众所周知Material Design(材质设计)是Google在2014年I/O大会上发布的一种新的设计规范。一经推出就好评如潮,个人是非常喜欢这种风格的,由于他只支持5.0及其以上的设备,开发者也只是去尝尝鲜,并没用在真实的项目中去,使得其在国内的市场并不是太好。随后不久Google就退出了其兼容库Android Design Support Library,兼容至2.1!这绝对是业界良心,极大的便利了我们这些开发者。这一兼容库可以让我们可以在自己的项目真实的去体验一把。百度谷歌一下,其实现在已经有个很多介绍这个支持库的文章,但是很多都并不太详细,大部分让人看了都似懂非懂,我之前也学习过这个库的用法,很久没看基本又忘了,最近我又重新开始学习了这个库,所以本文也主要是对这次学习的一个总结,当然也参考了其他很多的文章,算是站在巨人的肩膀上吧,当然这篇文章也为后来的学习者有更多的参考资料。
先来几张效果图吧:


感兴趣的也可以先看看,最后能做一个什么样的App:MDDemo.apk
说到这个兼容库,其实很多都是可以在Github去找到对应的效果的,其实我们也是可以去用Github上的那些开源项目,那么多的库都要一个一个去引用,还是非常的麻烦,我猜可能Google也是看到这些东西经常被开发者用在了项目中,索性自己将其封装成了一个库,以方便开发者的使用。这个库我们应该怎样去使用呢?这是本文讲解的重点。首先我们看看这个库怎么去引用到我们的项目中:
compile 'com.android.support:design:23.1.1'
我们只需将其添加到项目的依赖中去,然后同步一下就OK了。
添加了依赖之后我们再来看看这个库里面都有哪些控件吧,如下图,红色边框矩形框出来的就是这个库里面包含的控件,我们可以看到有AppBarLayout、CollapsingToolbarLayout、CoordinatorLayout,FloatingActionButton、NavigationView、Snackbar、TabLayout、TextInputLayout这八种,后面我会一个一个介绍用法,如果还没学过这些控件使用的本文可以手把手教你学会怎么去使用,如果之前有了解过的或者对这个还比较熟悉的,也可以继续看下去,就当做温习一下,顺便还可以帮我找出有表达不正确的地方。

1.Snackbar
SnackBar通过在屏幕底部展示简洁的信息,为一个操作提供了一个轻量级的反馈,并且在Snackbar中还可以包含一个操作,在同一时间内,仅且只能显示一个 Snackbar,它的显示依赖于UI,不像Toast那样可以脱离应用显示。它的用法和Toast很相似,唯一不同的就是它的第一个参数不是传入Context而是传入它所依附的父视图,但是他比Toast更强大。
我们来看看它的基本使用
Snackbar.make(mDrawerLayout, "SnackbarClicked", Snackbar.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
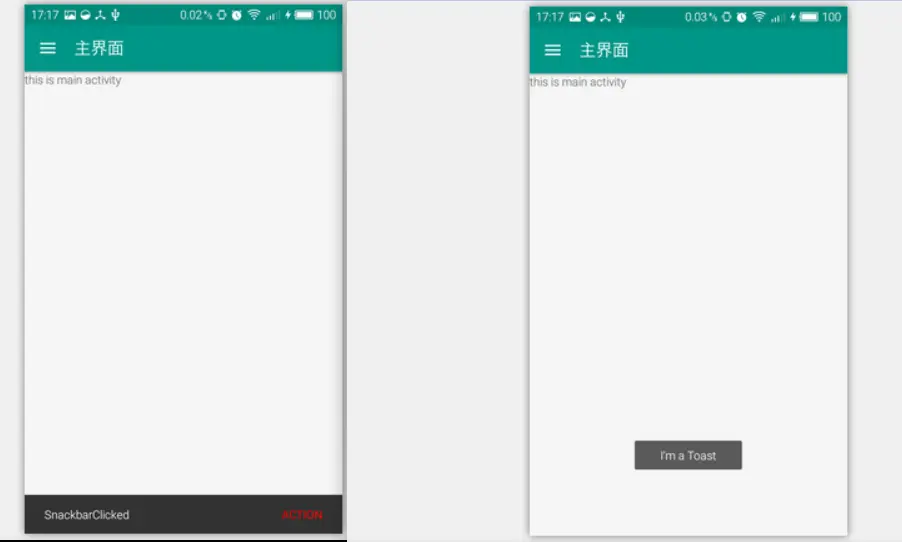
是不是和Toast很相似。我们来看看它的效果图:

