基本介绍
Redis(Remote Dictionary Server,远程字典服务器),是基于内存的NoSQL数据库。当前市面上比较知名的NoSQL数据库如下:
| 类型 | 主要产品 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| KV存储 | Redis、Memcached | 使用Key快速查找到value,Memcached支持String类型的value,redis还支持支持set、sortset、hash、list等类型 |
| 文档存储 | MongoDBCouchEB | 使用json或者类json的bson数据结构,存储类型为文档型,能实现部分关系数据库的功能 |
| 列存储 | HBaseCassandra | 按列进行数据存储,便于存储结构化或者半结构化的数据,方便做数据压缩,或者针对某一列或者几列的统计查询 |
| 图存储 | Neo4JFlockDB | 图形关系的存储,能够很好地弥补关系数据库在图形存储的不足 |
| 对象存储 | DB4oVersant | 通过类似面向对象语言的方式操作数据库,通过对象的方式存取数据库 |
| XML数据库 | Berkelery DB XMLBaseX | 高效存储xml数据,支持xml的内部查找语法,如Xquery、Xpath |
特点
Redis:独特的键值对模型
SQL数据库–处理表格
Memcached–键值对数据库,键值都是string
文档数据库–由json或者Bson组成文档
一旦数据库提供的数据结构不适合做某件事情的话,程序就会写起来非常的麻烦和不自然
Redis虽然也是键值对数据库但是和Memcached不同的是Redis不仅可以存储字符串也可以是其他五种数据结构中的任意一种
通过Redis不同的数据结构,用户可以使用Redis解决各式各样的问题。
使用Redis需要思考的第一个问题,使用哪种合适的数据结构把哪些功能的问题解决掉,有了多种多样的数据结构,方便解决问题。
基于内存的数据库
持久化功能:将内存数据持久化到磁盘,保证数据的安全,方便进行数据的备份和恢复
发布与订阅功能:将消息同时分发给多个客户端,用于构建广播系统
过期键功能:为键设置一个过期时间,让他在指定的时间之后自动被删除
事务功能:原子执行多个操作,并提供乐观锁功能,保证数据的安全性
Lua脚本功能:在服务器端原子地执行多个操作,完成多个功能,并且减少客户端与服务器之间通信往返的次数。
复制:为指定的Redis服务器创建一个或者多个复制品,用于提升数据的安全性,并分担读请求的负载
Sentinel:监控Redis服务器状态,并在服务器发生故障的时候,自动故障转移。
集群:创建分布式数据库,每个服务器分别执行一部分的写和读操作
安装过程
由于redis是使用c编写的所以运行需要安装gcc和tcl
yum install gcc tcl -y
解压、进入解压后的路径
然后执行make进行编译
然后执行make install进行安装,PREFIX指定安装路径
make PREFIX=/usr/local/redis/ install

然后进入到安装路径下bin路径
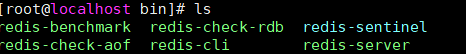
redis-server:redis服务区
redis-cli:redis客户端
redis-benchmark:Redis性能测试工具
redis-check-aof:aof文件修复工具
redis-check-rdb:
redis-sentinel:
启动可以直接通过redis-server来启动,默认端口6379
也可以将redis做成一个服务
将src/redis-sentinel文件拷贝到安装路径下的bin文件夹下(新版本在安装的时候已经复制过去了),然后添加环境变量即可
# redis home
export REDIS_HOME=/usr/local/redis
export PATH=$PATH:$REDIS_HOME/bin
保存,source一下
redis-server --help

