一、背景
在本打算写一篇关于Identityserver4 的文章时候,却发现自己对EndPoint -终结点路由还不是很了解,故暂时先放弃了IdentityServer4 的研究和编写;所以才产生了今天这篇关于EndPoint (终结点路由) 的文章。
还是跟往常一样,打开电脑使用强大的Google 和百度搜索引擎查阅相关资料,以及打开Asp.net core 3.1 的源代码进行拜读,同时终于在我的实践及测试中对EndPoint 有了不一样的认识,说到这里更加敬佩微软对Asp.net core 3.x 的框架中管道模型的设计。
我先来提出以下几个问题:
1.当访问一个Web 应用地址时,Asp.Net Core 是怎么执行到Controller 的Action的呢?
2.Endpoint 跟普通路由又存在着什么样的关系?
3.UseRouing() 、UseAuthorization()、UserEndpoints() 这三个中间件的关系是什么呢?
4.怎么利用Endpoint 编写自己的中间件以及Endpoint 的应用场景(时间有限,下回分享整理)
二、拜读源码解惑
Startup 代码
我们先来看一下Startup中简化版的代码,代码如下:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
}程序启动阶段:
•第一步:执行services.AddControllers() 将Controller的核心服务注册到容器中去
•第二步:执行app.UseRouting() 将EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件注册到http管道中
•第三步:执行app.UseAuthorization() 将AuthorizationMiddleware中间件注册到http管道中
•第四步:执行app.UseEndpoints(encpoints=>endpoints.MapControllers()) 有两个主要的作用:调用endpoints.MapControllers()将本程序集定义的所有Controller和Action转换为一个个的EndPoint放到路由中间件的配置对象RouteOptions中 将EndpointMiddleware中间件注册到http管道中
app.UseRouting() 源代码如下:
public static IApplicationBuilder UseRouting(this IApplicationBuilder builder)
{
if (builder == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder));
}
VerifyRoutingServicesAreRegistered(builder);
var endpointRouteBuilder = new DefaultEndpointRouteBuilder(builder);
builder.Properties[EndpointRouteBuilder] = endpointRouteBuilder;
return builder.UseMiddleware<EndpointRoutingMiddleware>(endpointRouteBuilder);
}EndpointRoutingMiddleware 中间件代码如下:
internal sealed class EndpointRoutingMiddleware
{
private const string DiagnosticsEndpointMatchedKey = "Microsoft.AspNetCore.Routing.EndpointMatched";
private readonly MatcherFactory _matcherFactory;
private readonly ILogger _logger;
private readonly EndpointDataSource _endpointDataSource;
private readonly DiagnosticListener _diagnosticListener;
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private Task<Matcher> _initializationTask;
public EndpointRoutingMiddleware(
MatcherFactory matcherFactory,
ILogger<EndpointRoutingMiddleware> logger,
IEndpointRouteBuilder endpointRouteBuilder,
DiagnosticListener diagnosticListener,
RequestDelegate next)
{
if (endpointRouteBuilder == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(endpointRouteBuilder));
}
_matcherFactory = matcherFactory ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(matcherFactory));
_logger = logger ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(logger));
_diagnosticListener = diagnosticListener ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(diagnosticListener));
_next = next ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(next));
_endpointDataSource = new CompositeEndpointDataSource(endpointRouteBuilder.DataSources);
}
public Task Invoke(HttpContext httpContext)
{
// There's already an endpoint, skip maching completely
var endpoint = httpContext.GetEndpoint();
if (endpoint != null)
{
Log.MatchSkipped(_logger, endpoint);
return _next(httpContext);
}
// There's an inherent race condition between waiting for init and accessing the matcher
// this is OK because once `_matcher` is initialized, it will not be set to null again.
