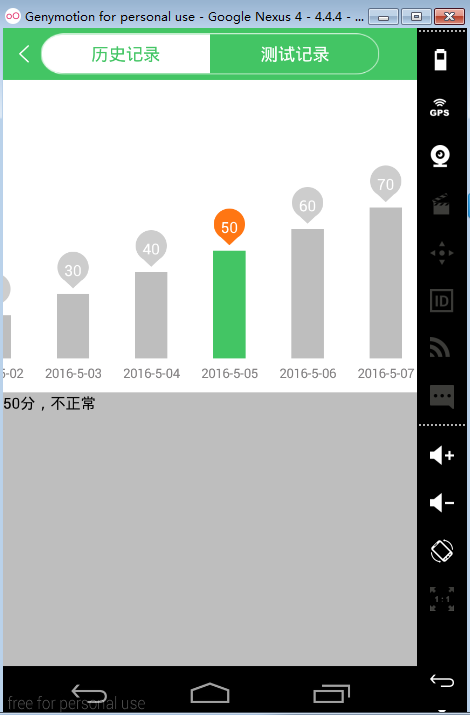
有个爱折腾的美工是个什么体验。。。那就是效果,也是,android也就是个UI,UI注重的是用户体验,良好的用户体验跟舒适的UI效果是分不开的。这次要做的效果就是,做完测试后提交的历史记录,以柱状图的形式呈现,那么把这个父布局设置成HorizontalScrollView,把树状图的滚动效果交给HorizontalScrollView,那么问题来了,HorizontalScrollView只能有一个子布局,那么就在这里面嵌套一层最好用的LinearLayout,把它的子布局方向设置成horizontal水平,然后把一个个子View创建出来,add进来就可以了。其中的难点就是嵌套了3层,如何获取子view,并监听它们了。。。不难,看完真的就好简单了。。。
1、按照我们的思路,我们写好xml文件
act_historytest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<HorizontalScrollView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:scrollbars="none" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/id_history"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="top"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
</LinearLayout>
</HorizontalScrollView>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/grey" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/situation_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="分数对应您的健康状况"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:textSize="14sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
historyresult_item.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="290dp"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:padding="10dp" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/his_date"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:text="2014.1.5"
android:textSize="12sp" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/his_length"
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="170dp"
android:layout_above="@id/his_date"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="@color/grey" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/his_count"
android:layout_above="@id/his_length"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:background="@drawable/noselect_result"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="32"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
android:textSize="14sp" />
</RelativeLayout>2、那么问题来了,到我们的java文件看看
ChartFragment.java文件代码如下
package com.example.chartdemo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.example.chartdemo.R.color;
import com.example.chartdemo.R.drawable;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.util.SparseArray;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ChartFragment extends Fragment implements OnClickListener {
private View view;
private LinearLayout mGallery;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
private TextView main_content;
private List<Integer> count; // 分数
private List<String> times; // 日期
private SparseArray<String> mySparse;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater,
@Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 动态加载布局
view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.act_historytest, container, false);
return view;
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
initView();
initData();
setOnListener();
}
private void setOnListener() {
if (mInflater == null)
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(getActivity());
for (int i = 0; i < count.size(); i++) {
View view = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.historyresult_item,
mGallery, false);
ImageView img = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.his_length);
// 获取图片的大小,自定义设置图片的高度
LayoutParams params = img.getLayoutParams();
params.height = count.get(i) * 4;
img.setLayoutParams(params);
TextView txt = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.his_date);
TextView txtdate = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.his_count);
txt.setText(times.get(i).toString());
txtdate.setText(String.valueOf(count.get(i)));
view.setId(i);// 设定view的id,把i设置成当前View的id
view.setOnClickListener(this);//每一个子项目注册监听事件
if (i == 0) {
// 默认选中第一个
img.setBackgroundResource(color.btn_login);
txtdate.setBackgroundResource(drawable.select_result);
txtdate.setTextColor(color.black);
}
mGallery.addView(view);
}
}
private void initData() {
// 测试数据
mySparse = new SparseArray<String>();
count = new ArrayList<Integer>();
times = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 10; i <= 90; i += 10) {
mySparse.put(i, "2016-5-0" + i / 10);
count.add(i);
times.add("2016-5-0" + i / 10);
}
}
private void initView() {
mGallery = (LinearLayout) view.findViewById(R.id.id_history);
