tcp多线程并发服务器
多线程服务器是对多进程服务器的改进,由于多进程服务器在创建进程时要消耗较大的系统资源,所以用线程来取代进程,这样服务处理程序可以较快的创建。据统计,创建线程与创建进程要快 10100 倍,所以又把线程称为“轻量级”进程。线程与进程不同的是:一个进程内的所有线程共享相同的全局内存、全局变量等信息,这种机制又带来了同步问题。
tcp多线程并发服务器框架:
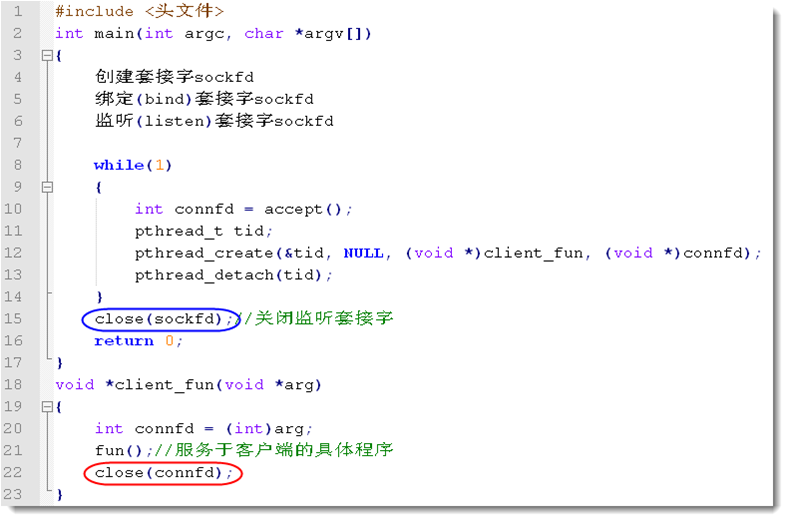
我们在使用多线程并发服务器时,直接使用以上框架,我们仅仅修改client_fun()里面的内容。代码示例:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- #include <pthread.h>
- /************************************************************************
- 函数名称: void *client_fun(void *arg)
- 函数功能: 线程函数,处理客户信息
- 函数参数: 已连接套接字
- 函数返回: 无
- ************************************************************************/
- void *client_fun(void *arg)
- {
- int recv_len = 0;
- char recv_buf[1024] = ""; // 接收缓冲区
- int connfd = (int)arg; // 传过来的已连接套接字
- // 接收数据
- while((recv_len = recv(connfd, recv_buf, sizeof(recv_buf), 0)) > 0)
- {
- printf("recv_buf: %s\n", recv_buf); // 打印数据
- send(connfd, recv_buf, recv_len, 0); // 给客户端回数据
- }
- printf("client closed!\n");
- close(connfd); //关闭已连接套接字
- return NULL;
- }
- //===============================================================
- // 语法格式: void main(void)
- // 实现功能: 主函数,建立一个TCP并发服务器
- // 入口参数: 无
- // 出口参数: 无
- //===============================================================
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- int sockfd = 0; // 套接字
- int connfd = 0;
- int err_log = 0;
- struct sockaddr_in my_addr; // 服务器地址结构体
- unsigned short port = 8080; // 监听端口
- pthread_t thread_id;
- printf("TCP Server Started at port %d!\n", port);
- sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); // 创建TCP套接字
- if(sockfd < 0)
- {
- perror("socket error");
- exit(-1);
- }
- bzero(&my_addr, sizeof(my_addr)); // 初始化服务器地址
- my_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
- my_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
- my_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
- printf("Binding server to port %d\n", port);
- // 绑定
- err_log = bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&my_addr, sizeof(my_addr));
- if(err_log != 0)
- {
- perror("bind");
- close(sockfd);
- exit(-1);
- }
- // 监听,套接字变被动
- err_log = listen(sockfd, 10);
- if( err_log != 0)
- {
- perror("listen");
- close(sockfd);
- exit(-1);
- }
- printf("Waiting client...\n");
- while(1)
- {
- char cli_ip[INET_ADDRSTRLEN] = ""; // 用于保存客户端IP地址
- struct sockaddr_in client_addr; // 用于保存客户端地址
- socklen_t cliaddr_len = sizeof(client_addr); // 必须初始化!!!
