ViewModel是Jetpack框架集合中不可或缺的重要库之一,替我们管理着项目框架中的数据,相当于一个LiveData的数据总管一样。
它将视图与数据分离,对数据进行管理,当应用横竖屏切换时,不再需要考虑数据的存储与恢复。
ViewModel的源码分析主要分为两步:对象的创建和销毁。
一,ViewModel的创建过程
1,先创建一个ViewModel的类如下
class HomeViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val _text = MutableLiveData<String>().apply {
value = "This is home Fragment"
}
val text: LiveData<String> = _text
}
2,创建ViewModel对象
val homeViewModel = ViewModelProvider(this).get(HomeViewModel::class.java)
这是官方指定的一种创建方式,见源码
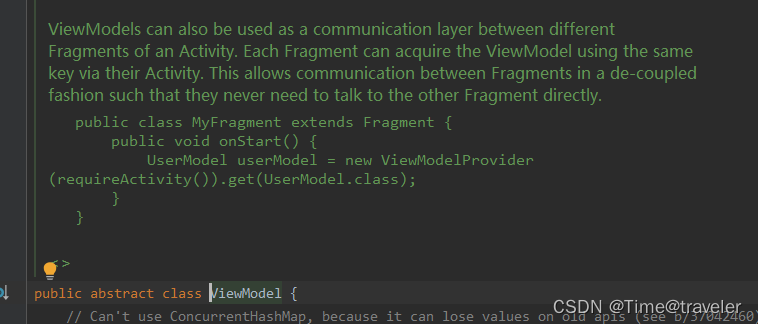
接下来就开始正在进入源码分析环节。
ViewModel对象的创建时,先创建了一个ViewModelProvider对象,并传入了当前上下文,然后再调用了它的get函数,传入了ViewModel的类
3,进入ViewModelProvider的构造函数,源码如下:
/**
* Creates {@code ViewModelProvider}. This will create {@code ViewModels}
* and retain them in a store of the given {@code ViewModelStoreOwner}.
* <p>
* This method will use the
* {@link HasDefaultViewModelProviderFactory#getDefaultViewModelProviderFactory() default factory}
* if the owner implements {@link HasDefaultViewModelProviderFactory}. Otherwise, a
* {@link NewInstanceFactory} will be used.
*/
public ViewModelProvider(@NonNull ViewModelStoreOwner owner) {
this(owner.getViewModelStore(), owner instanceof HasDefaultViewModelProviderFactory
? ((HasDefaultViewModelProviderFactory) owner).getDefaultViewModelProviderFactory()
: NewInstanceFactory.getInstance());
}
根据源码可知,构造函数中传入了一个ViewModelStoreOwner对象,我们进入ViewModelStoreOwner文件,发现它是一个接口,如下:
public interface ViewModelStoreOwner {
/**
* Returns owned {@link ViewModelStore}
*
* @return a {@code ViewModelStore}
*/
@NonNull
ViewModelStore getViewModelStore();
}
既然创建时是在Activity中传入的this,那Activity肯定是实现了ViewModelStoreOwner接口,并实现了getViewModelStore函数。
4,进入ComponentActivity中,可以看到它实现了ViewModelStoreOwner接口
public class ComponentActivity extends androidx.core.app.ComponentActivity implements
ContextAware,
LifecycleOwner,
//核心接口
ViewModelStoreOwner,
//ViewModel的创建工厂接口
HasDefaultViewModelProviderFactory,
SavedStateRegistryOwner,
OnBackPressedDispatcherOwner,
ActivityResultRegistryOwner,
ActivityResultCaller {
......
}
在第三步中创建ViewModelProvider对象时会调用owner.getViewModelStore()函数,并判断owner 是否是 HasDefaultViewModelProviderFactory类型的。
5,进入getViewModelStore函数
它调用的是ComponentActivity的getViewModelStore中,发现它直接创建了一个ViewModelStore对象并返回
//此处省略若干行
...............
@NonNull
@Override
public ViewModelStore getViewModelStore() {
if (getApplication() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Your activity is not yet attached to the "
+ "Application instance. You can't request ViewModel before onCreate call.");
}
ensureViewModelStore();
return mViewModelStore;
}
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess") /* synthetic access */
void ensureViewModelStore() {
if (mViewModelStore == null) {
//防止重复创建
NonConfigurationInstances nc =
(NonConfigurationInstances) getLastNonConfigurationInstance();
if (nc != null) {
// Restore the ViewModelStore from NonConfigurationInstances
mViewModelStore = nc.viewModelStore;
}
if (mViewModelStore == null) {
mViewModelStore = new ViewModelStore();
}
}
}
6,进入getDefaultViewModelProviderFactory函数,它创建了一个SavedStateViewModelFactory类型的对象并返回
@NonNull
@Override
public ViewModelProvider.Factory getDefaultViewModelProviderFactory() {
if (getApplication() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Your activity is not yet attached to the "
+ "Application instance. You can't request ViewModel before onCreate call.");
}
if (mDefaultFactory == null) {
mDefaultFactory = new SavedStateViewModelFactory(
getApplication(),
this,
getIntent() != null ? getIntent().getExtras() : null);
}
return mDefaultFactory;
}
7,ViewModelProvider的构造函数结束了,接下来就看一下get函数
private static final String DEFAULT_KEY =
"androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider.DefaultKey";
@NonNull
@MainThread
public <T extends ViewModel> T get(@NonNull Class<T> modelClass) {
String canonicalName = modelClass.getCanonicalName();
if (canonicalName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Local and anonymous classes can not be ViewModels");
}
//使用了默认的一个字符串加上类名拼接出一个key
return get(DEFAULT_KEY + ":" + canonicalName, modelClass);
}
@NonNull
@MainThread
public <T extends ViewModel> T get(@NonNull String key, @NonNull Class<T> modelClass) {
//从ViewModelStore中的HashMap中获取,防止重复创建
ViewModel viewModel = mViewModelStore.get(key);
if (modelClass.isInstance(viewModel)) {
//根据ViewModelProvider的构造函数可知,此处的mFactory是SavedStateViewModelFactory类型的(OnRequeryFactory是SavedStateViewModelFactory的父类)
if (mFactory instanceof OnRequeryFactory) {
((OnRequeryFactory) mFactory).onRequery(viewModel);
}
return (T) viewModel;
} else {
//noinspection StatementWithEmptyBody
if (viewModel != null) {
// TODO: log a warning.