var matcherTask = InitializeAsync();
if (!matcherTask.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
return AwaitMatcher(this, httpContext, matcherTask);
}
var matchTask = matcherTask.Result.MatchAsync(httpContext);
if (!matchTask.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
return AwaitMatch(this, httpContext, matchTask);
}
return SetRoutingAndContinue(httpContext);
// Awaited fallbacks for when the Tasks do not synchronously complete
static async Task AwaitMatcher(EndpointRoutingMiddleware middleware, HttpContext httpContext, Task<Matcher> matcherTask)
{
var matcher = await matcherTask;
await matcher.MatchAsync(httpContext);
await middleware.SetRoutingAndContinue(httpContext);
}
static async Task AwaitMatch(EndpointRoutingMiddleware middleware, HttpContext httpContext, Task matchTask)
{
await matchTask;
await middleware.SetRoutingAndContinue(httpContext);
}
}
[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)]
private Task SetRoutingAndContinue(HttpContext httpContext)
{
// If there was no mutation of the endpoint then log failure
var endpoint = httpContext.GetEndpoint();
if (endpoint == null)
{
Log.MatchFailure(_logger);
}
else
{
// Raise an event if the route matched
if (_diagnosticListener.IsEnabled() && _diagnosticListener.IsEnabled(DiagnosticsEndpointMatchedKey))
{
// We're just going to send the HttpContext since it has all of the relevant information
_diagnosticListener.Write(DiagnosticsEndpointMatchedKey, httpContext);
}
Log.MatchSuccess(_logger, endpoint);
}
return _next(httpContext);
}
// Initialization is async to avoid blocking threads while reflection and things
// of that nature take place.
//
// We've seen cases where startup is very slow if we allow multiple threads to race
// while initializing the set of endpoints/routes. Doing CPU intensive work is a
// blocking operation if you have a low core count and enough work to do.
private Task<Matcher> InitializeAsync()
{
var initializationTask = _initializationTask;
if (initializationTask != null)
{
return initializationTask;
}
return InitializeCoreAsync();
}
private Task<Matcher> InitializeCoreAsync()
{
var initialization = new TaskCompletionSource<Matcher>(TaskCreationOptions.RunContinuationsAsynchronously);
var initializationTask = Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref _initializationTask, initialization.Task, null);
if (initializationTask != null)
{
// This thread lost the race, join the existing task.
return initializationTask;
}
// This thread won the race, do the initialization.
try
{
var matcher = _matcherFactory.CreateMatcher(_endpointDataSource);
// Now replace the initialization task with one created with the default execution context.
// This is important because capturing the execution context will leak memory in ASP.NET Core.
using (ExecutionContext.SuppressFlow())
{
_initializationTask = Task.FromResult(matcher);
}
// Complete the task, this will unblock any requests that came in while initializing.
initialization.SetResult(matcher);
return initialization.Task;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Allow initialization to occur again. Since DataSources can change, it's possible
// for the developer to correct the data causing the failure.
_initializationTask = null;
// Complete the task, this will throw for any requests that came in while initializing.
initialization.SetException(ex);
return initialization.Task;
}
}
private static class Log
{
private static readonly Action<ILogger, string, Exception> _matchSuccess = LoggerMessage.Define<string>(
LogLevel.Debug,
new EventId(1, "MatchSuccess"),
"Request matched endpoint '{EndpointName}'");
private static readonly Action<ILogger, Exception> _matchFailure = LoggerMessage.Define(
LogLevel.Debug,
new EventId(2, "MatchFailure"),
"Request did not match any endpoints");
private static readonly Action<ILogger, string, Exception> _matchingSkipped = LoggerMessage.Define<string>(
LogLevel.Debug,
new EventId(3, "MatchingSkipped"),
"Endpoint '{EndpointName}' already set, skipping route matching.");
public static void MatchSuccess(ILogger logger, Endpoint endpoint)
{
_matchSuccess(logger, endpoint.DisplayName, null);
}
public static void MatchFailure(ILogger logger)
{
_matchFailure(logger, null);
}
public static void MatchSkipped(ILogger logger, Endpoint endpoint)
{
_matchingSkipped(logger, endpoint.DisplayName, null);
}
}
}我们从它的源码中可以看到,EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件先是创建matcher,然后调用matcher.MatchAsync(httpContext)去寻找Endpoint,最后通过httpContext.GetEndpoint()验证了是否已经匹配到了正确的Endpoint并交个下个中间件继续执行!
app.UseEndpoints() 源代码
public static IApplicationBuilder UseEndpoints(this IApplicationBuilder builder, Action<IEndpointRouteBuilder> configure)
{
if (builder == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder));
}
if (configure == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(configure));
}
VerifyRoutingServicesAreRegistered(builder);
VerifyEndpointRoutingMiddlewareIsRegistered(builder, out var endpointRouteBuilder);
configure(endpointRouteBuilder);
// Yes, this mutates an IOptions. We're registering data sources in a global collection which
// can be used for discovery of endpoints or URL generation.