- //获得一个已经建立的连接
- connfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &cliaddr_len);
- if(connfd < 0)
- {
- perror("accept this time");
- continue;
- }
- // 打印客户端的 ip 和端口
- inet_ntop(AF_INET, &client_addr.sin_addr, cli_ip, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
- printf("----------------------------------------------\n");
- printf("client ip=%s,port=%d\n", cli_ip,ntohs(client_addr.sin_port));
- if(connfd > 0)
- {
- //由于同一个进程内的所有线程共享内存和变量,因此在传递参数时需作特殊处理,值传递。
- pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, (void *)client_fun, (void *)connfd); //创建线程
- pthread_detach(thread_id); // 线程分离,结束时自动回收资源
- }
- }
- close(sockfd);
- return 0;
- }
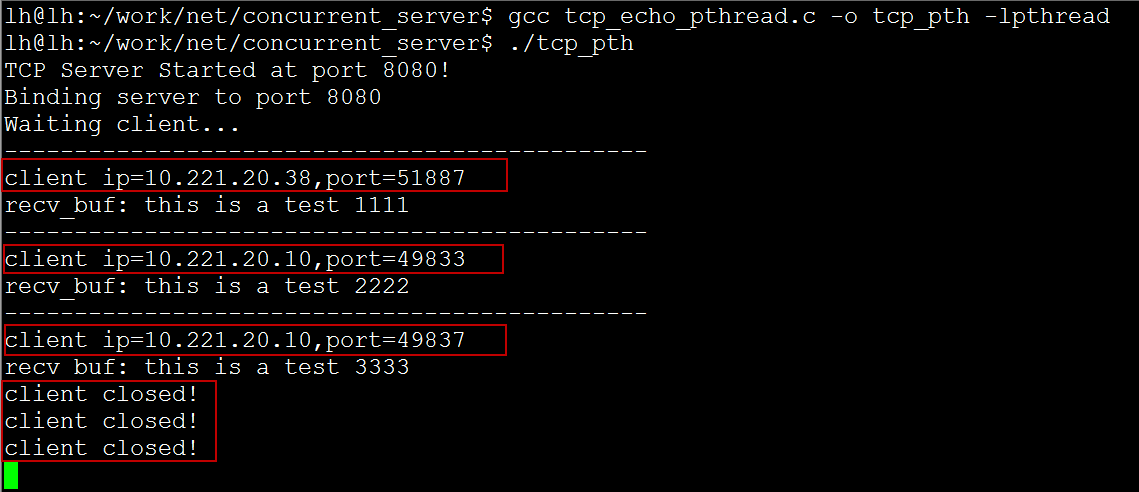
运行结果:
注意:
1.上面pthread_create()函数的最后一个参数是void *类型,为啥可以传值connfd?
- while(1)
- {
- int connfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &cliaddr_len);
- pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, (void *)client_fun, (void *)connfd);
- pthread_detach(thread_id);
- }
因为void *是4个字节,而connfd为int类型也是4个字节,故可以传值。如果connfd为char、short,上面传值就会出错
2.上面pthread_create()函数的最后一个参数是可以传地址吗?可以,但会对服务器造成不可预知的问题
- while(1)
- {
- int connfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &cliaddr_len);
- pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, (void *)client_fun, (void *)&connfd);
- pthread_detach(thread_id);
- }
原因:假如有多个客户端要连接这个服务器,正常的情况下,一个客户端连接对应一个 connfd,相互之间独立不受影响,但是,假如多个客户端同时连接这个服务器,A 客户端的连接套接字为 connfd,服务器正在用这个 connfd 处理数据,还没有处理完,突然来了一个 B 客户端,accept()之后又生成一个 connfd, 因为是地址传递, A 客户端的连接套接字也变成 B 这个了,这样的话,服务器肯定不能再为 A 客户端服务器了
2.如果我们想将多个参数传给线程函数,我们首先考虑到就是结构体参数,而这时传值是行不通的,只能传递地址。
这时候,我们就需要考虑多任务的互斥或同步问题了,这里通过互斥锁来解决这个问题,确保这个结构体参数值被一个临时变量保存过后,才允许修改。
- #include <pthread.h>
- pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 定义互斥锁,全局变量
- pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); // 初始化互斥锁,互斥锁默认是打开的
- // 上锁,在没有解锁之前,pthread_mutex_lock()会阻塞
- pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
- int connfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &cliaddr_len);
- //给回调函数传的参数,&connfd,地址传递
- pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, (void *)client_process, (void *)&connfd); //创建线程
- // 线程回调函数
- void *client_process(void *arg)
- {
- int connfd = *(int *)arg; // 传过来的已连接套接字
- // 解锁,pthread_mutex_lock()唤醒,不阻塞
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
- return NULL;
- }
示例代码:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- #include <pthread.h>
- pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 定义互斥锁,全局变量
- /************************************************************************
- 函数名称: void *client_process(void *arg)
- 函数功能: 线程函数,处理客户信息
- 函数参数: 已连接套接字
- 函数返回: 无
- ************************************************************************/
- void *client_process(void *arg)
- {