}
}
//SavedStateViewModelFactory继承KeyedFactory接口
if (mFactory instanceof KeyedFactory) {
viewModel = ((KeyedFactory) mFactory).create(key, modelClass);
} else {
viewModel = mFactory.create(modelClass);
}
//创建一个ViewModel对象,根据拼接的key存入ViewModelStore中的HashMap中
mViewModelStore.put(key, viewModel);
return (T) viewModel;
}
8,进入SavedStateViewModelFactory中的可知它继承自KeyedFactory,而KeyedFactory又继承了OnRequeryFactory,
public final class SavedStateViewModelFactory extends ViewModelProvider.KeyedFactory {
}
abstract static class KeyedFactory extends OnRequeryFactory implements Factory {
}
查看create函数发现它是通过反射的方式创建了一个ViewModel对象。
@NonNull
@Override
public <T extends ViewModel> T create(@NonNull String key, @NonNull Class<T> modelClass) {
boolean isAndroidViewModel = AndroidViewModel.class.isAssignableFrom(modelClass);
Constructor<T> constructor;
if (isAndroidViewModel && mApplication != null) {
constructor = findMatchingConstructor(modelClass, ANDROID_VIEWMODEL_SIGNATURE);
} else {
constructor = findMatchingConstructor(modelClass, VIEWMODEL_SIGNATURE);
}
// doesn't need SavedStateHandle
if (constructor == null) {
return mFactory.create(modelClass);
}
SavedStateHandleController controller = SavedStateHandleController.create(
mSavedStateRegistry, mLifecycle, key, mDefaultArgs);
try {
T viewmodel;
if (isAndroidViewModel && mApplication != null) {
viewmodel = constructor.newInstance(mApplication, controller.getHandle());
} else {
viewmodel = constructor.newInstance(controller.getHandle());
}
viewmodel.setTagIfAbsent(TAG_SAVED_STATE_HANDLE_CONTROLLER, controller);
return viewmodel;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to access " + modelClass, e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("A " + modelClass + " cannot be instantiated.", e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An exception happened in constructor of "
+ modelClass, e.getCause());
}
}
到此ViewModel的创建就完成了,接下来看一下ViewModelStore,它的代码很简单就这么几十行,内部创建了一个HashMap,以ViewModelProvider中拼接的字符串key,保存我们创建的ViewModel对象。
public class ViewModelStore {
private final HashMap<String, ViewModel> mMap = new HashMap<>();
final void put(String key, ViewModel viewModel) {
ViewModel oldViewModel = mMap.put(key, viewModel);
if (oldViewModel != null) {
oldViewModel.onCleared();
}
}
final ViewModel get(String key) {
return mMap.get(key);
}
Set<String> keys() {
return new HashSet<>(mMap.keySet());
}
/**
* Clears internal storage and notifies ViewModels that they are no longer used.
*/
public final void clear() {
for (ViewModel vm : mMap.values()) {
vm.clear();
}
mMap.clear();
}
}
二,ViewModel的销毁
根据ViewModel的创建过程可知,ViewModel对象销毁是和ViewModelStore息息相关,而ViewModelStore的创建是在ComponentActivity中,所以销毁也必定在这里面,在ComponentActivity中的构造函数中,通过lifecycle监听页面的销毁。
this.getLifecycle().addObserver(new LifecycleEventObserver() {
public void onStateChanged(@NonNull LifecycleOwner source, @NonNull Event event) {
if (event == Event.ON_DESTROY) {
ComponentActivity.this.mContextAwareHelper.clearAvailableContext();
//判断Activity是否非正常销毁
if (!ComponentActivity.this.isChangingConfigurations()) {
//回收ViewModel,并触发onCleared
ComponentActivity.this.getViewModelStore().clear();
}
}
}
});
isChangingConfigurations 函数就是判断是否因屏幕旋转导致触发的生命周期,这也就是为什么屏幕旋转后ViewModel中LiveData保存的值不会丢失。
总结
ViewModel的创建使用了工厂模式,创建完成后存入到ViewModelStore(ViewModelStore对象的创建是在Activity中)中的HashMap,Key是通过ViewModel的类名+默认的字符串,Value则是当前存入的ViewModel对象,当Activity/Fragment正常销毁时,会调用ViewModelStore中的Clear函数遍历删除HashMap中存入的ViewModel对象,然后触发onCleared函数。






















 420
420











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








