Vector现在基本已经被ArrayList取代。但是vector中有一个elements()方法,返回的是枚举类型 Enumeration<E>。
package com.test.list;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
public class VectorDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Vector<String> list = new Vector<String>();
list.add("Kevin");
list.add("John");
list.add("Clare");
list.add("Gary");
//使用elements()方法,返回的是枚举类型 Enumeration<E>
//枚举是Vector特有的取出方式
for(Enumeration<String> en = list.elements(); en.hasMoreElements();)
{
System.out.println(en.nextElement());
}
}
}
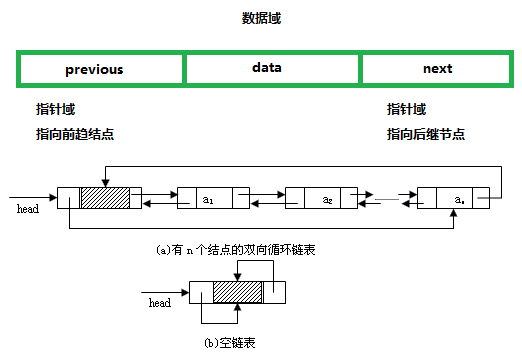
LinkedList底层是双向循环链表实现的。所以插入和删除效率较高,但查询较慢。
简单看看链表的形式。
双向链表
//模拟单向链表
package com.test.list;
public class NoteTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Note note1 = new Note("note1");
Note note2 = new Note("note2");
Note note3 = new Note("note3");
note1.next = note2;
note2.next = note3;
//显示note3的数据
System.out.println(note1.next.next.data);
// 新生成一个note4,将其插入到note1和note2的中间
Note note4 = new Note("note4");
note1.next = note4;
note4.next = note2;
//显示note3的数据
System.out.println(note1.next.next.next.data);
//将note4删除
note1.next = note2;
note4.next = null;
//显示note3的数据
System.out.println(note1.next.next.data);
}
}
class Note
{
String data; //存放节点数据本身
Note next; //存放指向下一个节点的引用
public Note(String data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
//模拟双向循环链表
package com.test.list;
public class NoteTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DoubleNote note1= new DoubleNote("note1");
DoubleNote note2= new DoubleNote("note2");
DoubleNote note3= new DoubleNote("note3");
note1.next = note2;
note2.previous = note1;
note2.next = note3;
note3.previous = note2;
note3.next = note1;
note1.previous = note3;
//添加note4,并将其插在note1和note2之间
DoubleNote note4 = new DoubleNote("note4");
note1.next = note4;
note4.previous = note1;
note4.next = note2;
note2.previous = note4;
//将note4删除
note1.next = note2;
note2.previous = note1;
note4.next = null;
note4.previous = null;
//显示note1的数据
System.out.println(note1.next.next.next.data);
}
}
class DoubleNote
{
DoubleNote previous;//前趋节点
String data; //数据本省
DoubleNote next; //后继节点
public DoubleNote(String data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
LikedList的一些特有方法,例如addFirst(), removeFirst()等。
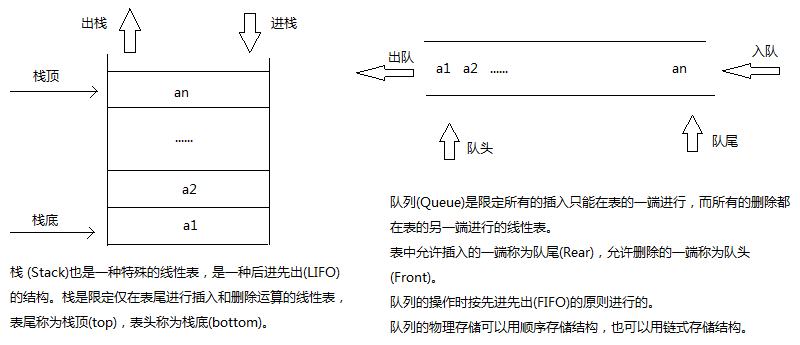
//使用LinkedList的方法模拟队列。
package com.test.list;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedListDemo1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.put("First");
queue.put("Second");
queue.put("Third");
//返回First
System.out.println(queue.get());
//返回Second
System.out.println(queue.get());
//返回false
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
}
}
class MyQueue
{
private LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
public void put(Object obj)
{
list.addLast(obj);
}
public Object get()
{
return list.removeFirst();
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return list.isEmpty();
}
}
//使用LinkedList的方法模拟栈
package com.test.list;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class LinkedListDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
MyStack stack = new MyStack();
stack.push("One");
stack.push("Two");
stack.push("Three");
stack.push("four");
for(int i = 0; i < 4 ;i++)
{
System.out.println(stack.size());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
}
class MyStack
{
private LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
public void push(Object obj)
{
//入栈
list.addFirst(obj);
}
public Object pop()
{
// 出栈,指从栈顶删除该元素并返回
return list.removeFirst();
}
public Object peek()
{
// 查看栈顶元素
return list.getFirst();
}
public int size()
{
return list.size();
}
}























 6739
6739

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








