Android打包apk时,有时候需要打各种渠道包,例如 豌豆荚、华为手机市场、小米市场、360市场等,那么每一种渠道打包时,都需要配置不同的数据元,如果渠道较多,那么打包也是一个体力活。还有,我们在开发项目中,有测试环境、生产环境、备用环境等,每次打包不同的环境,可能需要修改服务器IP以及端口号,那么打包也有点麻烦。那么针对以上这两种问题,到底有没有一个合适的方案可以解决呢!答案是肯定的!我们可以采用Ant来实现对Android应用的自动打包。
使用Ant编译打包Apk,IDE是基于Eclipse,如果你使用的是Android Studio,那么请查看使用Gradle如何打渠道包。
Ant安装以及配置
首先需要在Ant官网下载Ant下载链接,下载完成后,解压到磁盘的某一个跟目录下,接着需要在环境变量中配置,
在环境变量Path中添加 ;%ANT_HOME%/bin;%ANT_HOME%/lib;其中ANT_HOME是Ant的解压目录。例如‘E:\ant\apache-ant-1.9.7-bin\apache-ant-1.9.7’配置成功后,可以在dos中,输入命令 ‘ant -version’,如果输出结果,表示配置成功。展示一下我电脑上的结果截图,
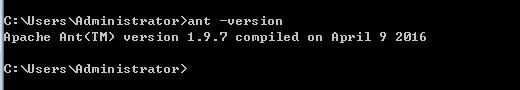
Ant编译打包
1. 创建一个Android项目。(具体操作就不多说了)
2. 使用Android SDK命令创建Ant的build.xml。命令‘android update project –path .’
具体步骤: 打开命令行工具,切换路径到项目所在的目录,然后使用 android update project –path . 命令,在当前目录下面创建build.xml文件,注意不要忘掉后面的 ‘.’,path 前面是两个‘-’。

