如何在一个程序中运行另外一个程序:exec系列调用
#include <unistd.h>
extern char **environ;
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...
/* (char *) NULL */);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...
/* (char *) NULL */);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ...
/*, (char *) NULL, char * const envp[]
*/);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[],
char *const envp[]);
// path 为程序路径,file为文件名(需要配置了环境变量才找得到),argv,arg都会被传递给新程序的main函数,evnp用于设置新程序的环境变量,若未设置则使用environexec不会关闭原程序打开的文件描述符,除非该文件描述符设置了SOCK_CLOEXEC等属性
失败才返回(-1)在原进程的调用点向下接着执行,成功则原程序exec之后的内容都不执行,调用后原进程的实体:代码段,数据段,堆栈等都被取代,只留下进程ID,等保持原样
使用execl,execl的第一个参数为路径
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
//使用execl()
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)
{
printf("parent process pid = %d\n",getpid());
}else if(pid==0){
//注意这里是可执行程序,而不是程序源码
execl("hello","hello",NULL);//第一个参数为路径,第二个为可执行程序名,以NULL结束
printf("child process\n");//因为是在子进程中使用exec族,所以此行代码不会被执行
}
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++){
printf("i = %d pid = %d\n",i,getpid());//此处的代码也只会有父进程的执行
}
return 0;
}
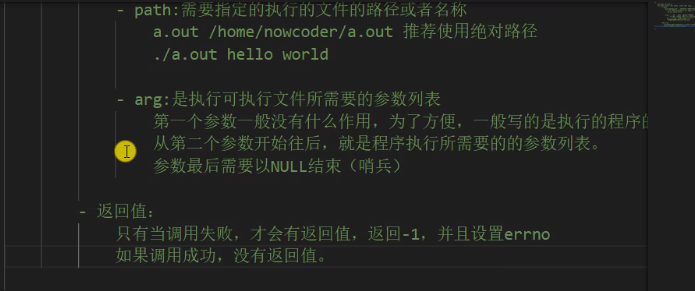
execlp的第一个参数为可执行文件名,不是路径
函数回到环境变量中查找指定的可执行文件,找不到就执行失败返回-1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
//使用execl()
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)
{
printf("parent process pid = %d\n",getpid());
}else if(pid==0){
//注意这里是可执行程序,而不是程序源码
execlp("ps","ps","aux",NULL);//第一个参数为可执行文件名,第二个为可执行程序名,以NULL结束
printf("child process\n");//因为是在子进程中使用exec族,所以此行代码不会被执行
}
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++){
printf("i = %d pid = %d\n",i,getpid());//此处的代码也只会有父进程的执行
}
return 0;
}
查看环境变量:echo $PATH
env在这里面找到PATH条目
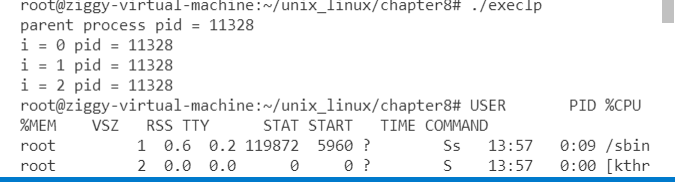
使用execvpe:会报错参数过多,但是man文档中写的是有三个参数
使用execve
//指定可执行文件搜索路径
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
//使用execl()
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)
{
