STR_TO_DATE:
You need to tell MySQL how to parse the string, and you do that byfiguring out the pattern and pass it to STR_TO_DATE() as the second parameter.
DATE_FORMAT:
This function is used to print the 'DATE' object in the way you want, you still need to tell the pattern to DATA_FORMAT(). The only one point is that you should pass a 'DATE' type variable to it, instead of a string, so you might need to convert the type before that, however, there are exceptions around.
MySQL Official Online Doc: 11.7. Date and Time Functions
The above doc describes all the functions that work on DATE & TIME.
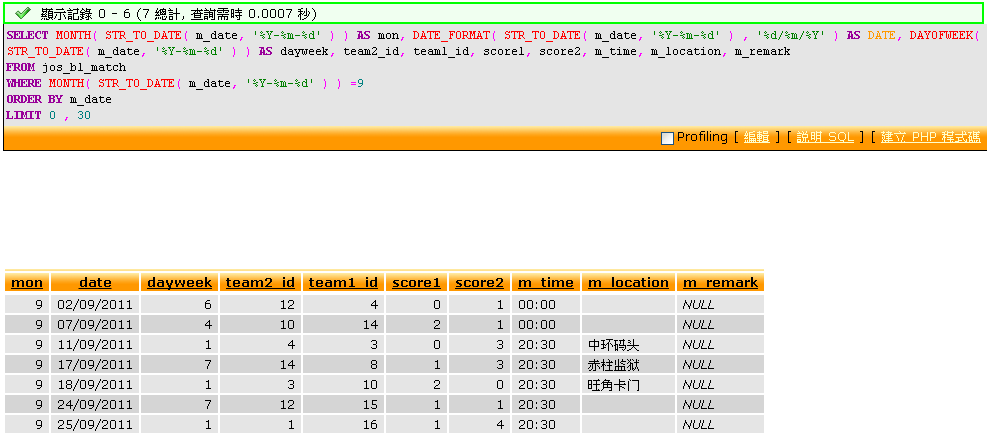
The query I design:
SELECT
MONTH( STR_TO_DATE( m_date, '%Y-%m-%d' ) ) AS mon,
DATE_FORMAT( STR_TO_DATE( m_date, '%Y-%m-%d' ) , '%d/%m/%Y' ) AS DATE,
DAYOFWEEK( STR_TO_DATE( m_date, '%Y-%m-%d' ) ) AS dayweek,
team2_id, team1_id, score1, score2, m_time, m_location, m_remark
FROM jos_bl_match
WHERE MONTH( STR_TO_DATE( m_date, '%Y-%m-%d' ) ) =9
ORDER BY m_date
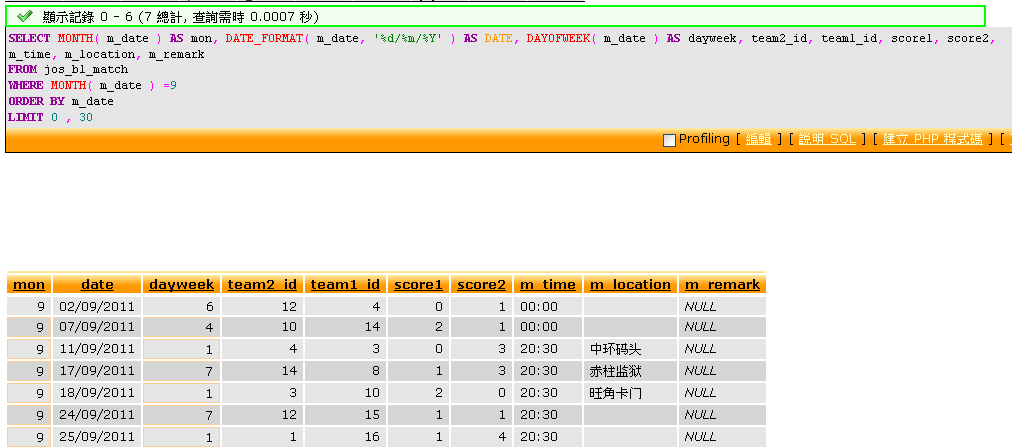
This is the normal way of thinking, but actually, MySQL use '0000-00-00' as format of date, so the string follows this format can be used as DATE type implicitly. That means, the STR_TO_DATE can be eliminated from our above query statement, and become:
SELECT
MONTH( m_date ) AS mon,
DATE_FORMAT( m_date , '%d/%m/%Y') AS date,
DAYOFWEEK( m_date) AS dayweek,
team2_id, team1_id, score1, score2, m_time, m_location, m_remark
FROM jos_bl_match WHERE MONTH( m_date ) = 9 ORDER BY m_dateHere is the performance comparison of the two methods, may be due to the data volume is too small, the time consumed is the same:
REFS:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3296725/parse-date-in-mysql
http://www.roseindia.net/sql/sqldate/mysql-date-parse.shtml
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1279061/php-parse-date-string























 904
904

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








