文章目录
动态SQL概述
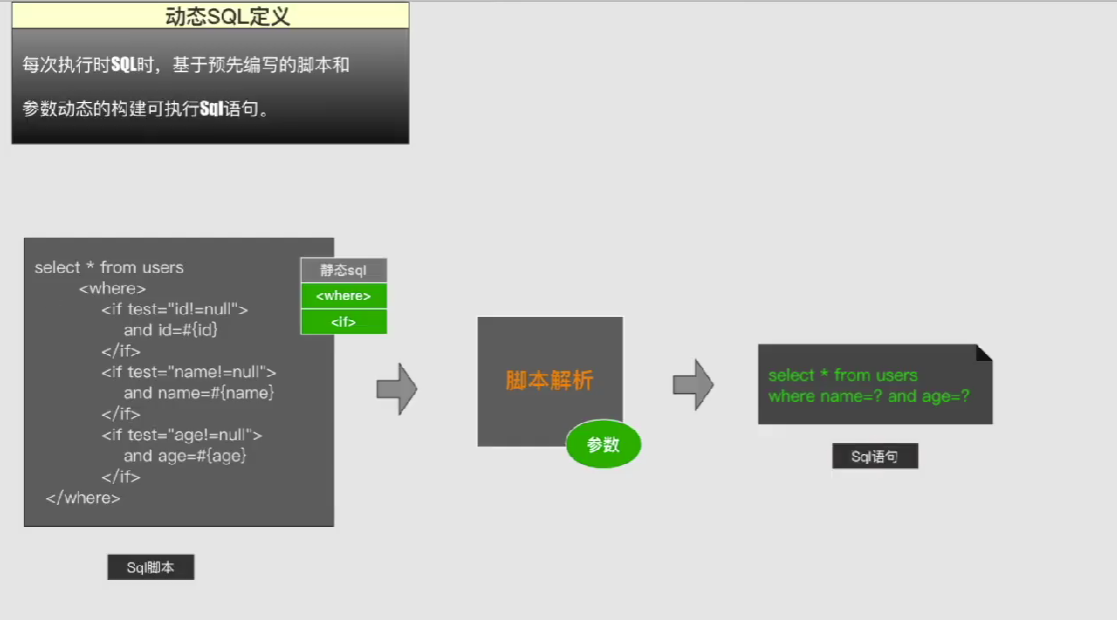
动态SQL是MyBatis 强大功能之一,他免除了在JAVA代码中拼装SQL字符串麻烦,同时保留了我们对SQL的自主控制,更方便进行SQL性能优化改造。
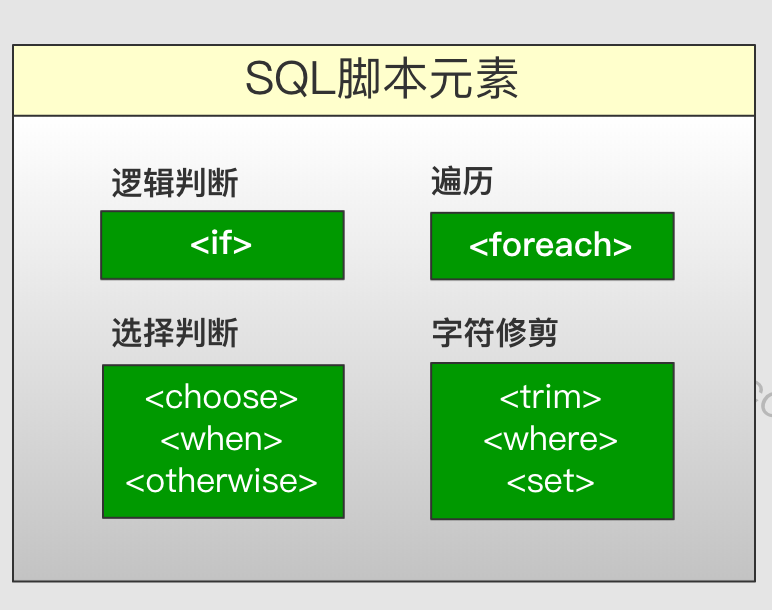
动态SQL中我们使用XML 脚本元素控制SQL的拼装,这都是日常开发中要用到元素,我们一起来回顾一下
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
if
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
在if元素中通过test接受一个OGNL逻辑表达式,可作常规的逻辑计算如:判空、大小、and、or 以及针对子属性的计算。
choose(when、otherwise)
choose 用于在多个条件当中选择其中一个,如果都不满足就使用otherwise中的值。类似java当中的switch。当然这种逻辑用if也能实现只是逻辑表达示相对复杂一些。还有就是if元素中是没有else元素相对应的。
trim(where、set)
trim 用于解决在拼装SQL 后,SQL语句会多出的问题 如下面的例子:
<select id="findBlog"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE
<if test="state != null">
AND state = #{state}
</if>
</select>
如果if 条件满足则最终生成一个SQL,语法上多了一个AND 字符
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE AND state = #{state}
而不满足,SQL也会错误 ,语法上多了一个 WHERE
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE
where 元素只会在子元素返回任何内容的情况下才插入 “WHERE” 子句。而且,若子句的开头为 “AND” 或 “OR”,where 元素也会将它们去除。where 元素等价于以下trim元素
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR ">
...
</trim>
Set 元素用于在修改多个字段时多出的逗号问题,其等价于以下trim元素
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
...
</trim>
foreach
该元素用于对集合值进行遍历,比如构建in的多个条件,或者进行批处理新增修改等。它允许你指定一个集合,声明可以在元素体内使用的集合项(item)和索引(index)变量。
OGNL表达式
OGNL全称是对象导航图语言(Object Graph Navigation Language)是一种JAVA表达式语言,MyBatis用它来实现动态 SQL 的功能。
OGNL的主要作用在于:根据对象的属性来进行值的获取或判断。它可以轻易的根据对象属性的路径访问对象内部的值。
OGNL能实现的主要功能有:
- 访问对象属性:user.name
- 调用方法:user.getName()
- 访问集合元素:user.orders[0]
- 判定是否存在某属性或方法:user.name?
- 调用静态类方法或属性:@java.lang.Math@PI
- 实现比较和算数运算:user.age > 18
- 实现逻辑运算:user.name && user.age < 30
所以OGNL给我们提供了一种简便的方式来操作和判断对象属性的值。我们可以通过"."的方式轻松实现对对象属性的各种操作。
MyBatis使用OGNL来实现动态SQL的各个功能:
- if:判断给定的OGNL表达式结果是否为true,如果为true则加入当前元素内容。
<if test="name != null"> name = #{name} </if> - choose、when、otherwise:相当于Java中的switch语句,根据第一个when中的OGNL表达式是否满足来决定包含哪个元素内容。
<choose> <when test="age > 18"> age > 18 </when> <when test="age == 18"> age == 18 </when> <otherwise> age < 18 </otherwise> </choose> - trim:用于处理字符串的前缀或后缀,其中prefixOverrides和suffixOverrides支持OGNL表达式。
<trim prefix="(" prefixOverrides="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=")">...</trim> - where:用于动态拼接sql的where条件语句,会自动去掉第一个and或or。其中test支持OGNL表达式。
<where> <if test="name != null"> name = #{name} </if> <if test="age != null"> and age = #{age} </if> </where> - set:用于动态拼接sql的set条件语句,会自动去掉最后一个逗号。其中test支持OGNL表达式。
<set> <if test="name != null"> name = #{name}, </if> <if test="age != null"> age = #{age} </if> </set> - forEach:用于迭代集合,它会迭代集合中的每个元素并执行标签体内容
<forEach items="${lists}" index="index" item="item" open="(" close=")" separator=","> #{item} </forEach>
可以看出,OGNL给MyBatis的动态SQL实现提供了强有力的支持。通过简单的OGNL表达式,我们可以判断给定条件是否满足,并决定是否包含某个sql片段,这为MyBatis的动态SQL功能带来了极高的灵活性。
所以,OGNL是MyBatis动态SQL实现的基石,它让MyBatis可以根据条件筛选加入需要的SQL语句,而不仅仅是简单的拼接,这使得MyBatis生成的SQL语句变得异常灵活和强大。
同时我们还要介绍一个工具类:ExpressionEvaluator
所以,ExpressionEvaluator主要提供了两个功能:
- 解析OGNL表达式:将表达式字符串解析成Expression对象,它代表了这个表达式内部的语义结构。
- 求值OGNL表达式:使用Expression对象和指定的对象图上下文来计算表达式最终结果。
它主要提供了以下API:
- parseExpression(String expression):解析OGNL表达式,返回Expression。
- evaluate(String expression, Object root):直接解析并求值表达式,根对象为root,返回结果。
- evaluate(Expression expr, Object root):使用Expression对象expr和根对象root来求值表达式,返回结果。
通过这些API,MyBatis可以将Mapper.xml中的OGNL表达式解析为Expression,然后使用参数对象来求值这个Expression得到最终结果,并据此决定下一步的动作。这使MyBatis可以非常清晰和灵活的支持OGNL表达式,实现动态SQL和延迟加载的功能。
BoundSql
我们前面在看源码的时候经常会看见BoundSql,那么它是什么呢?