执行redis-5.0.4/utils/install_server.sh会将redis安装成后台服务

上面说明了redis端口、配置、日志等文件
修改服务的名称
mv /etc/init.d/redis_6379 /etc/init.d/redisd

redis-cli --help可以查看客户端连接的帮助,如下
redis-cli 5.0.4
Usage: redis-cli [OPTIONS] [cmd [arg [arg ...]]]
-h <hostname> Server hostname (default: 127.0.0.1). 服务器地址
-p <port> Server port (default: 6379). 服务器上端口
-s <socket> Server socket (overrides hostname and port).
-a <password> Password to use when connecting to the server.
You can also use the REDISCLI_AUTH environment
variable to pass this password more safely
(if both are used, this argument takes predecence).
-u <uri> Server URI.
-r <repeat> Execute specified command N times.
-i <interval> When -r is used, waits <interval> seconds per command.
It is possible to specify sub-second times like -i 0.1.
-n <db> Database number. 数据库中多个database,默认16个,相互隔离
-x Read last argument from STDIN.
-d <delimiter> Multi-bulk delimiter in for raw formatting (default: \n).
-c Enable cluster mode (follow -ASK and -MOVED redirections).
--raw Use raw formatting for replies (default when STDOUT is
not a tty).
--no-raw Force formatted output even when STDOUT is not a tty.
--csv Output in CSV format.
--stat Print rolling stats about server: mem, clients, ...
--latency Enter a special mode continuously sampling latency.
If you use this mode in an interactive session it runs
forever displaying real-time stats. Otherwise if --raw or
--csv is specified, or if you redirect the output to a non
TTY, it samples the latency for 1 second (you can use
-i to change the interval), then produces a single output
and exits.
--latency-history Like --latency but tracking latency changes over time.
Default time interval is 15 sec. Change it using -i.
--latency-dist Shows latency as a spectrum, requires xterm 256 colors.
Default time interval is 1 sec. Change it using -i.
--lru-test <keys> Simulate a cache workload with an 80-20 distribution.
--replica Simulate a replica showing commands received from the master.
--rdb <filename> Transfer an RDB dump from remote server to local file.
--pipe Transfer raw Redis protocol from stdin to server.
--pipe-timeout <n> In --pipe mode, abort with error if after sending all data.
no reply is received within <n> seconds.
Default timeout: 30. Use 0 to wait forever.
--bigkeys Sample Redis keys looking for keys with many elements (complexity).
--memkeys Sample Redis keys looking for keys consuming a lot of memory.
--memkeys-samples <n> Sample Redis keys looking for keys consuming a lot of memory.
And define number of key elements to sample
--hotkeys Sample Redis keys looking for hot keys.
only works when maxmemory-policy is *lfu.
--scan List all keys using the SCAN command.
--pattern <pat> Useful with --scan to specify a SCAN pattern.
--intrinsic-latency <sec> Run a test to measure intrinsic system latency.
The test will run for the specified amount of seconds.
--eval <file> Send an EVAL command using the Lua script at <file>.
--ldb Used with --eval enable the Redis Lua debugger.
--ldb-sync-mode Like --ldb but uses the synchronous Lua debugger, in
this mode the server is blocked and script changes are
not rolled back from the server memory.
--cluster <command> [args...] [opts...]
Cluster Manager command and arguments (see below).
--verbose Verbose mode.
--no-auth-warning Don't show warning message when using password on command
line interface.
--help Output this help and exit.
--version Output version and exit.
Cluster Manager Commands:
Use --cluster help to list all available cluster manager commands.
Examples:
cat /etc/passwd | redis-cli -x set mypasswd
redis-cli get mypasswd
redis-cli -r 100 lpush mylist x
redis-cli -r 100 -i 1 info | grep used_memory_human:
redis-cli --eval myscript.lua key1 key2 , arg1 arg2 arg3
redis-cli --scan --pattern '*:12345*'
(Note: when using --eval the comma separates KEYS[] from ARGV[] items)
When no command is given, redis-cli starts in interactive mode.
Type "help" in interactive mode for information on available commands
and settings.
可以编辑安装的时候的配置文件
vim /etc/redis/6379.conf
如果需要配置远程访问需要注释文件中的
bind 127.0.0.1
在3.2版本之后需要远程访问还要修改
protected-mode yes
修改为
protected-mode no
然后可以使用
> redis-cli
连接或者加上数据库
> redis-cli -n 0
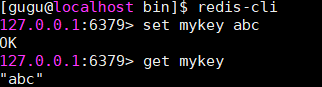
存储和查询数据库
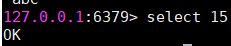
至此,安装完成
























 398
398











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