printf("parent process pid = %d\n",getpid());
}else if(pid==0){
//注意这里是可执行程序,而不是程序源码
char *arglist[] = {"./hello","hello",NULL};
char *envp[] = {"PATH=/root/unix_linux/chapter8",NULL};
execve("hello",arglist,envp);//第一个参数为可执行文件名,第二个为可执行程序名,以NULL结束
printf("child process\n");//因为是在子进程中使用exec族,所以此行代码不会被执行
}
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++){
printf("i = %d pid = %d\n",i,getpid());//此处的代码也只会有父进程的执行
}
return 0;
}
例如运行ls -la命令,调用execvp("ls",arglist);此处的arglist为命令行的字符串数组
流程:
第一个元素要置为程序名称,最后一个元素为NULL(0)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
char *arglist[3];
arglist[0] = "ls";
arglist[1] = "-l";
arglist[2] = 0;
printf("exec ls-l\n");
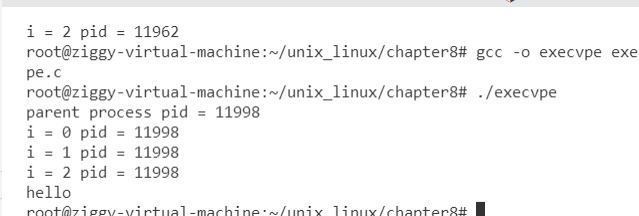
execvp("ls",arglist);
printf("ls -l done\n");
return 0;
}
/*
root@ziggy-virtual-machine:~/unix_linux/chapter8# gcc -o execdemo execdemo.c
root@ziggy-virtual-machine:~/unix_linux/chapter8# ./execdemo
exec ls-l
总用量 64
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8720 10月 26 15:25 execdemo
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 234 10月 26 15:25 execdemo.c
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8760 10月 26 14:37 forkdemo
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8712 10月 26 14:48 forkdemo2
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 248 10月 26 14:48 forkdemo2.c
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8760 10月 26 15:08 forkdemo.3
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 359 10月 26 15:08 forkdemo3.c
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 335 10月 26 14:37 forkdemo.c
*/指定环境变量查找路径:
关于execve:
第三个参数,即为envp数组,不是用于查找课执行程序的,而是为可执行程序运行期间增加新的环境变量
shell程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define ARGLEN 5
#define MAXARGS 20
int main()
{
char argbuf[ARGLEN];
fgets(argbuf,ARGLEN,stdin);//要留一位给'\0',所以只有ARGLEN-1位有效字符
printf("%d\n",strlen(argbuf)-1);
printf("%c\n",argbuf[strlen(argbuf)-1]);
printf("%s\n",argbuf);
if(argbuf[strlen(argbuf)]=='\0')