BoundSql不是直接的可执行SQL语句。它是一个封装了SQL语句相关信息的POJO类。
当我们调用Mapper中的方法时,MyBatis会解析对应的Mapper.xml文件,并根据我们传入的参数和动态SQL的条件生成最终要执行的SQL语句。这个SQL语句会被封装在BoundSql对象中。
BoundSql中包含的信息有:
- sql:生成的SQL语句本身。
- parameterMappings:sql语句中的参数映射信息。比如#{name}会映射为name等。
- parameters:传入的参数值的Map,键为参数名,值为参数值。
然后MyBatis会使用Configuration中的MappedStatement对象来执行这个SQL,MappedStatement中也包含了BoundSql。
那么MappedStatement和BoundSql有什么关系吗?
MappedStatement和BoundSql有着密切的关系。简单来说:
- MappedStatement表示Mapper.xml中一个查询或更新的定义信息。它包含了SQL语句的ID、参数映射等信息。
- BoundSql表示一个要执行的SQL语句的详细信息。它包含了实际的SQL语句、参数映射和参数值。
当我们调用Mapper接口的方法时,MyBatis会根据方法签名找到对应的MappedStatement。然后它会解析MappedStatement中的SQL语句,并根据我们传入的参数生成最终要执行的SQL,这个SQL会被包装在BoundSql对象中。
所以,一个MappedStatement会对应多个BoundSql,这取决于我们每次调用时传入的不同参数。但同一次调用只会产生一条BoundSql。
MappedStatement可以理解为MyBatis对一条语句的静态定义,而BoundSql是每次执行时动态产生的具体语句信息。
他们的关系可以表达为:
- 一个MappedStatement对应一个Mapper.xml中的查询或更新定义。
- 每次调用Mapper接口方法时,会产生一个BoundSql。
- 这个BoundSql包含了根据MappedStatement和传入参数生成的要执行的最终SQL语句以及参数信息。
- MyBatis会使用MappedStatement和这个BoundSql来执行SQL并返回结果。
动态SQL主流程分析
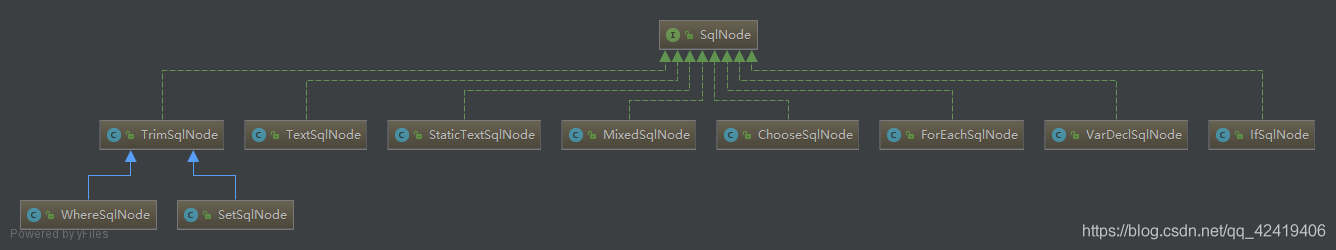
SqlNode
SqlNode是MyBatis中用于代表片段SQL的接口。
平时我们基于 MyBaits 框架进行编写的 Mapper.xml 中每一个 insert/update/delete/select 标签里面的每一行 SQL(包括 include 标签被替换成 SQL ) 文本被抽象为 SqlNode。
每个动态元素都会有一个与之对应的脚本类。如if 对应ifSqlNode、forEarch对应ForEachSqlNode 以此类推下去。:
- StaticTextSqlNode:纯 SQL 语句,不包含任何动态 SQL 语句,例如:
select * from user - TextSqlNode: SQL 语句中含有 ${} 占位符,例如
select * from ${user} - IfSqlNode:if/when 子标签里面的 SQL 语句;
- ChooseSqlNode:choose 子标签里面的 SQL 语句;
- ForEachSqlNode:foreach 子标签里面的 SQL 语句;
- VarDecSqlNode:bind 子标签里面的 SQL 语句;
- TrimSqlNode:trim 子标签里面的 SQL 语句;
- WhereSqlNode:where 子标签里面的 SQL 语句;
- SetSqlNode:set 子标签里面的 SQL 语句;
- MixedSqlNode: 如果 insert/update/delete/select 标签的 SQL 文本不止一行,则把所有的 SqlNode 组装在一起的 SqlNode。
SqlNode 接口只定义了一个 boolean apply(DynamicContext context) 方法,通过 DynamicContext 对象把各个 SqlNode 组装成一条完整的 SQL 语句。
每一部分SQL都是一个SqlNode,它们根据条件的判断会被包含或排除,最终组合成一条完整SQL语句。
这几种SqlNode可以相互嵌套,组成一棵SqlNode树。MyBatis会根据这个树和参数值来生成最终的SQL语句。
DynamicContext
DynamicContext 就像串串的竹签,而 SqlNode 就是竹签上一块块肉肉,一个竹签上的所有肉肉就是 MixedSqlNode,通过竹签把肉肉串在一起,就组成了美味的烧烤——SQL!!