//
// Each middleware gets its own collection of data sources, and all of those data sources also
// get added to a global collection.
var routeOptions = builder.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<IOptions<RouteOptions>>();
foreach (var dataSource in endpointRouteBuilder.DataSources)
{
routeOptions.Value.EndpointDataSources.Add(dataSource);
}
return builder.UseMiddleware<EndpointMiddleware>();
}
internal class DefaultEndpointRouteBuilder : IEndpointRouteBuilder
{
public DefaultEndpointRouteBuilder(IApplicationBuilder applicationBuilder)
{
ApplicationBuilder = applicationBuilder ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(applicationBuilder));
DataSources = new List<EndpointDataSource>();
}
public IApplicationBuilder ApplicationBuilder { get; }
public IApplicationBuilder CreateApplicationBuilder() => ApplicationBuilder.New();
public ICollection<EndpointDataSource> DataSources { get; }
public IServiceProvider ServiceProvider => ApplicationBuilder.ApplicationServices;
}代码中构建了DefaultEndpointRouteBuilder 终结点路由构建者对象,该对象中存储了Endpoint的集合数据;同时把终结者路由集合数据存储在了routeOptions 中,并注册了EndpointMiddleware 中间件到http管道中; Endpoint对象代码如下:
/// <summary>
/// Represents a logical endpoint in an application.
/// </summary>
public class Endpoint
{
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new instance of <see cref="Endpoint"/>.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="requestDelegate">The delegate used to process requests for the endpoint.</param>
/// <param name="metadata">
/// The endpoint <see cref="EndpointMetadataCollection"/>. May be null.
/// </param>
/// <param name="displayName">
/// The informational display name of the endpoint. May be null.
/// </param>
public Endpoint(
RequestDelegate requestDelegate,
EndpointMetadataCollection metadata,
string displayName)
{
// All are allowed to be null
RequestDelegate = requestDelegate;
Metadata = metadata ?? EndpointMetadataCollection.Empty;
DisplayName = displayName;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the informational display name of this endpoint.
/// </summary>
public string DisplayName { get; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets the collection of metadata associated with this endpoint.
/// </summary>
public EndpointMetadataCollection Metadata { get; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets the delegate used to process requests for the endpoint.
/// </summary>
public RequestDelegate RequestDelegate { get; }
public override string ToString() => DisplayName ?? base.ToString();
}Endpoint 对象代码中有两个关键类型属性分别是EndpointMetadataCollection 类型和RequestDelegate:
•EndpointMetadataCollection:存储了Controller 和Action相关的元素集合,包含Action 上的Attribute 特性数据等
•RequestDelegate :存储了Action 也即委托,这里是每一个Controller 的Action 方法
再回过头来看看EndpointMiddleware 中间件和核心代码,EndpointMiddleware 的一大核心代码主要是执行Endpoint 的RequestDelegate 委托,也即Controller 中的Action 的执行。
public Task Invoke(HttpContext httpContext)
{
var endpoint = httpContext.GetEndpoint();
if (endpoint?.RequestDelegate != null)
{
if (!_routeOptions.SuppressCheckForUnhandledSecurityMetadata)
{
if (endpoint.Metadata.GetMetadata<IAuthorizeData>() != null &&
!httpContext.Items.ContainsKey(AuthorizationMiddlewareInvokedKey))
{
ThrowMissingAuthMiddlewareException(endpoint);
}
if (endpoint.Metadata.GetMetadata<ICorsMetadata>() != null &&
!httpContext.Items.ContainsKey(CorsMiddlewareInvokedKey))
{
ThrowMissingCorsMiddlewareException(endpoint);
}
}
Log.ExecutingEndpoint(_logger, endpoint);
try
{
var requestTask = endpoint.RequestDelegate(httpContext);
if (!requestTask.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
return AwaitRequestTask(endpoint, requestTask, _logger);
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
Log.ExecutedEndpoint(_logger, endpoint);
return Task.FromException(exception);
}
Log.ExecutedEndpoint(_logger, endpoint);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
return _next(httpContext);
static async Task AwaitRequestTask(Endpoint endpoint, Task requestTask, ILogger logger)
{
try
{
await requestTask;
}
finally
{
Log.ExecutedEndpoint(logger, endpoint);
}
}
}疑惑解答:
1. 当访问一个Web 应用地址时,Asp.Net Core 是怎么执行到Controller 的Action的呢?