main_content = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.situation_content);
}
/*注意这里的mGallery是我们把自定义好的view后一个个add进来的
*view容器,mGallery.getChildAt(v.getId()),刚好是以位置
*进行排序add进来的,这里获取的id也就是上面的i
*/
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 至于这里为什么要用for循环的话。。。额,那就是是要做刷新,刷新整个视图
for (int i = 0; i < mGallery.getChildCount(); i++) {
if (v.getId() == i) {
// 获取点击的子视图
TextView txtdate = (TextView) mGallery.getChildAt(v.getId())
.findViewById(R.id.his_date);
TextView txtcount = (TextView) mGallery.getChildAt(v.getId())
.findViewById(R.id.his_count);
ImageView img = (ImageView) mGallery.getChildAt(v.getId())
.findViewById(R.id.his_length);
img.setBackgroundResource(color.btn_login);
txtcount.setBackgroundResource(drawable.select_result);
txtdate.setTextColor(color.black);
int count = Integer.parseInt(txtcount.getText().toString());
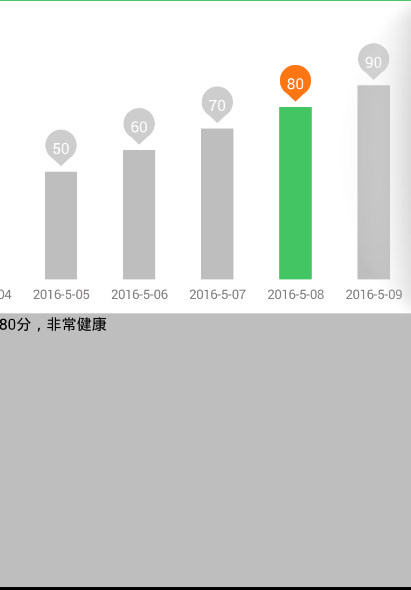
if (count >= 80) {
main_content.setText(count + "分,非常健康");
} else if (count >= 60) {
main_content.setText(count + "分,正常");
} else {
main_content.setText(count + "分,不正常");
}
} else {
// 获取未点击的视图
TextView txtdate = (TextView) mGallery.getChildAt(i)
.findViewById(R.id.his_date);
TextView txtcount = (TextView) mGallery.getChildAt(i)
.findViewById(R.id.his_count);
ImageView img = (ImageView) mGallery.getChildAt(i)
.findViewById(R.id.his_length);
img.setBackgroundResource(color.grey);
txtcount.setBackgroundResource(drawable.noselect_result);
txtdate.setTextColor(color.white);
}
}
}
}
3、然后就实现好了,然后同时,美工又默默地加了分页效果,我特么。。。还是忍了。那么我们就用fragment吧,常说的碎片,最后在外面包裹一层Activity。。。
MainActivity.java中的代码
package com.example.chartdemo;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.view.Window;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.RadioGroup;
import android.widget.RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
private RadioGroup radTab;
// 将fragment初始化为数组便于管理
Fragment[] fragmentGroup = { new ChartFragment(), new ListFragment() };
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.act_testrecord);
initView();
initData();
setonListener();
}
private void setonListener() {
// 点击switch更换界面
radTab.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
switch (checkedId) {
case R.id.rb_left:
setFragment(0);
break;
case R.id.rb_right:
setFragment(1);
break;
}
}
});
}
private void initData() {
setFragment(0);// 默认在左边
}
private void initView() {
radTab = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.rgb_switch);
}
// 显示选中的fragment
private void setFragment(int showId) {
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.record_content, fragmentGroup[showId]).commit();
}
}
4、看下另一边的listview,主要考量的就是圆角效果(corners),虚线效果(line),描边效果(stroke),实心效果(solid),也就是人们常说的用shape.xml文件对视图进行美化
最主要的就是那个虚线效果了。。。不百度,真不清楚,还要关闭硬件加速才能显示。。。
shape_line.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="line" >
<stroke
android:dashGap="3dp"
android:dashWidth="3dp"
android:width="1dp"
android:color="@color/gray" />
<size android:height="2dp" />
</shape>上代码:
ListFragment.java
package com.example.chartdemo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
public class ListFragment extends Fragment {
private View view;
private ListView testListView;
@Override
@Nullable
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater,
@Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.act_historyverication, container,
false);
// 关闭activity的硬件加速功能,为了显示虚线
view.setLayerType(View.LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
return view;
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
initView();
initData();
setListener();
}
private void setListener() {
}
private void initData() {
List<String> testL = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
testL.add(i + "");
}
testListView.setAdapter(new testAdapter(getActivity(),
R.layout.historyverication_item, testL));
}
private void initView() {
testListView = (ListView) view.findViewById(R.id.lvverication);
}
}
然后我觉得这个功能比较容易拓展的功能有产品列表,附图。利用了HorizontalScrollView可以很容易实现
最后,总结下,其实我有偷懒的地方,就是标头那个切换其实是使用了xml文件中的selector进行图片的切换,其实我第一反应是用tabHost的。。。但是无奈碎片横行啊,fragment的使用。然后就是我年轻不懂事,没用android自带的图表类库,其实实现的方式挺简单的,也很符合正常的逻辑。。。纯手工,我给自己点赞
最后附上demo下载源码:http://download.csdn.net/detail/z_zt_t/9560642























 986
986

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