烧烤怎么少了佐料,就如 SQL 语句怎么少了参数呢?参数保存在 DynamicContext 中 bindings 字段中。通过 getSql() 方法获取 StringJoiner 拼接 SQL 语句。
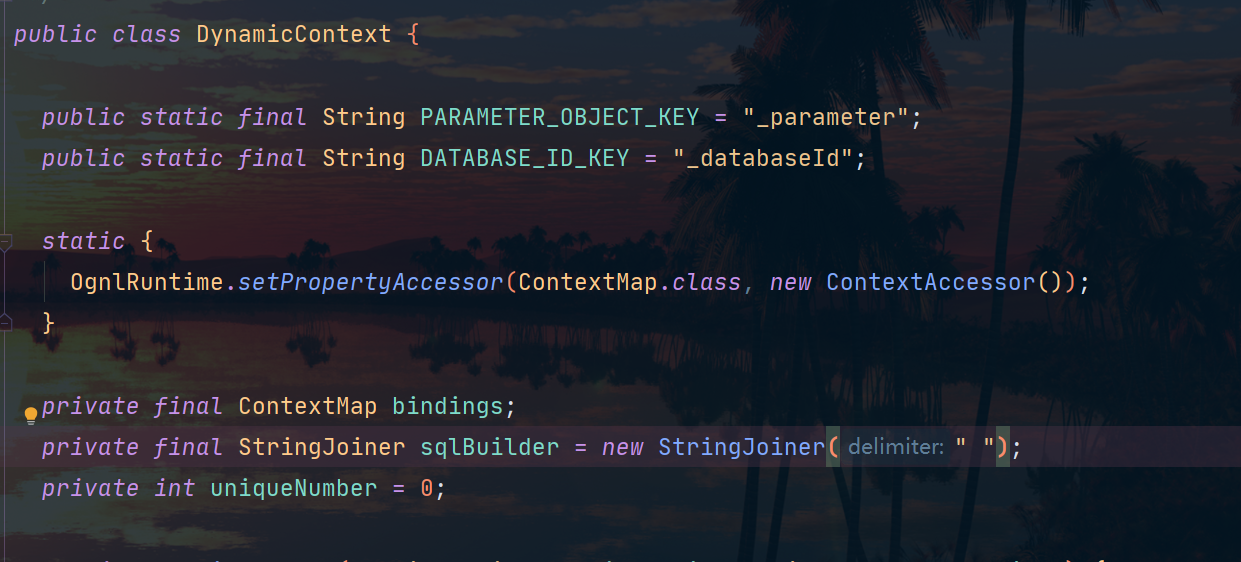
- PARAMETER_OBJECT_KEY:表示参数对象的Key,MyBatis会使用这个Key来从上下文中获取编译时传入的参数对象。
- DATABASE_ID_KEY:表示数据库标识的Key,MyBatis会使用这个Key来从上下文中获取当前数据库的标识,如“MySQL”。
- ContextMap:代表上下文Map,MyBatis会在此Map中保存各种与当前上下文相关的数据,如参数对象、数据库标识等。
- StringJoiner:用于拼接和格式化WHERE子句或SET子句中的SQL片段,这使得生成的SQL更加整洁。
- uniqueNumber:代表一个整数,在遍历集合时用于生成结果集的别名,防止SQL语法错误。
源码解析
StaticTextSqlNode
由于不包含任何动态 SQL 所以不依赖实参来拼接 SQL 语句
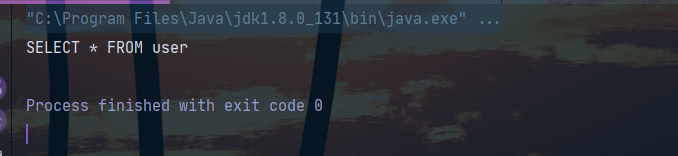
public class StaticTextSqlNodeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
SqlNode staticTextSqlNode = new StaticTextSqlNode("SELECT * FROM user ");
DynamicContext dynamicContext = new DynamicContext(configuration, null);
staticTextSqlNode.apply(dynamicContext);
String sql = dynamicContext.getSql();
System.out.println(sql);
}
}
StaticTextSqlNode 的源码:
public class StaticTextSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final String text;
public StaticTextSqlNode(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}
}
StaticTextSqlNode 源码非常简单就是把 SQL 语句通过 DynamicContext 的 appendSql() 方法拼接在之前的 SQL 语句后面。
TextSqlNode
由于 SQL 语句中含有 ${} 占位符,要解析占位符所以需要参数。
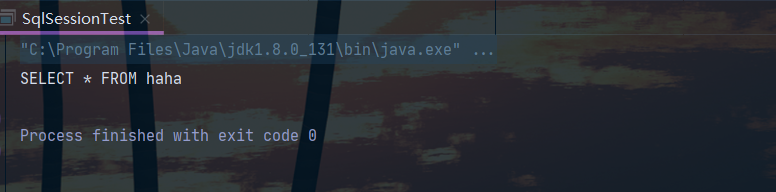
public class TextSqlNodeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
Map<String, Object> paraMap = new HashMap<>();
// 把注释放放开并把下面put 方法注解之后会发现解析 ${} 占位符的值为空字符串
// Map<String, Object> paraMap = null;
paraMap.put("user", "haha");
// paraMap.put("user", "'user'");
SqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode("SELECT * FROM ${user}");
DynamicContext dynamicContext = new DynamicContext(configuration, paraMap);
textSqlNode.apply(dynamicContext);
String sql = dynamicContext.getSql();
System.out.println(sql);
}
}
TextSqlNode的源码:
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
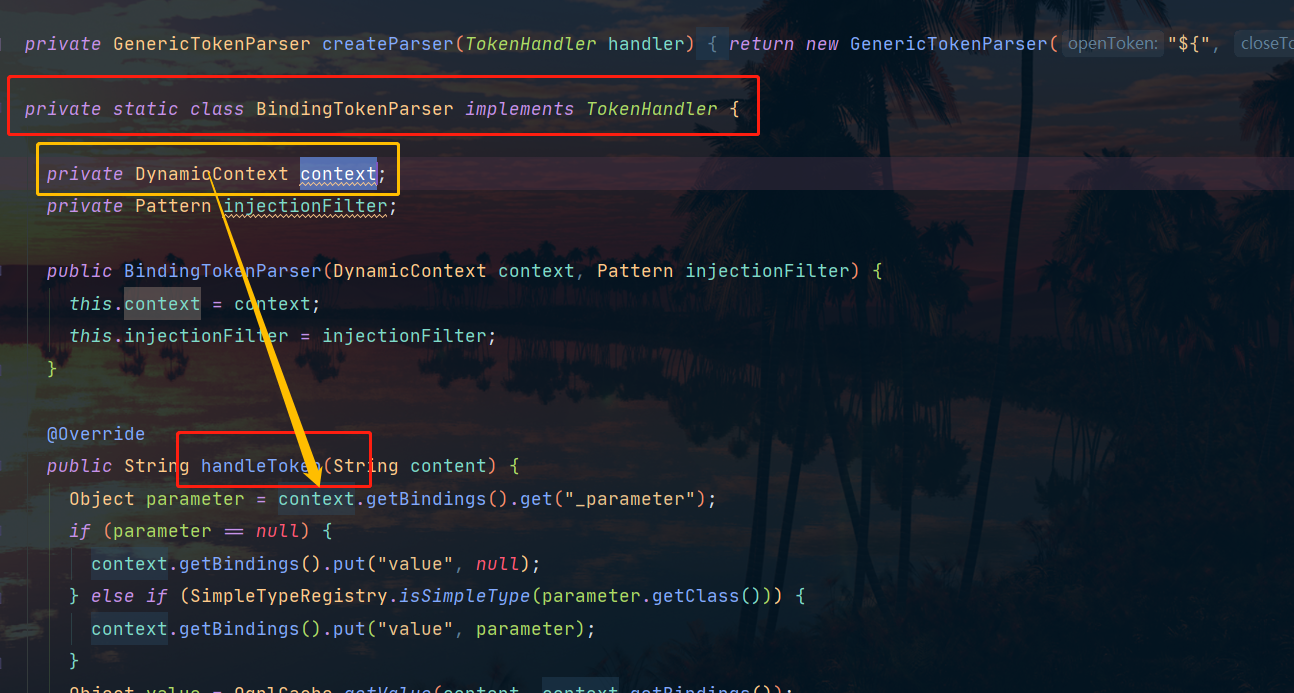
// 通过 createParse 获取 GenericTokenParser(通用令牌解析器) 对象(主要是解决 ${} 占位符)。
// 如果发现 ${} 占位符则通过 BindingTokenParser 的 handleToken(String) 方法返回值替换 ${} 占位符
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));
return true;
}
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
// 通过 DynamicContext 获取实参
Object parameter = context.getBindings().get("_parameter");
if (parameter == null) {
context.getBindings().put("value", null);
} else if (SimpleTypeRegistry.isSimpleType(parameter.getClass())) {
// SimpleTypeRegistry 中 SIMPLE_TYPE_SET 包含的类则存在 DynamicContext 参数中
context.getBindings().put("value", parameter);
}
// 通过 OGNL 从实参中获取 ${} 占位符的值
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(content, context.getBindings());
String srtValue = value == null ? "" : String.valueOf(value); // issue #274 return "" instead of "null"
checkInjection(srtValue);
return srtValue;
}
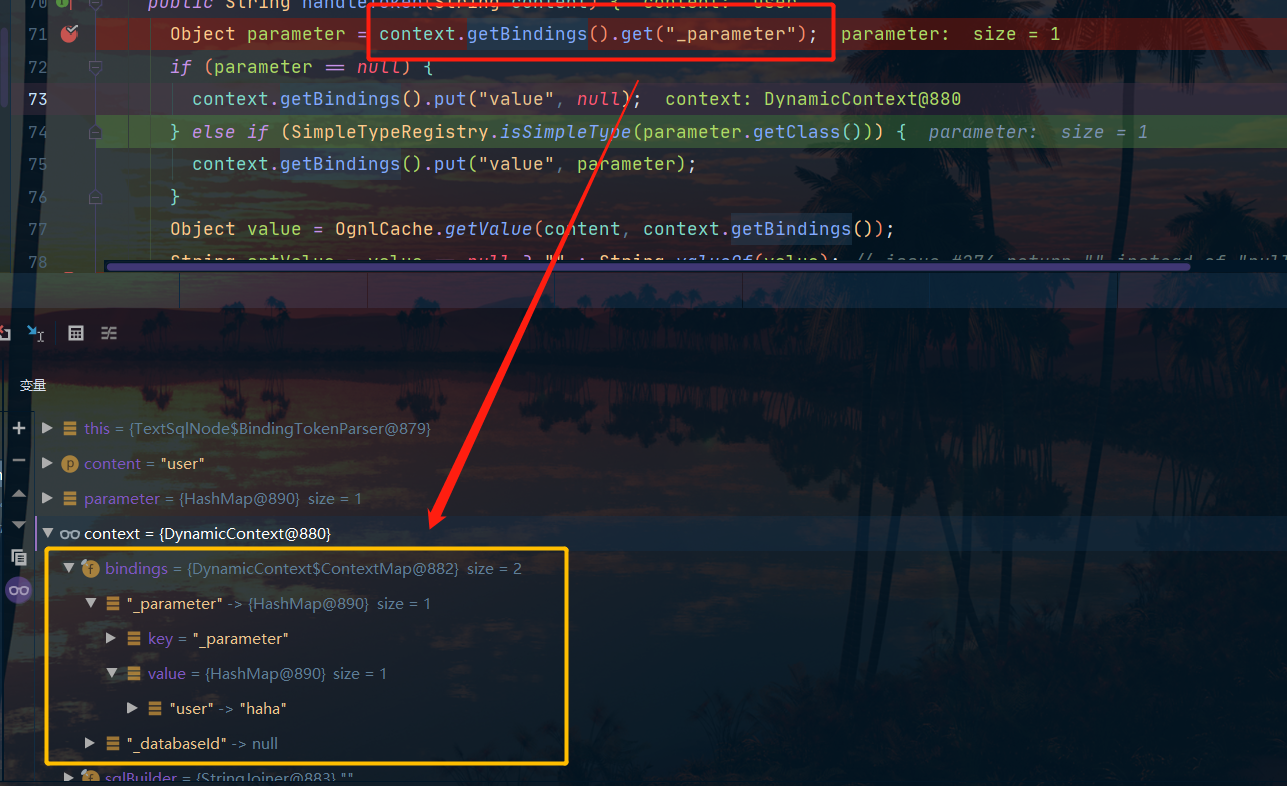
可以看到我们的参数是从DynamicContext中的一个map中拿到的
这个GenericTokenParser 是TextSqlNode的一个静态内部类
IfSqlNode
if/when 子标签里面的 SQL 语句抽象,只要 if 标签里面的 test 表达式为 true 时才拼接 if 标签里面的 SQL 语句。
public class IfSqlNodeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// 实参对象
