题目一:用Math方法实现0<=num<=10。
Math.floor(Math.random() * 10)
//然后提一下Math常用的方法:x
Math.floor(x) 返回小于或等于x的最大整数。
Math.random():随机生成[0-1)的浮点数,包括0但是不包括1.
Math.round(x):返回x进行四舍五入的数字,如果x是小于0的话,那么就是五舍六入。
Math.raoud(-2.5)//输出:-2
Math.max(1,2,3,4),返回这一组数据中的最大值,不能够传数组,每一个数字会做隐式的转换,往Number类型的数据进行转换,转换不了就返回NaN。
Math.min(1,2,3)和max同理。
题目二:forEach的循环的终止
方法一:可以修改循环数组的长度。
let arr = ["first", "sencod", "third", "fourth"];
arr.forEach((item, index) => {
if (item == "third") {
arr.length = index + 1//在这里对arr的长度进行了修改,所以这一次循环就是最后一次循环,所以就不会再进入下一次循环。
}
console.log(item);
})
方法二:可以通过抛出错误进行结束
let arr = ["first", "sencod", "third", "fourth"];
try {
arr.forEach((item, index) => {
if (item == "third") {
throw new Error("error")//在这里把错误抛出,然后catch进行接收
}
console.log(item);
})
} catch (e) {
console.log("错误", e);//如果不想看到,直接可以把这一句去掉
}
题目三:统计字符或者字符串在一个字符串出现的次数
方法一:利用递归
{
//统计字符或者字符串在一个字符串出现的次数
let count = 0;
function strCount(s, str, n) {
if (s.length == 0) return
let index;
if (s.length == 1) {//判断是字符还是字符串
index = str.indexOf(s, n);//s就是要寻找的字符,n就是从str的哪个索引开始寻找。
if (index != -1) {//不存在该字符的话index就是-1
count++ //计数进行++
n = index + 1; //然后修改下一次寻找的开始索引
strCount(s, str, n)
}
} else {
if (s.length > 1) { //这里是判断字符串在str中出现的次数
index = str.indexOf(s, n);
if (index != -1) {
count++
n = index + s.length;
strCount(s, str, n)
}
}
}
}
strCount("ka", "hgakalakahhkaka")
console.log(count);//输出 4
}
方法二:利用while循环判断index是否等于-1
{
function fn(s, str) {
let index = 0;
let count = 0;
if (s.length == 0) return;
if (s.length == 1) {
while (index != -1) {
index = str.indexOf(s, index + 1)//在上一次找到的该字符的索引的下一个位置在开始寻找
if (index != -1) count++;
}
} else {
while (index != - 1) {
index = str.indexOf(s, index);
if (index != -1) {
index = index + s.length;
count++
}
}
}
console.log(count);
}
fn("ka", "kajkaffkaflf")
}
题目三:冒泡排序:
{
let a = [5, 9, 20, 80, 2, 4, 6, 55, 11, 25]
function maopao(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {//外层控制循环的趟数
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {//内层进行比较
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
let temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp
}
}
}
return arr
}
let b = maopao(a)
console.log(b);
}
题目四:说出输出结果
{
var foo = { n: 2 };
(function (foo) {
console.log(foo.n);//2 这里的foo在内部不是一个函数,就不用考虑函数和变量的提升优先级,所以这里的foo直接就是形参传过来的。
var foo = { n: 3 }
console.log(foo.n);//3
})(foo)
console.log(foo.n);//2
}
//
{
function fn() {
console.log(1);
};
(function (fn) {
fn()//2 因为内部有一个函数的fn,函数的声明提升,函数的提升比变量的提升优先,所以这里就直接使用内部的fn函数。
function fn() {
console.log(2);
}
fn()//2
})(fn)
fn();//1
}
题目五:console.log(true||false&&false, true&&false||true)
输出 true true
&&比||的优先级高
题目六:说出打印结果:
{
//首先碰到同步代码就直接执行,碰到异步代码就先放入任务队列,等待同步代码执行完再执行异步代码。
//这里的promise1和promise2就是保存一个Promise实例,且保存了它的状态。
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//首先执行这里的同步代码,直接打印
console.log('promise1')
resolve('resolve1') //因为这里调用了resolve方法,所以promise1的状态就是fulfilled。
})
//这里有.then所以是异步的,会等待所有的同步代码执行完成后再执行。
const promise2 = promise1.then(res => {//.then方法执行完成后也会返回一个Promise对象。
console.log(res)//这里没有设置resolve和reject,所有它的状态就是pending。
})
console.log('1', promise1);
console.log('2', promise2);
//输出结果:
// promise1
// 1 Promise {<fulfilled>:'resolve1' }
// 2 Promise {<pending> }
// resolve1
}
通过new Promise创建实例,返回的就是一个Promise对象,且保存了它的状态。
题目七:说出打印结果:
{
function showCase(value) {
switch (value) {//这里用的是严格比较:===
case 'A':
console.log('Case A');
break;
case 'B':
console.log('Case B');
break;
case undefined:
console.log('Case undefined');
break;
default:
console.log('Case default');
}
}
showCase(new String('A'));//这里的new产生的字符串和“A”是不等的
}
结果输出:“Case default”
为啥 字面量创建的字符串和构造函数创建的不等?
{
let str = 'A';
let value = new String('A');
console.log(str === value);//返回false
//想一下:用构造函数创建的实例,都会有__proto__属性,那么都有属性了,那么它还是一个单纯的字符串吗?
//typeof来判断一下:
console.log(typeof str);//输出 "string"
console.log(typeof value);//输出:"object"
}
用控制台打印:
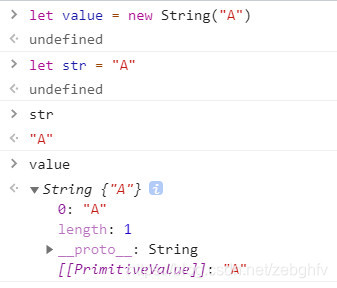
所以str === value不成立,但是str === value[0]就成立。
题目八:
{
var str = "我非常喜欢编程";
str.length = 3;
console.log(str);
}
输出结果:“我非常喜欢编程”
字符串虽然有长度,但是的它的截断方法不生效,数组的话就会生效。
例如用数组:
{
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
arr.length = 2;
console.log(arr);//输出 [1,2]
}





















 143
143











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










