本文插图摘自李沐《动手学深度学习》https://zh.d2l.ai/chapter_convolutional-modern/resnet.html
1. 动机
alexnet的核心思想是堆叠深度,只要网络够深,就能学习好的特征
但是alexnet的设计没有标准性。
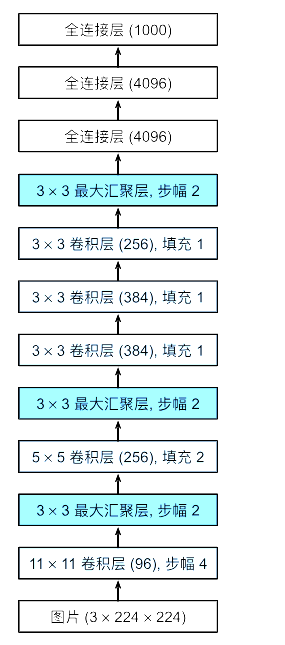
能不能用“标准、统一”的形式来构建神经网络,并科学证明深度是提升性能的关键因素?
2. 解决方案
只用最简单的零件构建网络——3x3卷积
3x3卷积相对于5x5卷积的优点:
1. 两层3x3卷积(Conv -> ReLU -> Conv -> ReLU)的感受野和一层5x5卷积相同,
2. 两层3x3卷积额外一次引入非线性,意味着表达能力更强
3. 两层3x3训练参数更少(2 * 3 * 3 = 18)
3. 工程实现
使用VGG Block替代AlexNet的所有部分
3.1 VGG块定义
若干conv2d(带填充)和ReLU堆叠,最后接2x2最大池化
维度变换:
def vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
layers = []
for _ in num_convs:
layers.append(nn.conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
layers.append(nn.ReLU())
in_channels = out_channels # 第2个block开始,维度变化为out_channels -> out_channels
layers.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)3.2 VGG网络定义
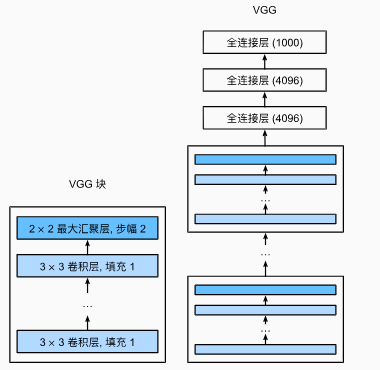
以VGG11为例,由5个vgg块组成,前两个块含有1个cnn,后三个块含有2个cnn
11 = 2x1 + 3*2 + 3(FNN)
# conv_arch定义了每个块的卷积数量和输出通道数
conv_arch = ((1, 64), (1, 128), (2, 256), (2, 512), (2, 512))
def vgg(conv_arch, in_channels=1):
conv_blks = []
for (num_convs, out_channel) in conv_arch:
conv_blks.append(vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels))
in_channels = out_channels
return nn.Sequential(
*conv_blks, nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(out_channels * 7 * 7, 4096), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 10)
)使用批次大小为1,维度为(1, 224, 224)来测试,目标:10分类
x = torch.randn(size=(1, 1, 224, 224))
net = vgg(conv_arch)
for blk in net:
x = blk(x)
print(blk.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t',X.shape)结果
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 56, 56])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 28, 28])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7])
Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 25088])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