Map<String, Object> paraMap = new HashMap<>();
paraMap.put("user", "user");
SqlNode staticTextSqlNode = new StaticTextSqlNode("SELECT * FROM user");
// 构建 IfSqlNode 对象,传入 if 标签里面的 SQL 抽象和 test 表达式
SqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(staticTextSqlNode, "user != null");
DynamicContext dynamicContext = new DynamicContext(configuration, paraMap);
// 通过 DynamicContext 拼接 SQL
ifSqlNode.apply(dynamicContext);
// 获取 SQL 语句
String sql = dynamicContext.getSql();
// 控制台输出
System.out.println(sql);
}
}
IfSqlNode的源码:
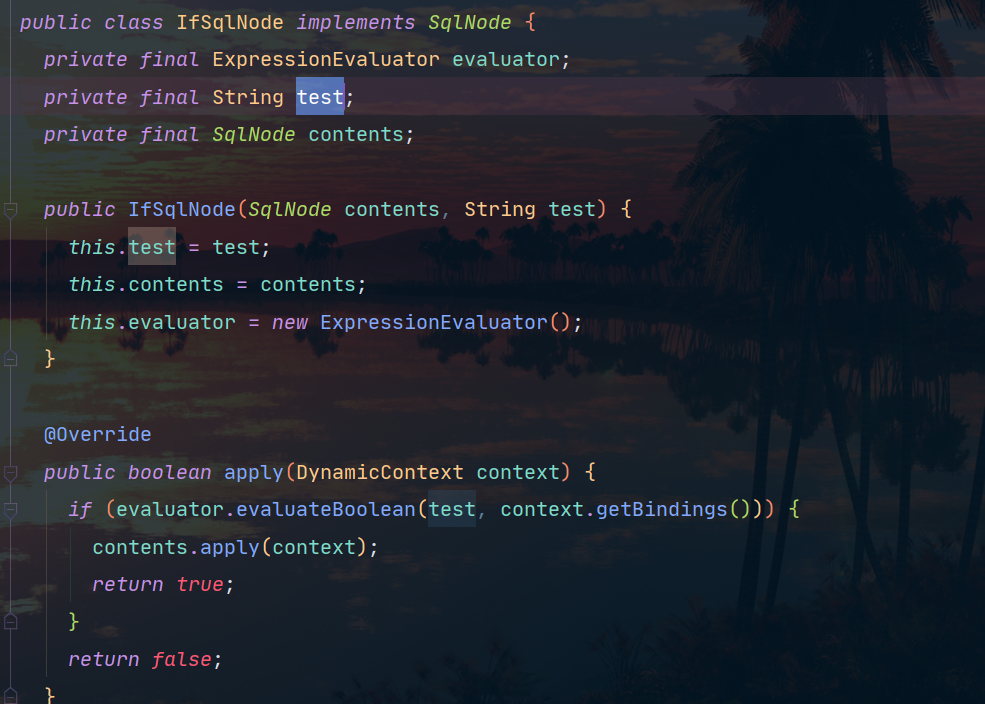
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 通过 OGNL 判断 test 表达式是否成立,表达式里面涉及的属性值通过
// DynamicContext 传入的实参获取。如果成立折拼接 SQL 语句
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
ChooseSqlNode
choose 子标签里面的 SQL 语句抽象,当 when 标签里面的 test 表达式成立时才会拼接里面的 SQL 语句,否则取 otherwise 标签里面的 SQL 语句。类似于 Java 里面的 if… else if…else 语句,只执行一个分支逻辑。
public class ChooseSqlNodeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// 实参对象
Map<String, Object> paraMap = new HashMap<>();
paraMap.put("name", "文海");
SqlNode staticTextSqlNode = new StaticTextSqlNode("SELECT * FROM user WHERE 1 = 1");
// 构建 IfSqlNode 对象,传入 if 标签里面的 SQL 抽象和 test 表达式
SqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(new StaticTextSqlNode(" AND name = #{name}"), "name != null");
SqlNode defaultSqlNode = new StaticTextSqlNode(" AND name = 'wenhai'");
DynamicContext dynamicContext = new DynamicContext(configuration, paraMap);
// 通过 DynamicContext 拼接 SQL
staticTextSqlNode.apply(dynamicContext);
// 通过 DynamicContext 拼接 SQL
ChooseSqlNode chooseSqlNode = new ChooseSqlNode(Collections.singletonList(ifSqlNode), defaultSqlNode);
chooseSqlNode.apply(dynamicContext);
// 获取 SQL 语句
String sql = dynamicContext.getSql();
// 控制台输出
System.out.println(sql);
}
}
ChooseSqlNode的源码:
// 通过构造函数传入 when 标签 SQL 抽象和 otherwise 标签的 SQL 抽象
public ChooseSqlNode(List<SqlNode> ifSqlNodes, SqlNode defaultSqlNode) {
this.ifSqlNodes = ifSqlNodes;
this.defaultSqlNode = defaultSqlNode;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 如果一个分支条件满足就不再执行后面的逻辑
for (SqlNode sqlNode : ifSqlNodes) {
if (sqlNode.apply(context)) {
return true;
}
}
// 前面的 when 标签里面的表达式都不满足,并且有兜底的 otherwise 标签则拼接里面的 SQL
if (defaultSqlNode != null) {
defaultSqlNode.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
ForEachSqlNode
foreach 子标签里面的 SQL 抽象,可以通过标签里面的 item 和 index 设置的变量获取对应的值。index 是数组以及集合的索引值而 Map 类型则是 key 里面的值,item 则是数组以及集合里面的元素而 Map 类型则是 value 里面的值。
public class ForeachSqlNodeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// 实参对象
Map<String, Object> paraMap = new HashMap<>();
// Map<String, String> param = new HashMap<>();
// param.put("wenhai", "文海");
// param.put("wenhai2", "文海2");
// paraMap.put("map", param);
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("wenhai");
list.add("wenhai2");
paraMap.put("list", list);
DynamicContext dynamicContext = new DynamicContext(configuration, paraMap);
SqlNode staticTextSqlNode = new StaticTextSqlNode("SELECT * FROM user WHERE name in");