- int recv_len = 0;
- char recv_buf[1024] = ""; // 接收缓冲区
- int connfd = *(int *)arg; // 传过来的已连接套接字
- // 解锁,pthread_mutex_lock()唤醒,不阻塞
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
- // 接收数据
- while((recv_len = recv(connfd, recv_buf, sizeof(recv_buf), 0)) > 0)
- {
- printf("recv_buf: %s\n", recv_buf); // 打印数据
- send(connfd, recv_buf, recv_len, 0); // 给客户端回数据
- }
- printf("client closed!\n");
- close(connfd); //关闭已连接套接字
- return NULL;
- }
- //===============================================================
- // 语法格式: void main(void)
- // 实现功能: 主函数,建立一个TCP并发服务器
- // 入口参数: 无
- // 出口参数: 无
- //===============================================================
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- int sockfd = 0; // 套接字
- int connfd = 0;
- int err_log = 0;
- struct sockaddr_in my_addr; // 服务器地址结构体
- unsigned short port = 8080; // 监听端口
- pthread_t thread_id;
- pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); // 初始化互斥锁,互斥锁默认是打开的
- printf("TCP Server Started at port %d!\n", port);
- sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); // 创建TCP套接字
- if(sockfd < 0)
- {
- perror("socket error");
- exit(-1);
- }
- bzero(&my_addr, sizeof(my_addr)); // 初始化服务器地址
- my_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
- my_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
- my_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
- printf("Binding server to port %d\n", port);
- // 绑定
- err_log = bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&my_addr, sizeof(my_addr));
- if(err_log != 0)
- {
- perror("bind");
- close(sockfd);
- exit(-1);
- }
- // 监听,套接字变被动
- err_log = listen(sockfd, 10);
- if( err_log != 0)
- {
- perror("listen");
- close(sockfd);
- exit(-1);
- }
- printf("Waiting client...\n");
- while(1)
- {
- char cli_ip[INET_ADDRSTRLEN] = ""; // 用于保存客户端IP地址
- struct sockaddr_in client_addr; // 用于保存客户端地址
- socklen_t cliaddr_len = sizeof(client_addr); // 必须初始化!!!
- // 上锁,在没有解锁之前,pthread_mutex_lock()会阻塞
- pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
- //获得一个已经建立的连接
- connfd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &cliaddr_len);
- if(connfd < 0)
- {
- perror("accept this time");
- continue;
- }
- // 打印客户端的 ip 和端口
- inet_ntop(AF_INET, &client_addr.sin_addr, cli_ip, INET_ADDRSTRLEN);
- printf("----------------------------------------------\n");
- printf("client ip=%s,port=%d\n", cli_ip,ntohs(client_addr.sin_port));
- if(connfd > 0)
- {
- //给回调函数传的参数,&connfd,地址传递
- pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, (void *)client_process, (void *)&connfd); //创建线程
- pthread_detach(thread_id); // 线程分离,结束时自动回收资源
- }
- }
- close(sockfd);
- return 0;
- }
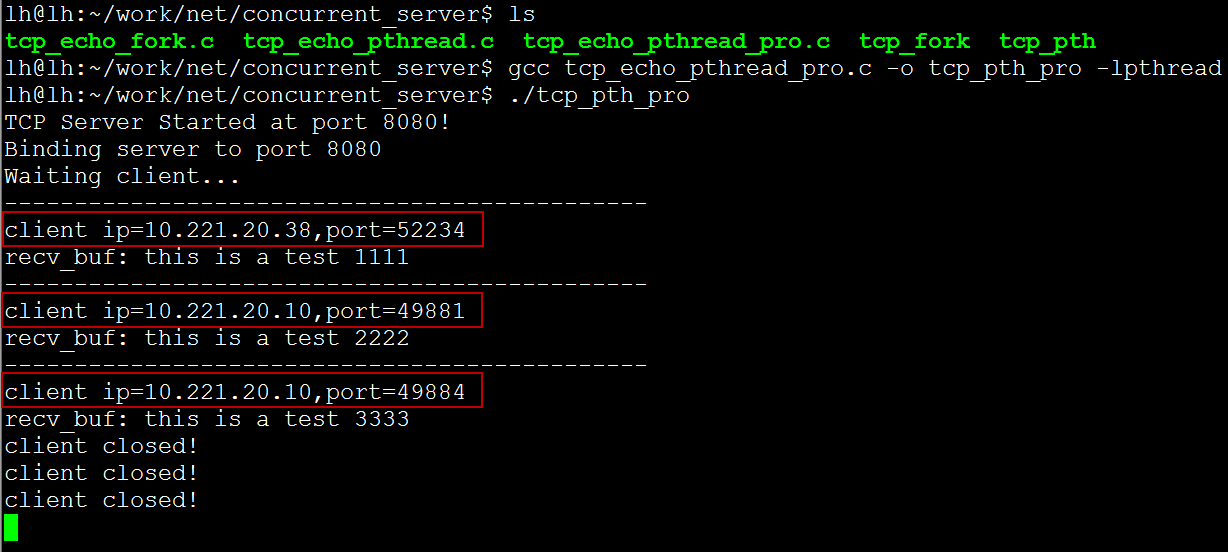
运行结果:






















 770
770

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








