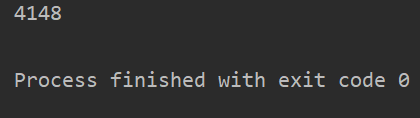
执行结果:
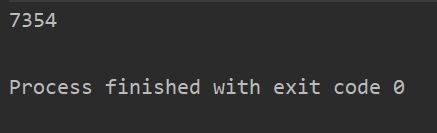
可以看到,在数据量为方式一五倍的情况下,用时却是方式一的三分之一,效率提高了很多。
实现方式三:
之前我们在学事务时,第一步操作就是将mysql的自动提交给关掉,那么我们可以想到,每次执行完一次缓存的数据,就主动提交一次,是不是又会浪费一些时间呢?那是不是可以通过控制自动提交来使效率提高呢?是的!
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class BigInsert3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Connection c = MyUnit.getConnection();
//设置为不自动提交数据
c.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "insert into people(name) values(?)";
PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 1;i <= 1000000;i++){
ps.setString(1,"name_"+i);
//"攒"sql
ps.addBatch();
if(i % 500 == 0){
//执行
ps.executeBatch();
//清空
ps.clearBatch();
}
}
//提交数据
c.commit();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - begin);
MyUnit.closeResource(c,ps);
}
}
执行结果:























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