{
printf("yes\n");
}
return 0;
}
/*
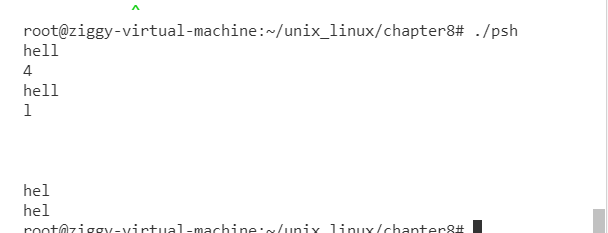
root@ziggy-virtual-machine:~/unix_linux/chapter8# ./psh1 hello
3
l
hell
yes
*/
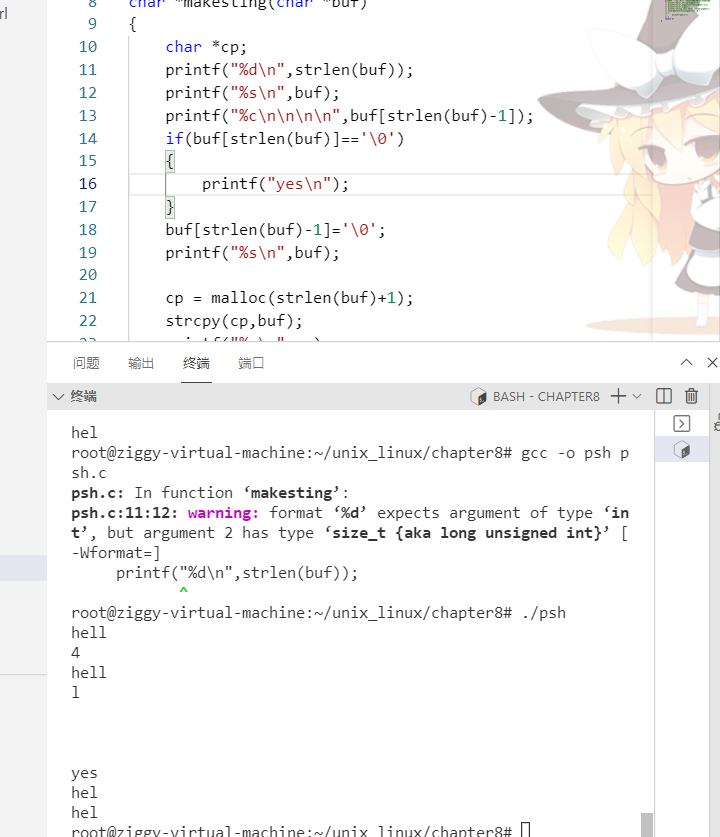
char *makesting(char *buf)
{
char *cp;
printf("%d\n",strlen(buf));
printf("%s\n",buf);
printf("%c\n\n\n\n",buf[strlen(buf)-1]);
buf[strlen(buf)-1]='\0';
printf("%s\n",buf);
cp = malloc(strlen(buf)+1);
strcpy(cp,buf);
printf("%s\n",cp);
// buf[]
return NULL;
}
为什么此函数中要将最后一位置为'\0'
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ARGLEN 100
#define MAXARGS 20
char *makesting(char *buf)
{
char *cp;
// printf("%d\n",strlen(buf));
// printf("%s\n",buf);
// printf("%c\n\n\n\n",buf[strlen(buf)-1]);
// if(buf[strlen(buf)]=='\0')
// {
// printf("yes\n");
// }
// buf[strlen(buf)]='\0';//这样是错的
printf("%d\n",strlen(buf));
//生成字符串,c风格字符串是'\0'结尾,例如ls:strlen(buf) = 3,l,s分别在0,1下标处,所以应该在下标为2处设为'\0',
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';
// printf("%s\n",buf);
cp = malloc(strlen(buf)+1);
strcpy(cp,buf);
// printf("%s\n",cp);
return cp;
}
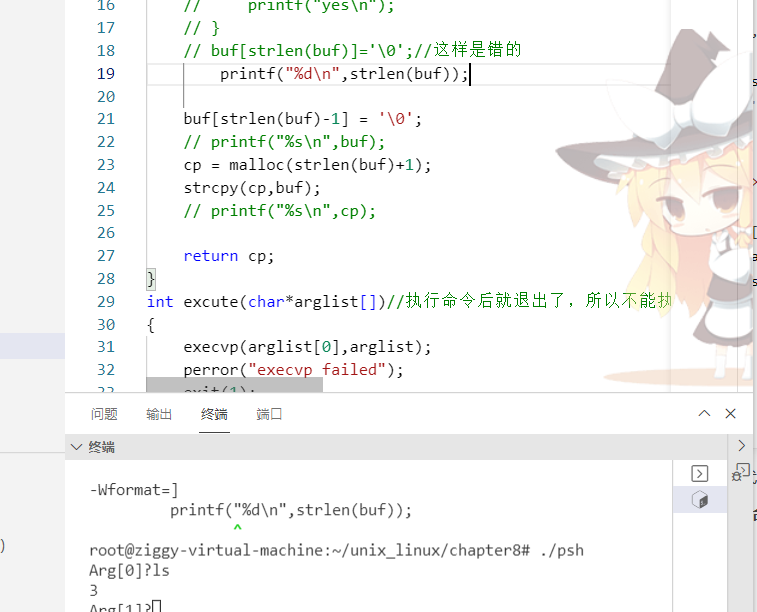
int excute(char*arglist[])//执行命令后就退出了,所以不能执行多条命令,且exec在错误时才返回值,且此原进程的代码被清除,会在此进程运行新的exec中的代码,所以shell无法接收新命令
{
execvp(arglist[0],arglist);
perror("execvp failed");
exit(1);
}
int main()
{
char argbuf[ARGLEN];
int numsargs = 0;//用于记录一条命令的当前参数
char* arglist[MAXARGS+1];
while(numsargs<MAXARGS)
{
printf("Arg[%d]?",numsargs);
if(fgets(argbuf,ARGLEN,stdin)&&*argbuf!='\n')
{
arglist[numsargs++] = makesting(argbuf);
}//要留一位给'\0',所以只有ARGLEN-1位有效字符
else
{
if(numsargs>0)
{
arglist[numsargs] = NULL;
excute(arglist);//执行程序
numsargs = 0;//reset参数个数,以便执行下一条命令
}
}
}
return 0;
}execvp用命令指定的程序代码覆盖了shell代码,然后在命令指定的程序中运行结束后退出,所以shell无法接收新命令
所以要启动新进程来运行命令指定的程序

exec用新的程序替换原进程的用户区
为什么要设置strlen(buf)-1位'\0':
实现一个真正的shell
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ARGLEN 100
#define MAXARGS 20
char *makesting(char *buf)
{
char *cp;