// 通过 DynamicContext 拼接 SQL
staticTextSqlNode.apply(dynamicContext);
// String collection = "map";
String collection = "list";
String item = "item";
String index = "index";
String open = "(";
String close = ")";
String separator = ",";
ForEachSqlNode forEachSqlNode = new ForEachSqlNode(configuration, new StaticTextSqlNode("#{index}"), collection, index, item, open, close, separator);
forEachSqlNode.apply(dynamicContext);
// 获取 SQL 语句
String sql = dynamicContext.getSql();
// 控制台输出 :SELECT * FROM user WHERE name in ( #{__frch_index_0} , #{__frch_index_1} )
// 同时 DynamicContext 里面的 _parameter 多出以 __frch_#index_n 和 __frch_#item_n 属性值
// 便于后续通过
System.out.println(sql);
}
}
ForEachSqlNode的源码:
/**
* ForEachSqlNode 构造函数
*
* @param configuration 全局 Configuration 对象
* @param contents foreach 标签里面的 SQL 抽象
* @param collectionExpression foreach 标签里面的 collection 属性值
* @param index foreach 标签里面的 index 属性值
* @param item foreach 标签里面的 item 属性值
* @param open foreach 标签里面的 open 属性值
* @param close foreach 标签里面的 close 属性值
* @param separator foreach 标签里面的 separator 属性值
*/
public ForEachSqlNode(Configuration configuration, SqlNode contents, String collectionExpression, String index, String item, String open, String close, String separator) {
this.evaluator = new ExpressionEvaluator();
this.collectionExpression = collectionExpression;
this.contents = contents;
this.open = open;
this.close = close;
this.separator = separator;
this.index = index;
this.item = item;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 获取参数列表
Map<String, Object> bindings = context.getBindings();
// 通过 OGNL 获取 collectionExpression 表达式的值,该值不能为 null,
// 只能是 Iterable 实例和数组已经 Map 实例,其他都会报错
final Iterable<?> iterable = evaluator.evaluateIterable(collectionExpression, bindings);
if (!iterable.iterator().hasNext()) {
return true;
}
// 是否是第一次,第一次不用拼接 separator 值
boolean first = true;
// 如果设置了 open 属性值,则先拼接 open 属性值
applyOpen(context);
int i = 0;
for (Object o : iterable) {
DynamicContext oldContext = context;
// 如果是第一次或者是分隔符没有设置则通过 PrefixedContext 包装 DynamicContext 对象
// 在 appendSql 方法进行拼接 SQL 时候加上设置的前缀(此处就是 “”)
if (first || separator == null) {
context = new PrefixedContext(context, "");
} else {
context = new PrefixedContext(context, separator);
}
// 获取唯一序列号递增用于集合的索引
int uniqueNumber = context.getUniqueNumber();
// 为 DynamicContext 中的类型为 ContextMap 属性保存 foreach 遍历对应的值
// 以 __frch_#{index}_uniqueNumber 和 __frch_#{item}_uniqueNumber 为 key
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map.Entry<Object, Object> mapEntry = (Map.Entry<Object, Object>) o;
applyIndex(context, mapEntry.getKey(), uniqueNumber);
applyItem(context, mapEntry.getValue(), uniqueNumber);
} else {
applyIndex(context, i, uniqueNumber);
applyItem(context, o, uniqueNumber);
}
// 通过 FilteredDynamicContext 包装 PrefixedContext 替换 foreach 标签里面
// 以 #{} 占位符并且使用正则表达式匹配 item 以及 index 属性值为 __frch_#{index}_uniqueNumber 和 __frch_#{item}_uniqueNumber
contents.apply(new FilteredDynamicContext(configuration, context, index, item, uniqueNumber));
if (first) {