3. 在IDE上刷新工程,可以看到项目根目录下多了build.xml以及local.properties两个文件。
local.properties指明了我们的android SDK的目录。
build.xml则是ant构建的脚本,里面其实大部分都是注释,这是因为生成的这个build.xml直接引用了android SDK自带的构建脚本。
下面列举build.xml文件的标签。
1.project标签。
project标签是构建文件的根标签。
它有如下属性:
name属性:项目名。
default属性:指定project默认执行时执行的target的名称,表示默认的运行目标。
basedir属性:指定项目的基准目录。
description属性:项目的描述。2.target标签。
target可以看做是一个任务,一个项 目标签下可以有一个或多个target标签。一个target标签可以依赖其他的target标签。
它有如下属性:
name属性:指定target元素的名称。
depends属性:用于描述target之间的依赖关系。
if属性:用于验证指定的属性是否存在,若不存在,所在target将不会被执行。
unless 属性:该属性的功能与 if 属性的功能正好相反,它也用于验证指定的属性是否存在,若不存在,所在 target 将会被执行。
description 属性:该属性是关于 target 功能的简短描述和说明。3.property 标签
property 用于定义变量或参数的定义。
它有如下属性:
name属性:变量名字
value属性:变量值4.mkdir标签
mkdir该标签用于创建一个目录,它有一个属性dir用来指定所创建的目录名。
5.jar标签
jar用来生成一个JAR文件。
常用属性有:
dir : 表示要创建目录的路径(包含要创建的目录)。6.javac标签
javac该标签用于编译一个或一组java文件。
常用属性有:
srcdir : 表示需要编译的java文件的目标文件夹,一般是项目的src文件夹。
destdir : 表示编译之后的class文件存放的位置,一般是build/classes。7.java标签
java该标签用来执行编译生成的.class文件。
8.delete标签
delete该标签用于对文件或目录进行删除。
PS:Ant的depends属性指定了target的执行顺序。Ant会依照depends属性中target出现顺序依次执行每个target。在执行之前,首先需要执行它所依赖的target。一个target只能被执行一次,即使有多个target依赖于它。如果没有if或unless属性,target总会被执行。
build.xml文件内容如下,有两个文件是需要用户自己手动创建的,并存放在当前项目目录下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project name="ant_app" default="help">
<!-- The local.properties file is created and updated by the 'android' tool.
It contains the path to the SDK. It should *NOT* be checked into
Version Control Systems. -->
<property file="local.properties" />
<!-- The ant.properties file can be created by you. It is only edited by the
'android' tool to add properties to it.
This is the place to change some Ant specific build properties.
Here are some properties you may want to change/update:
source.dir
The name of the source directory. Default is 'src'.
out.dir
The name of the output directory. Default is 'bin'.
For other overridable properties, look at the beginning of the rules
files in the SDK, at tools/ant/build.xml
Properties related to the SDK location or the project target should
be updated using the 'android' tool with the 'update' action.
This file is an integral part of the build system for your
application and should be checked into Version Control Systems.
-->
<!-- 此文件需要我们自己创建-->
<property file="ant.properties" />
<!-- if sdk.dir was not set from one of the property file, then
get it from the ANDROID_HOME env var.
This must be done before we load project.properties since
the proguard config can use sdk.dir -->
<property environment="env" />
<condition property="sdk.dir" value="${env.ANDROID_HOME}">
<isset property="env.ANDROID_HOME" />
</condition>
<!-- The project.properties file is created and updated by the 'android'
tool, as well as ADT.
This contains project specific properties such as project target, and library
dependencies. Lower level build properties are stored in ant.properties
(or in .classpath for Eclipse projects).
This file is an integral part of the build system for your
application and should be checked into Version Control Systems. -->
<loadproperties srcFile="project.properties" />
<!-- quick check on sdk.dir -->
<fail
message="sdk.dir is missing. Make sure to generate local.properties using 'android update project' or to inject it through the ANDROID_HOME environment variable."
unless="sdk.dir"
/>
<!--
Import per project custom build rules if present at the root of the project.
This is the place to put custom intermediary targets such as:
-pre-build
-pre-compile
-post-compile (This is typically used for code obfuscation.
Compiled code location: ${out.classes.absolute.dir}
If this is not done in place, override ${out.dex.input.absolute.dir})
-post-package
-post-build
-pre-clean
-->
<!-- 此文件需要我们自己创建-->
<import file="custom_rules.xml" optional="true" />
<!-- Import the actual build file.
To customize existing targets, there are two options:
- Customize only one target:
- copy/paste the target into this file, *before* the
<import> task.
- customize it to your needs.
- Customize the whole content of build.xml
- copy/paste the content of the rules files (minus the top node)
into this file, replacing the <import> task.
- customize to your needs.
***********************
****** IMPORTANT ******
***********************
In all cases you must update the value of version-tag below to read 'custom' instead of an integer,
in order to avoid having your file be overridden by tools such as "android update project"
-->
<!-- version-tag: 1 -->
<!-- 表示我们引用了sdk的ant的build文件-->
<import file="${sdk.dir}/tools/ant/build.xml" />
</project>ant.properties文件定义一些变量例如keystore密码,apk存放目录等;而custom_rules.xml这个文件就是用户自定义的编译规则文件。(ant.properties文件和custom_rules.xml文件需要我们手动创建)
ant.properties文件的内容大致如下所示,其中keystore密码和alias密码可以不指定(防泄漏),那么在命令执行的过程中会要求你输入,
#keystore文件存放目录
key.store=E:\\me.keystore
#keystore别名
key.alias=me_keystore
#keystore密码
key.store.password=xxxxxxx
#组织密码
key.alias.password=xxxxxxx
#apk.dir表示存放最终生成apk的目录
apk.dir=./apk
#定义项目名称
app.name=ant_app
#渠道号,多个渠道号用逗号分隔
market_channels=91,360,wandoujia,baidu
#测试环境服务器配置
test.server.url=192.168.1.110:8080/xinxing
#生产环境服务器配置
rel.server.url=188.132.121.121:9000/xinxing
#测试环境标识 给apk命名的时候用
test.tag.name=test
#生产环境标识 给apk命名的时候用
release.tag.name=release
#版本号
version=1.2.1ant.properties文件,我们创建好以后,其他项目是可以通用的。下面看看最复杂的、也是最难的custom_rules.xml文件的内容,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project name="custom_rules" >
<!-- 引用ant-contlib这个扩展包,声明一下 -->
<taskdef resource="net/sf/antcontrib/antcontrib.properties" >
<classpath>
<pathelement location="${ant.ANT_HOME}/lib/ant-contrib-1.0b3.jar" />
</classpath>
</taskdef>
<!-- 定义一个时间变量,打完包后跟渠道号一起命名apk -->
<tstamp>
<format
pattern="yyyyMMddhhmm"
property="pktime"
unit="hour" />
</tstamp>
<!-- 定义一个版本号变量,打完包后一起命名apk -->
<property name="version" value="${test.server.url}" />
<!-- 创建apk存放目录 -->
<mkdir dir="${apk.dir}" >
</mkdir>
<!-- 替换参数 然后打包APK -->
<target name="replace_parameter" >
<!-- 替换服务器配置 -->
<replaceregexp
byline="false"
encoding="UTF-8"
flags="g" >
<!-- 这个是正则表达式匹配hostconfig中server的值 -->
<regexp pattern="server>(.*)</server" />
<substitution expression="server>${server_url}</server" />
<fileset
dir=""
includes="res/xml/hostconfig.xml" />
</replaceregexp>
</target>
<!-- 打包测试环境命令就用这个 -->
<target name="deploytest" >
<!-- 传服务器配置参数到 replace_parameter这个打包target -->
<antcall target="replace_parameter" >
<param
name="server_url"
value="${test.server.url}" />
</antcall>
<antcall target="foreach_replacechannel" >
<!-- apk命名时候用到的参数 -->
<param
name="deploy_environment"
value="${test.tag.name}" />
</antcall>
</target>
<!-- 打包生产环境命令就用这个 -->
<target name="deployrel" >
<!-- 传服务器配置参数到 replace_parameter这个打包target -->
<antcall target="replace_parameter" >
<param
name="server_url"
value="${rel.server.url}" />
</antcall>
<antcall target="foreach_replacechannel" >
<!-- apk命名时候用到的参数 -->
<param
name="deploy_environment"
value="${release.tag.name}" />
</antcall>
</target>
<!-- 循环打包的target -->
<target name="foreach_replacechannel" >
<!-- 开始循环打包,从market_channels参数中取出一个渠道号用channel标识,然后通过正则修改manifest文件 -->
<foreach
delimiter=","
list="${market_channels}"
param="channel"
target="modify_manifest" >
</foreach>
</target>
<target name="modify_manifest" >
<replaceregexp
byline="false"
encoding="UTF-8"
flags="g" >
<regexp pattern="android:value="(.*)" android:name="UMENG_CHANNEL"" />
<substitution expression="android:value="${channel}" android:name="UMENG_CHANNEL"" />
<fileset
dir=""
includes="AndroidManifest.xml" />
</replaceregexp>
<!-- 这里设置最终生成包的存放目录以及apk的名称,注意这里是文件名称,所以变量中不允许出现违规字符,否则将无法生成最终的apk(会出现output is not valid 的错误) -->
<property
name="out.final.file"
location="${apk.dir}/${app.name}_${channel}_${deploy_environment}_${pktime}_${version}.apk" />
<antcall target="clean" />
<antcall target="release" />
</target>
</project>以上每一段代码都有注释,相信仔细看几遍的,就会看懂。
经过以上几部操作,我们就可以使用命令打包了。
PS:
1.其中hostconfig.xml是服务地址配置文件,位于‘res/xml’中,打包不同的环境时,就需要修改这个文件。
2.可能有好几个渠道包,那么就需要循环打包,ant没有提供类似for循环这样的功能,所以,我们需要一个拓展包即ant-contrib-1.0b3.jar,ant-contrib-1.0b3.jar下载后,将该jar包放到ant的lib包中即可。
下面就是打包了!
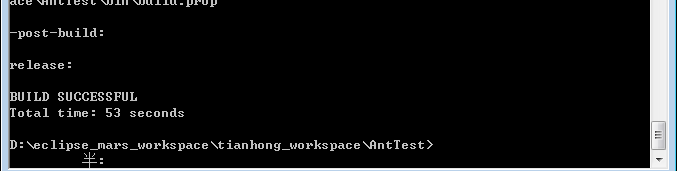
首先在命令行下,定位到项目所在的目录,输入打包命令‘ant deploytest’ (测试环境),等一会,提示如下截图所示,说明打包成功,
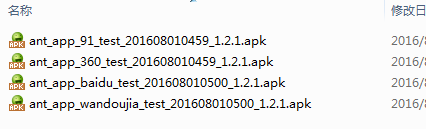
在项目的工作目录下,有一个‘apk’文件夹,我们打开该文件夹,便会看到,各个渠道包了!截图如下所示:
我们打生产环境,输入命名‘ant deployrel’,然后在‘apk’文件夹中,各个渠道包了!截图如下所示:

