代理模式
静态代理
- 抽象角色:一般会使用一个接口或者抽象类实现(如租房这个接口)
//租房接口
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}
- 真实角色:被代理的角色(如房东)
//房东
public class Host implements Rent{
@Override
public void rent() {
System.out.println("房东要出租房子");
}
}
- 代理角色:对真实角色进行代理(如中介),代理真实角色后,一般会进行一些附属操作(如收中介费)
public class Proxy implements Rent{
private Host host;
public Proxy(){};
public Proxy(Host host)
{
this.host=host;
}
//代理帮忙租房子
@Override
public void rent() {
host.rent();
seeHouse();
fare();
}
//中介带你看房
public void seeHouse()
{
System.out.println("中介带你看房");
}
//收中介费
public void fare()
{
System.out.println("收中介费");
}
}
- 客户:访问代理对象(如需要租房的人)
//去租房
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Host host=new Host();
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(host);
proxy.rent();
}
}
优点
- 可以使真实角色操作更加纯粹,不需要去关注一些公共业务
- 公共业务交给代理角色,实现业务的分工
- 公共业务扩展的时候,方便管理
缺点
- 一个真实角色就会产生一个代理角色,真实角色过多时,代码量会翻倍
动态代理
动态代理的代理类是动态生成的,不是我们直接写好的,程序在整个运行过程中不存在代理类。以基于接口的jdk动态代理为例,需要了解两个类,reflect包下的InvocationHandler和Proxy。
- 自定义一个类用来动态生成代理类,实现InvocationHandler接口:
//用这个类自动生成代理类
public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
}
- 在这个类里面声明要实现的接口
//被代理的接口
private Rent rent;
public void setRent(Rent rent) {
this.rent = rent;
}
- 生成得到代理类
//生成得到代理类
public Object getProxy()
{
//这个代码是死的,只需要改实现的接口就可以了
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
this.getClass().getClassLoader(),
rent.getClass().getInterfaces(),
this);
}
- 重写InvocationHandler的invoke()方法,处理代理实例,利用反射机制,返回结果
//处理代理实例,并返回结果
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
seeHouse();
//用invoke来执行,使用反射机制
Object invoke = method.invoke(rent, args);
fare();
return invoke;
}
//中介带你看房
public void seeHouse()
{
System.out.println("中介带你看房");
}
//收中介费
public void fare()
{
System.out.println("收中介费");
}
- 实现类中测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
//真实角色
Host host=new Host();
//代理角色,现在没有,要通过代理处理程序生成代理类
ProxyInvocationHandler proxyInvocationHandler = new ProxyInvocationHandler();
//让代理实现接口,host实现了接口,直接传host
proxyInvocationHandler.setRent(host);
//得到代理类
Rent proxy = (Rent) proxyInvocationHandler.getProxy();
proxy.rent();
}
好处
- 一个动态代理类代理的是一个接口,一般是对应一类业务。
- 一个动态代理类可以代理多个类,只要他们实现了同一个接口。
- 避免了静态代理一个真实角色就会产生一个代理角色,真实角色过多时,代码量会翻倍的缺点。
AOP
概述
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面编程),可以说是 OOP(面向对象) 的补充和完善。OOP 定义了从上到下的关系,但并不适合定义从左到右的关系,例如权限认证、日志、事务处理。这些导致了大量代码的重复,而不利于各个模块的重用。而AOP技术将那些与业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的逻辑或责任封装起来,便于减少系统的重复代码,降低模块间的耦合度,并有利于未来的可操作性和可维护性。若不使用 AOP,则会出现代码纠缠,即交叉业务逻辑与主业务逻辑混合在一起。这样,会使主业务逻辑变的混杂不清。在不影响业务类的情况下,实现动态增强。
导入依赖——AspectJ
对于 AOP 这种编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现。 Spring就是其中之一,可以完成面向切面编程。AspectJ 这个框架也实现了 AOP 的功能,且其实现方式更为简捷,使用更为方便,而且还支持注解式开发。所以, Spring 又将 AspectJ 的对于 AOP 的实现也引入到了自己的框架中。在Spring 中使用 AOP 开发时,一般使用 AspectJ 的实现方式。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.3.16.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>4.3.16.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
AOP约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
实现方式
1. 使用Spring的API接口
- AspectJ 定义了专门的表达式用于指定切入点。表达式的原型是:
例如定义切入点表达式
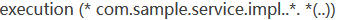
- execution(): 表达式主体。
- 第一个*号:表示返回类型, *号表示所有的类型。
- 包名:表示需要拦截的包名,后面的两个句点表示当前包和当前包的所有子包,com.sample.service.impl包、子孙包下所有类的方法。
- 第二个*号:表示类名,*号表示所有的类。
- 最后这个星号表示方法名,*号表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.zmqcode.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.zmqcode.log.Log"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.zmqcode.log.AfterLog"/>
<aop:config>
<!--切入点,execution(要执行的位置)-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.zmqcode.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--执行环绕增加,在哪个切入点执行什么方法-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
.* 表示这个类下面的所有方法
(…) 表示任意参数
- AfterReturningAdvice 后置通知
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行了"+method.getName()+"方法,返回结果为:"+returnValue);
}
}
- MethodBeforeAdvice 前置通知
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
@Override
/**
* method 要执行的目标对象的方法
* target 目标对象
*/
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"被执行了");
}
}
2. 自定义切面
不用Spring封装好的API了,自己写一个切面。
自定义一个类,起到一个日志作用:
public class DiyPointCut {
public void before()
{
System.out.println("======方法执行前======");
}
public void after()
{
System.out.println("======方法执行后======");
}
}
<!--方式二:自定义类-->
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="diy" class="com.zmqcode.diy.DiyPointCut"/>
<aop:config>
<!--自定义一个切面,ref:要引用的类-->
<aop:aspect ref="diy">
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.zmqcode.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--通知,这里用的是自己定义的before方法-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
3. 使用注解实现AOP
@Aspect:标注这是一个切面
@Before :前置通知
@After:后置通知
@Pointcut:定义切入点
//标注这个类是一个切面
@Aspect
public class AnnotationPointcut {
//注解的内容写切入点
@Before("execution(* com.zmqcode.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before()
{
System.out.println("======方法执行前======");
}
@After("execution(* com.zmqcode.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after()
{
System.out.println("======方法执行后======");
}
}
当较多的通知增强方法使用相同的 execution 切入点表达式时,编写、维护均较为麻烦。AspectJ 提供了@Pointcut 注解,用于定义 execution 切入点表达式。其用法是,将@Pointcut 注解在一个方法之上,以后所有的 execution 的 value 属性值均可使用该方法名作为切入点。代表的就是@Pointcut 定义的切入点。这个使用@Pointcut 注解的方法一般使用 private 的标识方法,即没有实际作用的方法。
//标注这个类是一个切面
@Aspect
public class AnnotationPointcut {
//注解的内容写切入点
@Before("pc()")
public void before()
{
System.out.println("======方法执行前======");
}
@After("pc()")
public void after()
{
System.out.println("======方法执行后======");
}
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zmqcode.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
private void pc()
{}
}
开启注解支持:
<!--方式三:使用注解实现-->
<bean id="annotationPointcut" class="com.zmqcode.diy.AnnotationPointcut"/>
<!--开启注解支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>






















 243
243











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