first = !((PrefixedContext) context).isPrefixApplied();
}
context = oldContext;
i++;
}
// 如果 foreach 标签里面的 close 属性设置了则拼接在 SQL 语句后面
applyClose(context);
context.getBindings().remove(item);
context.getBindings().remove(index);
return true;
}
剩余的 SqlNode 就不分析了都是类似,通过包装 DynamicContext 以达到效果
动态脚本结构
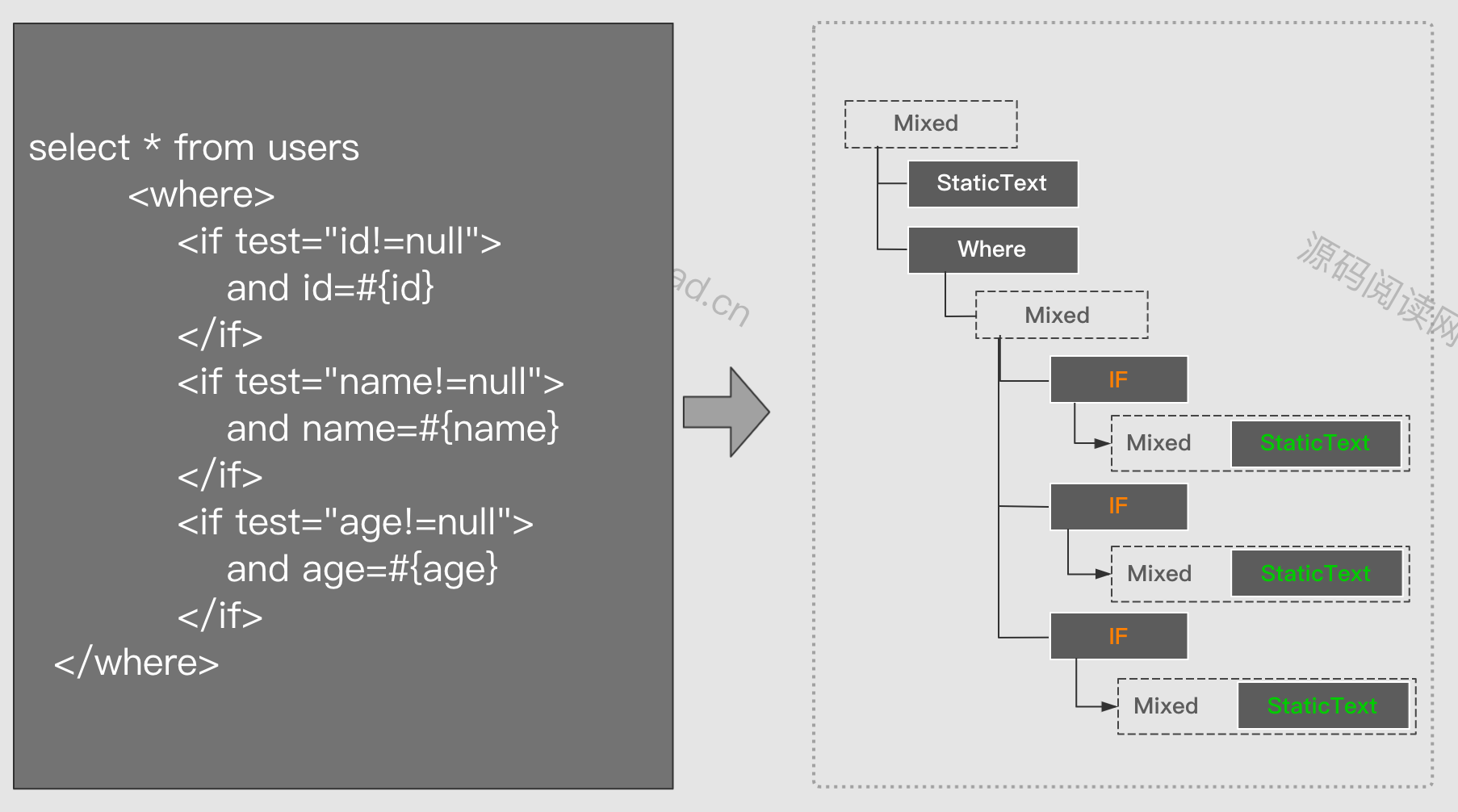
脚本之间是呈现嵌套关系的。比如if元素中会包含一个MixedSqlNode ,而MixedSqlNode下又会包含1至1至多个其它节点。最后组成一棵脚本语法树。如下面左边的SQL元素组成右边的语法树。在节点最底层一定是一个StaticTextNode或 TextNode
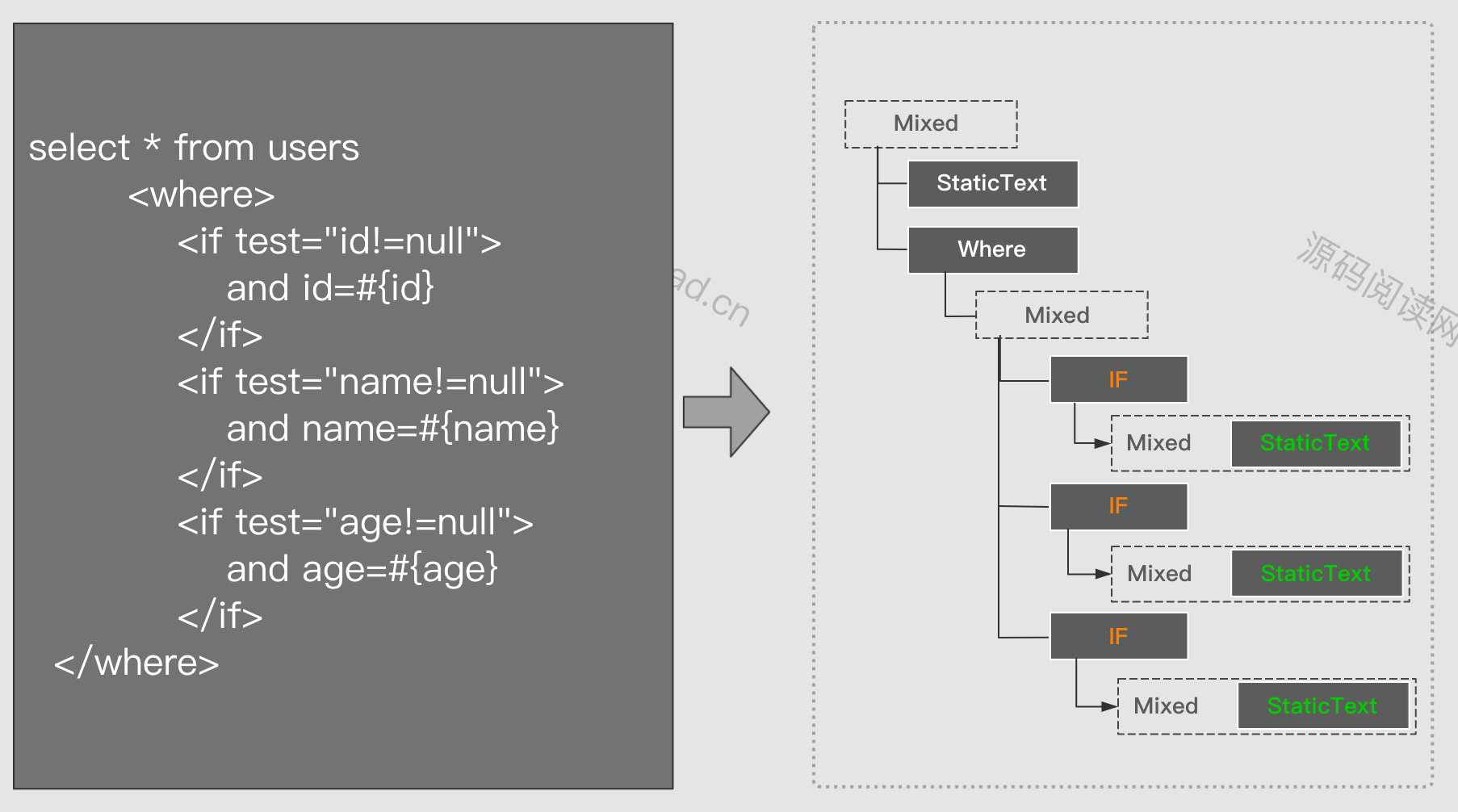
动态脚本执行
SqlNode的接口非常简单,就只有一个apply方法,方法的作用就是执行当前脚本节点逻辑,并把结果应用到DynamicContext当中去。
public interface SqlNode {
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
如IfSqlNode当中执行 apply时先计算If逻辑,如果通过就会继续去访问它的子节点。直到最后访问到TextNode 时把SQL文本添加至 DynamicContext。 通过这种类似递归方式Context就会访问到所有的的节点,并把最后最终符合条件的的SQL文本追加到 Context中。
//IfSqlNode
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {//计算if表达示
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//StaticTextSqlNode
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}
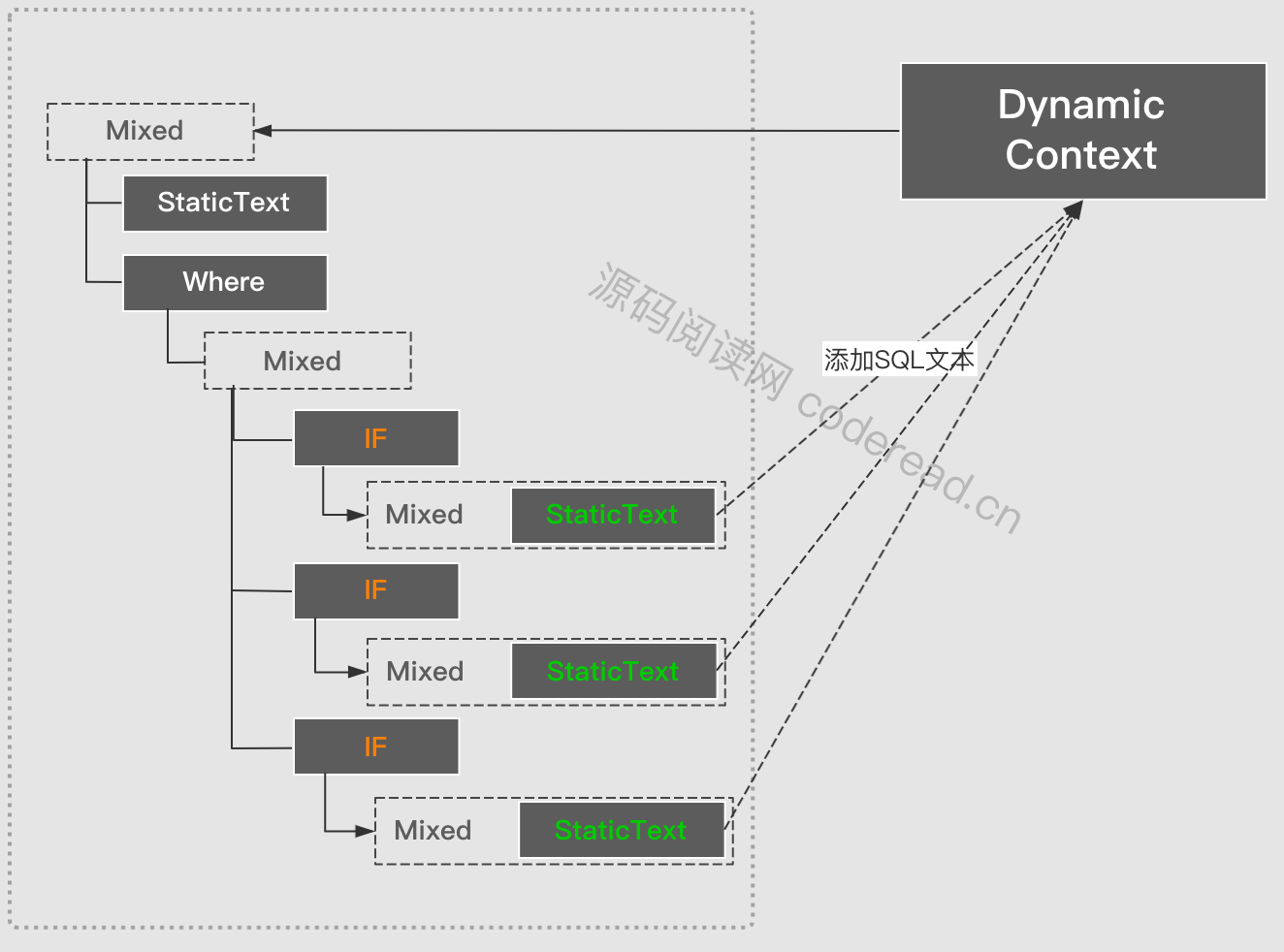
访问完所有节点之后,就会生成一个SQL字符串,但这个并不是可直接执行的SQL,因为里面的参数还是表达式的形式#{name=name} 就需要通过SqlSourceBuilder 来构建可执行的SQL和参数映射ParameterMapping 。然后才能生成BoundSql。下图表示了在上下文中执行所有节点之后,最生成BoundSql。

看源码从动态SQL到BoundSql 过程中,中间还经过了一次StaticSqlSource 生成?为什么要这么做呢,以及从XML中解析出的SqlNode集存储在哪?这里又要有一个新的概念SqlSource SQL源。
SqlSource
SqlNode 通过 DynamicContext 串联 SqlNode 间 SQL 的拼接,其实这个功能是通过 SqlSource 来完成的。通过 SqlSource 接口的 getBoundSql() 方法获取 BoundSql,BoundSql 里面有完整的 SQL 语句以及参数列表和实参。SqlSource 表示从 XML 文件或注释中读取的映射语句的内容。它创建的 SQL 将根据从用户接收到的输入参数传递给数据库。
SqlSource与SqlNode有什么关系?
- 在MyBatis中,SqlSource和SqlNode都是用来封装SQL语句的类。
- SqlNode是MyStaticTextSqlNode、IfSqlNode、WhereSqlNode等,每个SqlNode都会处理一个SQL片段。这些SqlNode可以组合在一起,形成一个SQL语句的树形结构。
- SqlSource则是将SQL语句的树形结构拼接成一个完整的SQL语句,并提供了参数映射功能。SqlSource通常由SqlNode组成,通过解析Mapper.xml文件中的SQL语句树形结构,将最终拼接好的SQL传递给JDBC执行器。
- 因此,SqlNode是生成SqlSource的中间产物。SqlNode通过解析Mapper.xml文件,形成树形结构的SQL语句,SqlSource则是将这些SQL语句拼接成完整的SQL,并进行参数映射,最终交给JDBC执行器执行的对象。
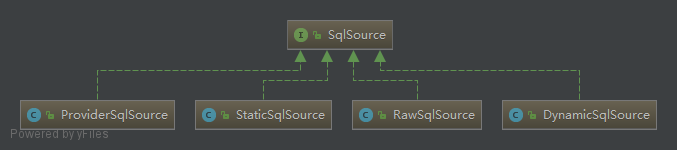
SqlSource有以下几类:
- DynamicSqlSource:针对
动态 SQL和${}占位符的 SQL - RawSqlSource:针对
#{}占位符的 SQL - ProviderSqlSource:针对
@*Provider注解 提供的 SQL - StaticSqlSource:仅包含有
?占位符的 SQL
Mybatis在处理#{}时,会将sql中的#{}替换为?号,调用PreparedStatement的set方法来赋值;
Mybatis在处理${}时,就是把${}替换成变量的值。
StaticSqlSource
/**
* {@link StaticSqlSource} 实例里面的 SQL 语句仅包含 ? 占位符。
*
* @author wenhai
* @date 2021/7/20
* @see SqlSource
* @see RawSqlSource
* @see StaticSqlSource
* @see DynamicSqlSource
* @see ProviderSqlSource
*/
public class StaticSqlSourceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}";
SqlSource staticSqlSource = new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql);
BoundSql boundSql = staticSqlSource.getBoundSql(5L);
System.out.println(boundSql.getSql());
}
}
运行上述程序控制台输出 SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id} ,不做任何处理。
public class StaticSqlSource implements SqlSource {
// SQL 语句
private final String sql;
// 参数映射列表
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
// 全局 Configuration 对象
private final Configuration configuration;