答:程序启动的时候会把所有的Controller 中的Action 映射存储到routeOptions 的集合中,Action 映射成Endpoint终结者 的RequestDelegate 委托属性,最后通过UseEndPoints 添加EndpointMiddleware 中间件进行执行,同时这个中间件中的Endpoint 终结者路由已经是通过Routing匹配后的路由。
2. EndPoint 跟普通路由又存在着什么样的关系?
答:Ednpoint 终结者路由是普通路由map 转换后的委托路由,里面包含了路由方法的所有元素信息EndpointMetadataCollection 和RequestDelegate 委托。
3. UseRouting() 、UseAuthorization()、UseEndpoints() 这三个中间件的关系是什么呢?
答:UseRouting 中间件主要是路由匹配,找到匹配的终结者路由Endpoint ;UseEndpoints 中间件主要针对UseRouting 中间件匹配到的路由进行 委托方法的执行等操作。 UseAuthorization 中间件主要针对 UseRouting 中间件中匹配到的路由进行拦截 做授权验证操作等,通过则执行下一个中间件UseEndpoints(),具体的关系可以看下面的流程图:
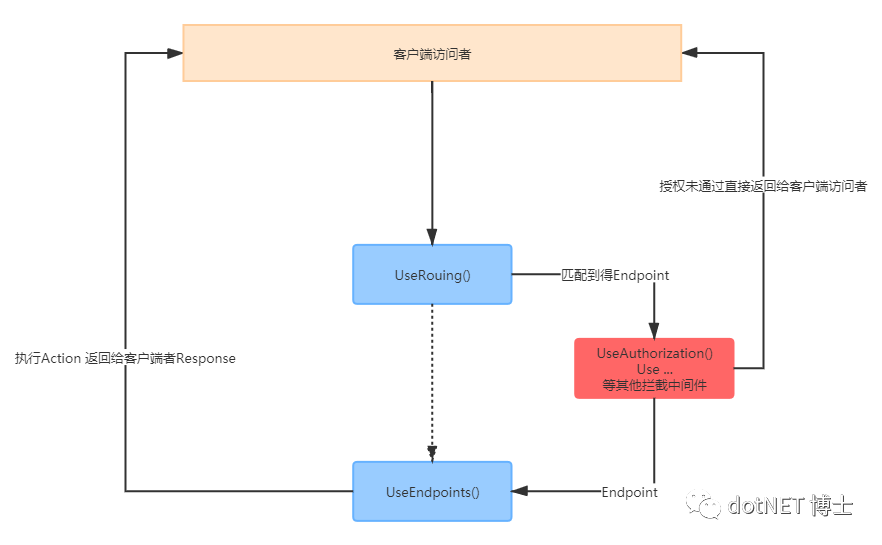
上面流程图中省略了一些部分,主要是把UseRouting 、UseAuthorization 、UseEndpoint 这三个中间件的关系突显出来。
转载自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/N_JsWwgTo4DIXHMUA9gM3Q
补充图1
The ASP.NET Core request pipeline consists of a sequence of request delegates, called one after the other. The following diagram demonstrates the concept. The thread of execution follows the black arrows.
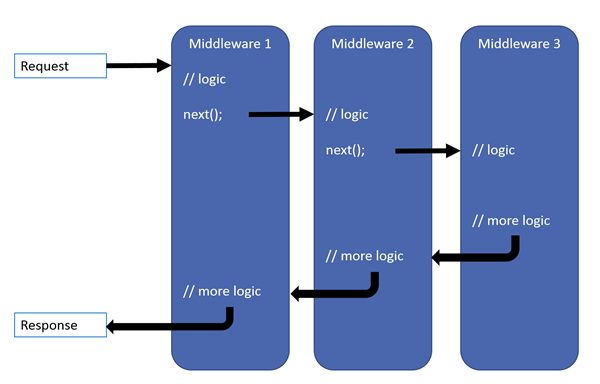
Each delegate can perform operations before and after the next delegate. Exception-handling delegates should be called early in the pipeline, so they can catch exceptions that occur in later stages of the pipeline.
补充图2
The following diagram shows the complete request processing pipeline for ASP.NET Core MVC and Razor Pages apps. You can see how, in a typical app, existing middlewares are ordered and where custom middlewares are added. You have full control over how to reorder existing middlewares or inject new custom middlewares as necessary for your scenarios.