是不是看着比Toast舒服多了
好了,我们再来看看一个包含Action的Snackbar怎么使用
Snackbar.make(mDrawerLayout, "SnackbarClicked", Snackbar.LENGTH_SHORT).setAction("Action", new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "I'm a Toast", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}).setActionTextColor(Color.RED).show();
这里我给Snackbar设置了一个Action,设置其文字颜色为红色,并带有了一个点击事件,在单击这个Action后就弹出一个Toast,效果图如下
2.TextInputLayout
使用过EditText的同学肯定知道,有一个叫hint的属性,它可以提示用户此处应该输入什么内容,然而当用户输入真实内容之后,hint的提示内容就消失了,用户的体验效果是十分不好的,TextInputLayout的出现解决了这个问题。
我们来看看这个控件的是怎么使用的
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="10dp"
tools:context="burgess.com.materialdesignstudy.MDTextViewActivity">
<!--TextInputLayout的颜色来自style中的colorAccent的颜色-->
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit_username"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="用户名/手机号"
android:inputType="textEmailAddress" />
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit_pwd"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="密码"
android:inputType="textPassword" />
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
</LinearLayout>
其实这个控件的使用非常简单,我们只需在EditText外面再嵌套一个TextInputLayout就行了。我们来看看效果
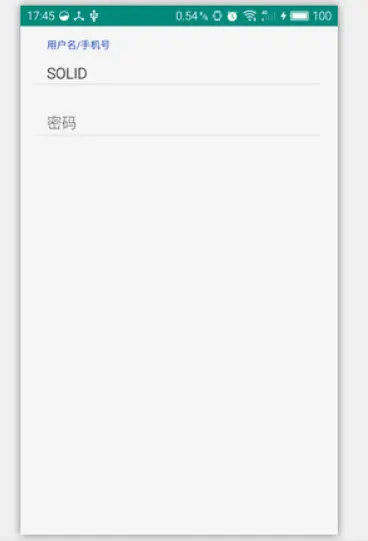
还是很不错的,当用户在输入的时候hint的内容就会跑到输入内容的上边去,其中TextInputLayout中字体的颜色是style文件中的colorAccent(关于colorAccent是什么,文末有一张图看了就清楚了)的颜色。
3.FloatingActionButton
FloatingActionButton从名字可以看出它是一个浮动的按钮,它是一个带有阴影的圆形按钮,可以通过fabSize来改变其大小,主要负责界面的基本操作,这个按钮总体来说还是比较简单的。
我们来看看它的一些属性:
- 默认FloatingActionButton 的背景色是应用主题的 colorAccent(其实MD中的控件主题默认基本都是应用的这个主题),可以通过app:backgroundTint 属性或者setBackgroundTintList (ColorStateList tint)方法去改变背景颜色。
- 上面提到 Floating action button 的大小尺寸,可以用过app:fabSize 属性设置(normal or mini)
- android:src 属性改变 drawable
- app:rippleColor设置点击 button 时候的颜色(水波纹效果)
- app:borderWidth设置 button 的边框宽度
- app:elevation设置普通状态阴影的深度(默认是 6dp)
- app:pressedTranslationZ设置点击状态的阴影深度(默认是 12dp)
怎么去使用:
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab_search"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|end"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:src="@android:drawable/ic_dialog_email"
app:borderWidth="2dp"
app:fabSize="normal"
app:rippleColor="#ff0000" />
其效果图如下:

## 4.CoordinatorLayout
我们来看看官方对他的描述:
- CoordinatorLayout is a super-poweredFrameLayout.
- CoordinatorLayout is intended for two primary use cases:
1.As a top-level application decor or chrome layout
2.As a container for a specific interaction with one or more child views
从这里我们可以知道它是一个增强版的FrameLayout,他可以协调其子View的交互,控制手势机滚动技巧。这个控件十分的强大,用处也十分的广泛。就比如刚才说的FloatingActionButton如果用CoordinatorLayout 作为FloatingActionButton的父布局,它将很好的协调Snackbar的显示与FloatingActionButton。


这两个动态图来源于网上,效果是显而易见的,原谅我用的手机测试,所以没法录制动态图(如果有人知道怎么去录制的请告知)。
还有它的另外一个比较重要的用处是控制协调内容区和AppBarLayout的滚动,这个后面会讲到。这个控件还是比较复杂的,用多了就能慢慢体会到他的强大之处。我对这个控件的还不是那么的清楚,所以在这里提供一篇关于CoordinatorLayout 用法的译文: 掌握 Coordinator Layout
## 5.NavigationView
抽屉式的导航控件,有了他我们可以使得导航更简单。我们可以直接通过菜单资源文件生成所需的元素。下图左边的即是NavigationView。

下面我们来看看它是怎么实现的吧。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.v4.widget.DrawerLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/drawer_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<!--内容区-->
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout
android:id="@+id/main_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<include
android:id="@+id/appbar"
layout="@layout/toolbar" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/frame_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_below="@+id/appbar"
android:scrollbars="none"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior" />
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
<!--左侧导航菜单-->
<android.support.design.widget.NavigationView
android:id="@+id/navigation_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="start"
app:headerLayout="@layout/navigation_header"
app:menu="@menu/drawer" />
</android.support.v4.widget.DrawerLayout>
可以看到这里我们是以DrawerLayout作为其父布局,对于DrawLayout他可以实现一种抽屉式的侧滑效果,这里不多做讲解,这里只简单说一点:DrawLayout中的第一个布局是内容布局,第二个是菜单布局。现在我们直接定位到NavigationView,我们看到这里有app:headerLayout="@layout/navigation_header"、app:menu="@menu/drawer"这两行代码,其中headerLayout是设置其头部的布局,这个布局我们可以随便写,就和写普通的布局文件一样的。对于menu就是菜单项的配置了,其配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<group android:checkableBehavior="single">
<item
android:id="@+id/navigation_item_home"
android:icon="@drawable/iconfont_home"
android:title="首页" />
<item
android:id="@+id/navigation_item_blog"
android:icon="@drawable/iconfont_blog"
android:title="我的博客" />
<item
android:id="@+id/navigation_item_about"
android:icon="@drawable/iconfont_about"
android:title="关于" />
</group>
</menu>
就这么简单,我们要实现上述的效果就只要这些就足够了。但是如果我们想要对Item添加一个点击的事件怎么做呢?请看下面:
private void setNavigationViewItemClickListener() {
mNavigationView.setNavigationItemSelectedListener(new NavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public boolean onNavigationItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.navigation_item_home:
mToolbar.setTitle("首页");
switchFragment("MainFragment");
break;
case R.id.navigation_item_blog:
mToolbar.setTitle("我的博客");
switchFragment("BlogFragment");
break;
case R.id.navigation_item_about:
mToolbar.setTitle("关于");
switchFragment("AboutFragment");
break;
default:
break;
}
item.setChecked(true);
mDrawerLayout.closeDrawer(Gravity.LEFT);
return false;
}
});
}
上面的代码很清楚了,就是为NavigationView添加了一个OnNavigationItemSelectedListener的监听事件,然后我们就可以做我们想做的事了。
## 6. AppBarLayout、CollapsingToolbarLayout、TabLayout
这三个控件我用一个例子一下讲解了,在实际的使用中这三个控件还是经常会组合在一起的。
- AppBarLayout :其继承于LinearLayout,使用AppBarLayout可以让包含在其中的子控件能响应被标记了ScrollingViewBehavior的的滚动事件(要与CoordinatorLayout 一起使用),利用它我们可以很容易的去实现视差滚动效果,这样所你可能还是不太懂,千言万语不如一张图来的直接爽快(这样图还是来源于网上,其蓝色的部分就是AppBarLayout,内容区就是被标记了ScrollingViewBehavior的,可以看到效果是不是挺不错的)。