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql) {
this(configuration, sql, null);
}
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 直接构建 BoundSql 对象返回
return new BoundSql(configuration, sql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
}
从 StaticSqlSource#getBoundSql 方法中可以看出在获取 BoundSql 对象时不会对原 SQL 语句进行任何处理。
DynamicSqlSource
/**
* {@link DynamicSqlSource} 包含动态 SQL 和 ${} 占位符
*
* @author wenhai
* @date 2021/7/20
* @see SqlSource
* @see RawSqlSource
* @see StaticSqlSource
* @see DynamicSqlSource
* @see ProviderSqlSource
*/
public class DynamicSqlSourceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// 实参对象
Map<String, Object> paraMap = new HashMap<>();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("wenhai");
list.add("wenhai2");
paraMap.put("list", list);
paraMap.put("id", 5);
SqlNode staticTextSqlNode = new StaticTextSqlNode("SELECT * FROM user WHERE");
SqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(" id = ${id} AND name IN");
String collection = "list";
String item = "item";
String index = "index";
String open = "(";
String close = ")";
String separator = ",";
ForEachSqlNode forEachSqlNode = new ForEachSqlNode(configuration, new StaticTextSqlNode("#{item}"), collection, index, item, open, close, separator);
SqlNode mixedSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(Arrays.asList(staticTextSqlNode, textSqlNode, forEachSqlNode));
SqlSource sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, mixedSqlNode);
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(paraMap);
System.out.println(boundSql.getSql());
}
}
运行上述程序控制台输出 SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = 5 AND name IN ( ? , ? )
public class DynamicSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final SqlNode rootSqlNode;
public DynamicSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 构建 DynamicContext 对象来处理 SqlNode
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
// 通过 SqlSourceBuilder#parse 方法来处理通过 DynamicContext 拼接过的 SQL
// 主要处理 #{} 占位符替换成 ? 占位符和获取 ParameterMapping 列表
// 构建 StaticSqlSource 对象
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 设置参数比如 foreach 标签的里面的额外参数等
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}
}
通过 DynamicSqlSouce#getBoundSql() 方法获取 BoundSql 对象时对 SqlNode 进行了处理,如果是动态 SQL 以及 含义 ${} 占位符的 SQL 语句根据传入的实参进行拼接和替换,如果是 #{} 占位符进行 ?替换,最后通过 StaticSqlSource 构建 BoundSql。
RawSqlSource
/**
* {@link RawSqlSource} 不包含动态 SQL 和 ${} 占位符
*
* @author wenhai
* @date 2021/7/20
* @see SqlSource
* @see RawSqlSource
* @see StaticSqlSource
* @see DynamicSqlSource
* @see ProviderSqlSource
*/
public class RawSqlSourceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
SqlNode sqlNode = new StaticTextSqlNode("SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}");
SqlSource sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, sqlNode, Long.class);
System.out.println(sqlSource.getBoundSql(5L).getSql());
}
}
运行上述程序控制台输出 SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ? ,如果把 #{} 占位符缓存 ${} 占位符或者把 SqlNode 换成别的动态 SqlNode 会出现啥样子结果呢?