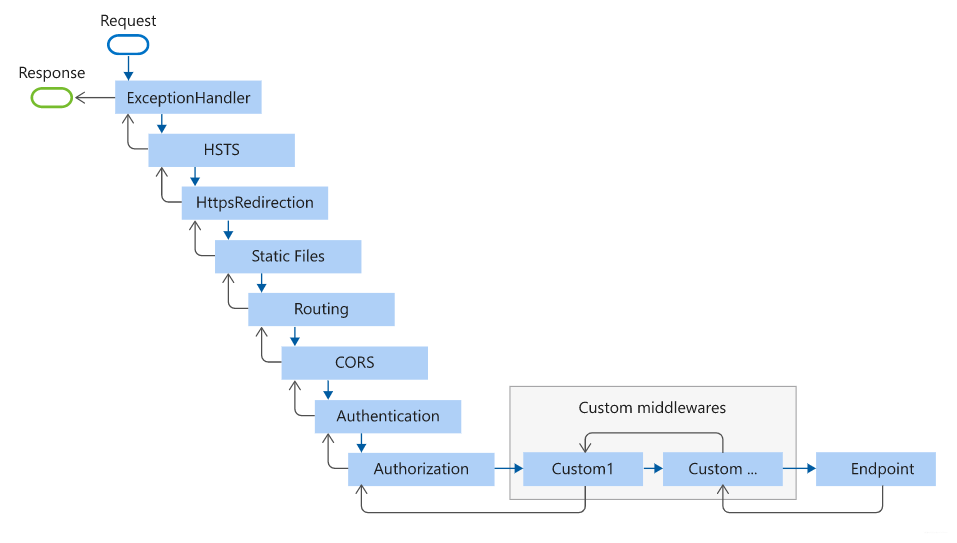
The Endpoint middleware in the preceding diagram executes the filter pipeline for the corresponding app type—MVC or Razor Pages.
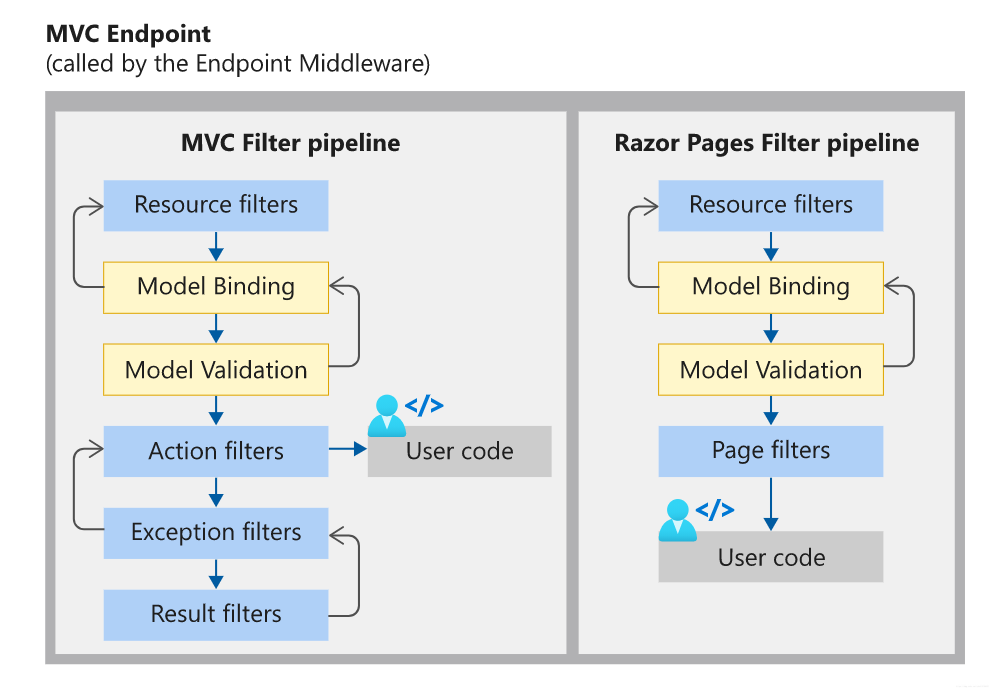
The order that middleware components are added in the
Startup.Configuremethod defines the order in which the middleware components are invoked on requests and the reverse order for the response. The order is critical for security, performance, and functionality.
参考:





















 1477
1477











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