// printf("%d\n",strlen(buf));
// printf("%s\n",buf);
// printf("%c\n\n\n\n",buf[strlen(buf)-1]);
// if(buf[strlen(buf)]=='\0')
// {
// printf("yes\n");
// }
// buf[strlen(buf)]='\0';//这样是错的
// printf("%d\n",strlen(buf));
//生成字符串,c风格字符串是'\0'结尾,例如ls:strlen(buf) = 3,l,s分别在0,1下标处,所以应该在下标为2处设为'\0',
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';
// printf("%s\n",buf);
cp = malloc(strlen(buf)+1);
strcpy(cp,buf);
// printf("%s\n",cp);
return cp;
}
int excute(char*arglist[])//执行命令后就退出了,所以不能执行多条命令,且exec在错误时才返回值,且此原进程的代码被清除,会在此进程运行新的exec中的代码,所以shell无法接收新命令
{
int pid,status;
pid = fork();
switch (pid)
{
case -1:
perror("fork failed");
break;
case 0:
execvp(arglist[0],arglist);
perror("execvp failed");
exit(1);
break;
default:
while(wait(&status)!=pid);//等待子进程返回
printf("child exited with status %d,%d\n",status>>8,status&0377);
}
}
int main()
{
char argbuf[ARGLEN];
int numsargs = 0;//用于记录一条命令的当前参数
char* arglist[MAXARGS+1];
while(numsargs<MAXARGS)
{
printf("Arg[%d]?",numsargs);
if(fgets(argbuf,ARGLEN,stdin)&&*argbuf!='\n')
{
arglist[numsargs++] = makesting(argbuf);
}//要留一位给'\0',所以只有ARGLEN-1位有效字符
else
{
if(numsargs>0)
{
arglist[numsargs] = NULL;
excute(arglist);//执行程序
numsargs = 0;//reset参数个数,以便执行下一条命令
}
}
}
return 0;
}#运行结果
root@ziggy-virtual-machine:~/unix_linux/chapter8# ./psh2 Arg[0]?ls
Arg[1]?-l
Arg[2]?demodir
Arg[3]?
总用量 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 10月 26 22:49 new.cpp
child exited with status 0,0
Arg[0]?ls
Arg[1]?
demodir forkdemo2 forkdemo.c psh2
execdemo forkdemo2.c psh psh2.c
execdemo.c forkdemo.3 psh1 psh.c
forkdemo forkdemo3.c psh1.c waitdemo.c
child exited with status 0,0
Arg[0]?shell流程:
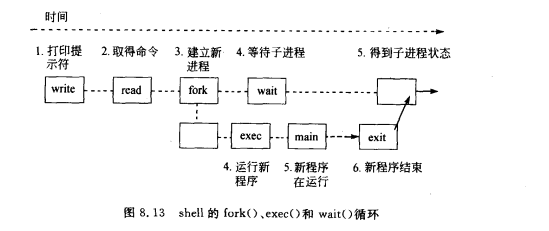
需要改进的点,会产生的错误:
退出此shell程序的唯一方法是ctrl+c
如果在psh2等待子进程运行时按此键,则其生成的SIGINT信号会杀死运行的子进程和psh2进程
原因:键盘信号发给所有连接的进程
psh2,和子进程都连接到终端,按下中断键,驱动向所有这个终端控制的进程发送SIGINT信号





















 1408
1408











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