- CollapsingToolbarLayout :让Toolbar可伸缩,在伸缩的时候决定ToolBar是移除屏幕和固定在最上面。由于Toolbar 只能固定到屏幕顶端并且不能做出好的动画效果,所以才有了这个Layout的出现。
- TabLayout :这个其实和我们之前使用的第三方库ViewPagerIndicator是很类似的,一般都和ViewPager一起使用,效果如下图:

基本知道他们是干什么用的了,下面就让我们动手,看看到底怎么用吧。
先来几张下面我们要实现的效果。由于我是真机测试,没法录制动态图,这里就用几张静态图代替了。

布局文件(这个是很重要的,很多的效果都是直接在布局文件中配置的):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Dark.ActionBar">
<android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout
android:id="@+id/collapsing_toolbar_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
app:contentScrim="?attr/colorPrimary"
app:expandedTitleMarginEnd="64dp"
app:expandedTitleMarginStart="48dp"
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/iv_book_image"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:scaleType="centerInside"
android:transitionName="transition_book_img"
app:layout_collapseMode="parallax"
app:layout_collapseParallaxMultiplier="0.7" />
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
app:layout_collapseMode="pin"
app:popupTheme="@style/ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Light" />
</android.support.design.widget.CollapsingToolbarLayout>
</android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="10dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#292929"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_rating"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:layout_marginTop="2dp"
android:textColor="#FF6347"
android:textSize="14sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_msg"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="2dp"
android:textColor="#575757"
android:textSize="12sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/sliding_tabs"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:tabGravity="fill"
app:tabMode="scrollable" />
<android.support.v4.view.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/viewpager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
我们来分析一下这个布局文件:
1.最外层的布局用的是CoordinatorLayout,因为这里面有很多的动画,CoordinatorLayout可以很好的去协调里面的动画。在android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout下面的那个LinearLayout被标记了appbar_scrolling_view_behavior,这样一来AppBarLayout就能响应LinearLayout中的滚动事件。
2.再来看看CollapsingToolbarLayout,其中contentScrim是设置其内容区的颜色,layout_scrollFlags取了scroll和exitUntilCollapsed两个值。
layout_scrollFlags的Flag包括:
- scroll: 所有想滚动出屏幕的view都需要设置这个flag,没有设置这个flag的view将被固定在屏幕顶部。
- enterAlways: 这个flag让任意向下的滚动都会导致该view变为可见,当向上滑的时候Toolbar就隐藏,下滑的时候显示。
- enterAlwaysCollapsed: 顾名思义,这个flag定义的是何时进入(已经消失之后何时再次显示)。假设你定义了一个最小高度(minHeight)同时enterAlways也定义了,那么view将在到达这个最小高度的时候开始显示,并且从这个时候开始慢慢展开,当滚动到顶部的时候展开完。
- exitUntilCollapsed: 同样顾名思义,这个flag时定义何时退出,当你定义了一个minHeight,这个view将在滚动到达这个最小高度的时候消失。
只看概览可能还是不会太清楚,注意一定要多实践,感兴趣的读者可以一个一个去试一试效果。
3.定位到ImageView,有这两个属性是我们平常用没看到的,说明我写在注释上了
app:layout_collapseMode="parallax"//这个是配置当ImageView消失或者显示时候有一种视差滚动效果 app:layout_collapseParallaxMultiplier="0.7"//视差因子,越大视差特效越明显,最大为1
4.Toolbar中有一个app:layout_collapseMode="pin" 这个确保Toolbar在AppBarLayout折叠的时候仍然被固定在屏幕的顶部
布局文件就到这,我们来看看Activity中的逻辑
/*
Created by _SOLID
Date:2016/3/30
Time:20:16
*/
public class BookDetailActivity extends BaseActivity {
private String mUrl;
private Toolbar mToolbar;
private CollapsingToolbarLayout mCollapsingToolbarLayout;
private ImageView mIvBook;
private BookBean mBookBean;
private TextView mTvTitle;
private TextView mTvMsg;
private TextView mTvRating;
private ViewPager mViewPager;