到这儿,有个疑问,打包是成功了,但是hostconfig.xml和渠道名称是不是真的和我们所配置的一致?那么我们就检验一下,反编译生成的apk,看看里面的数据。
需要查看apk的xml文件,我们需要apktool.jar,具体操作,详见Android安全攻防战,反编译与混淆技术完全解析
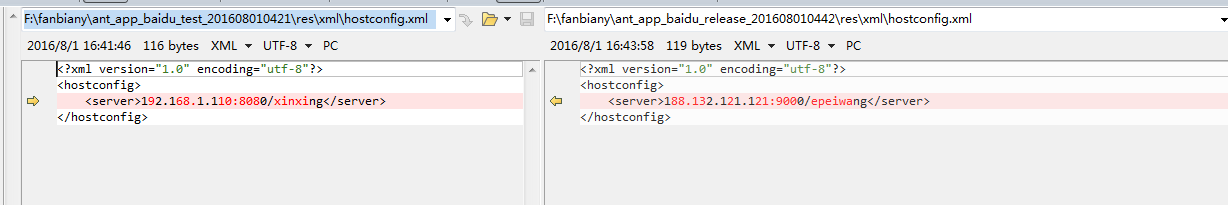
我反编译了ant_app_baidu_release_201608010442.apk和ant_app_baidu_test_201608010421.apk,分别对比他们中的内容,截图如下所示:
hostconfig.xml文件对比
AndroidManifest.xml文件对比

可以看出,使用ant打的包和我们的配置是一致的!
补充:当Android项目依赖了其他项目(library)时,在使用ant 打包,需要注意,首先需要进入到library项目所在的目录,输入命令 android update lib-project -p ./ (注意是 lib-project);
执行完之后,你会发现第三方工程目录下多了build.xml文件和local.properties文件。然后你再执行打包命令就可以成功打包了。
总结
使用Android SDK命令生成来build.xml和local.properties,custom_rules.xml和ant.properties任何项目中都可以通用。
PS:文章参考了windows下Android利用ant自动编译、修改配置文件、批量多渠道,打包生成apk文件
ant-contrib-1.0b3.jar的下载链接
ant-contrib-1.0b3.jar






















 1814
1814

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








