示例:
配置文件:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd"
default-lazy-init="false">
<bean id="student" class="com.spring.bean.Student">
<property name="name" value="${test}"/>
</bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:test2.properties,classpath:test.properties"/>
</beans>test.properties:
test:studytest2.properties:
test:play实例:
package com.spring.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
@Data
public class Student extends Person {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public String show(String str) {
System.out.println("Studeng:test()");
return str;
}
}
测试:
@org.junit.Test
public void test7() throws InterruptedException {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Student bean =(Student)context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("Student:"+bean.getName());
}结果:

源码分析:自定义标签解析PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser
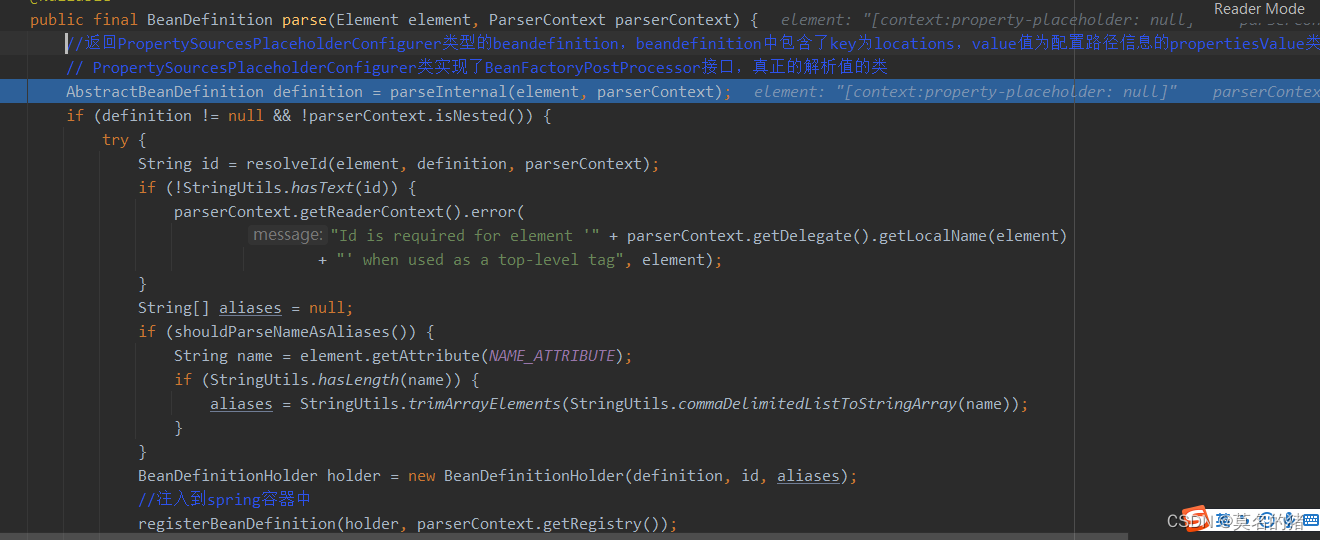
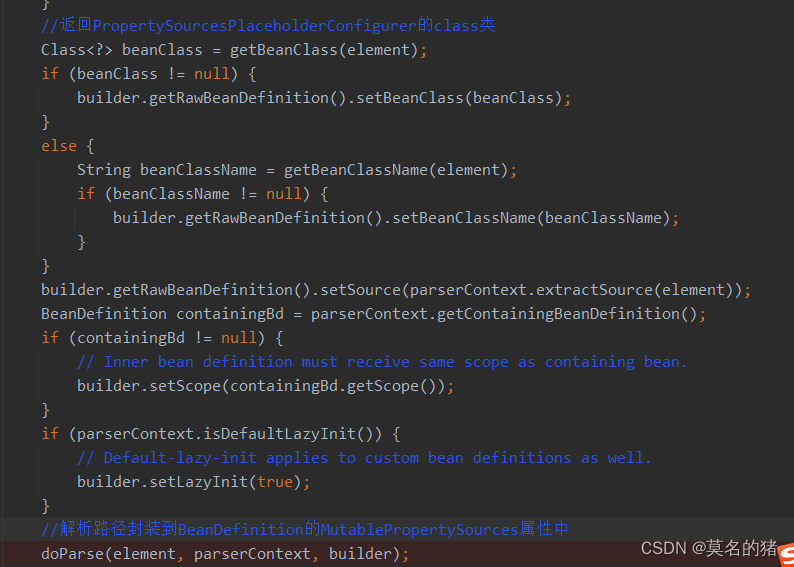
解析配置文件中的值并赋值:PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口

在这儿加入到embeddedValueResolvers容器中:


以解析string为例:


解析@value注解,通过AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor

这里从embeddedValueResolvers容器中获取解析:

注意:如果多个配置文件中的key值相同,value值会取最后配置的,因为会覆盖掉前面的值,例如: <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:test2.properties,classpath:test.properties"/>最后name的值为study;




















 6万+
6万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