private TabLayout mTabLayout;
@Override
protected void initView() {
//设置Toolbar
mToolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.toolbar);
setSupportActionBar(mToolbar);
getSupportActionBar().setHomeButtonEnabled(true);//决定左上角的图标是否可以点击
getSupportActionBar().setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(true);//决定左上角图标的右侧是否有向左的小箭头
mToolbar.setNavigationOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
onBackPressed();
}
});
mCollapsingToolbarLayout = (CollapsingToolbarLayout) findViewById(R.id.collapsing_toolbar_layout);
mIvBook = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iv_book_image);
mTvTitle = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_title);
mTvMsg = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_msg);
mTvRating = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_rating);
mViewPager = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.viewpager);
mTabLayout = (TabLayout) findViewById(R.id.sliding_tabs);
mTabLayout.addTab(mTabLayout.newTab().setText("作者信息"));
mTabLayout.addTab(mTabLayout.newTab().setText("章节"));
mTabLayout.addTab(mTabLayout.newTab().setText("书籍简介"));
}
@Override
protected int setLayoutResourseID() {
return R.layout.activity_book_detail;
}
@Override
protected void init() {
mUrl = getIntent().getStringExtra("url");
}
@Override
protected void initData() {
SolidHttpUtils.getInstance().loadString(mUrl, new SolidHttpUtils.HttpCallBack() {
@Override
public void onLoading() {
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(String result) {
Gson gson = new Gson();
mBookBean = gson.fromJson(result, BookBean.class);
mCollapsingToolbarLayout.setTitle(mBookBean.getTitle());
mTvTitle.setText(mBookBean.getTitle());
mTvMsg.setText(mBookBean.getAuthor() + "/" + mBookBean.getPublisher() + "/" + mBookBean.getPubdate());
mTvRating.setText(mBookBean.getRating().getAverage() + "分");
SolidHttpUtils.getInstance().loadImage(mBookBean.getImages().getLarge(), mIvBook);
BookInfoPageAdapter adapter = new BookInfoPageAdapter(BookDetailActivity.this, mBookBean, getSupportFragmentManager());
mViewPager.setAdapter(adapter);
mTabLayout.setupWithViewPager(mViewPager);
}
@Override
public void onError(Exception e) {
}
});
}
}
其实并不难,这里只需注意一点,当Toolbar被CollapsingToolbarLayout包裹的时候,设置标题是设置CollapsingToolbarLayout的,而不是Toolbar。
好了终于写完了,差不多写了接近4个小时,好累的说,现在整个人都是晕晕的。
源码献上:MaterialDesignDemo
参考链接:
Android的材料设计兼容库(Design Support Library)
Material Design控件使用
Floating Action Button(翻译)
Material Design 中文版
Android Design Support Library概览
附(一些控件使用使用应注意的地方):
1.在使用CardView的时候,一定要注意,当CardView的宽和高填充父容器的时候,CardView的margin最好要比cardElevation大,不然就看不到立体的效果。
2.我们知道ListView有一个onItemClick的事件,但是RecyclerView却没有,那么我们应该怎样去设置呢?其实很简单,关于RecyclerView设置item的点击事件,只需在创建ViewHolder的时候,给填充的View设置单击事件即可。
3.在使用android.support.design.widget.AppBarLayout的时候内容区最好使用android.support.v4.widget.NestedScrollView,之前我的内容区用的是ScrollView,在往上拉的时候AppBarLayout一直没有动画效果,折腾了几个小时都没找到原因。最后逼不得用Android Studio创建了一个他自带的关于AppBarLayout的模板项目,看到他用的是NestedScrollView作为内容区,我果断就把我的内容区换成了这个,立马就有动画效果了。
NestedScrollView官方的描述:
NestedScrollView is just likeScrollView, but it supports acting as both a nested scrolling parent and child on both new and old versions of Android. Nested scrolling is enabled by default.
如果感觉还不错的就给个喜欢支持一下吧,有问题请留言,谢谢
最后附一张MD的主题色解析图:























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