public class RawSqlSource implements SqlSource {
// 存储构建好的 StaticSqlSource
private final SqlSource sqlSource;
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 通过 getSql 方法获取 SQL 语句,此时没有传入实参,所以那些动态 SQL 和 ${} 占位符
// 无法处理,只能处理 #{} 占位符的 SqlNode
this(configuration, getSql(configuration, rootSqlNode), parameterType);
}
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 通过 SqlSourceBuilder#parse 方法替换 #{} 占位符为 ? 并构建 #{} 占位符的参数映射列表
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<>());
}
private static String getSql(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, null);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
return context.getSql();
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 直接通过 StaticSqlSource#getBoundSql 获取 BoundSql 实例
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
}
通过源码分析可以回答例子里面提出的问题。如果是 ${} 占位符则不处理,动态 SQL 有可能会报错或者处理后的 SQL 语句不完整等。
ProviderSqlSource
/**
* {@link ProviderSqlSource} @*Provider 注解提供的 SQL
*
* @author wenhai
* @date 2021/7/21
* @see SqlSource
* @see RawSqlSource
* @see StaticSqlSource
* @see DynamicSqlSource
* @see ProviderSqlSource
*/
public class ProviderSqlSourceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
SelectProvider provider = UserMapper.class.getMethod("select", String.class).getAnnotation(SelectProvider.class);
SqlSource providerSqlSource = new ProviderSqlSource(configuration, provider, null, null);
System.out.println(providerSqlSource.getBoundSql("wenhai").getSql());
}
public String getSql() {
return "SELECT * FROM user WHERE name = #{name}";
}
interface UserMapper {
@SelectProvider(type = ProviderSqlSourceDemo.class, method = "getSql")
List<User> select(String name);
}
}
运行上述程序控制台输出 SELECT * FROM user WHERE name = ?
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 通过 @*Provider 注解元信息通过反射调用方法拿到 SQL,
// 然后通过 XMLLanguageDriver#createSqlSource 方法解析 SQL 语句
// 获取 DynamicSqlSource/RawSqlSource -> StaticSqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = createSqlSource(parameterObject);
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
总结一下:
根据 SQL 来源解析 SQL 获取 SqlNode,根据 SqlNode 获取对应的 SqlSource 是 DynamicSqlSource 还是 RawSqlSource。如果是 DynamicSqlSource 根据实参拼接动态 SQL 和处理 ${} 占位符,然后通过 SqlSourceBuilder#parse() 方法转换为 StaticSqlSource,而 RawSqlSource 在实例化的时候就已经通过 SqlSourceBuilder#parse() 方法转换为 StaticSqlSource,不依赖实参所以性能比 DynamicSqlSource 快。ProviderSqlSource 通过解析 SQL 语句之后通过 XMLLanguageDriver#createSqlSource() 方法获取 DynamicSqlSource 或者 RawSqlSource。
总结
在上层定义上每个Sql映射(MappedStatement)中都会包含一个SqlSource 用来获取可执行Sql(BoundSql)。SqlSource又分为原生SQL源与动态SQL源,以及第三方源。其关系如下图:
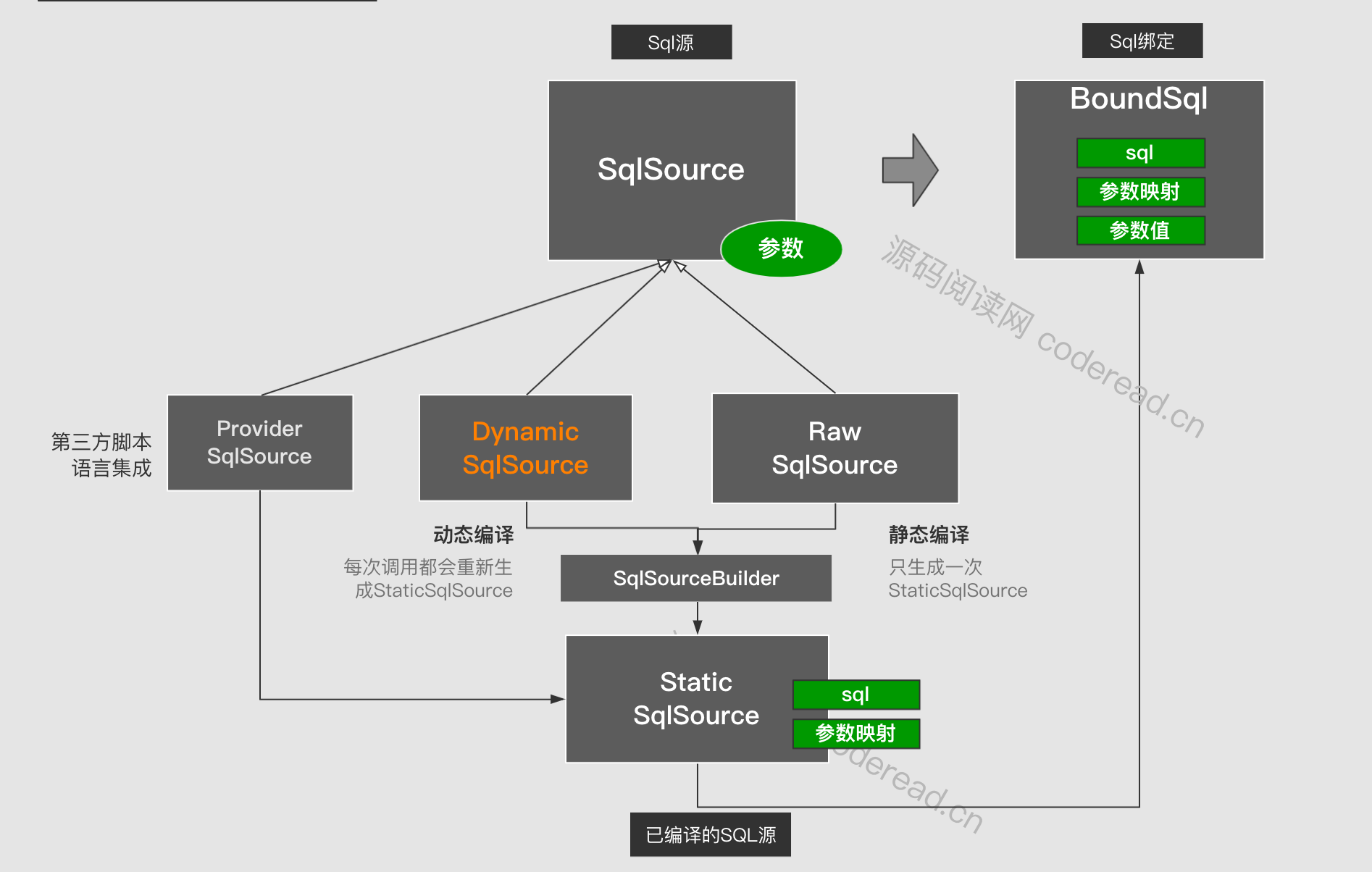
- ProviderSqlSource :第三方法SQL源,每次获取SQL都会基于参数动态创建静态数据源,然后在创建BoundSql
- DynamicSqlSource:动态SQL源包含了SQL脚本,每次获取SQL都会基于参数又及脚本,动态创建创建BoundSql
- RawSqlSource:不包含任何动态元素,原生文本的SQL。但这个SQL是不能直接执行的,需要转换成BoundSql
- StaticSqlSource:包含可执行的SQL,以及参数映射,可直接生成BoundSql。前面三个数据源都要先创建StaticSqlSource然后才创建BoundSql。
SqlSource解析过程
SqlSource 是基于XML解析而来,解析的底层是使用Dom4j 把XML解析成一个个子节点,在通过 XMLScriptBuilder 遍历这些子节点最后生成对应的Sql源。其解析流程如下图:
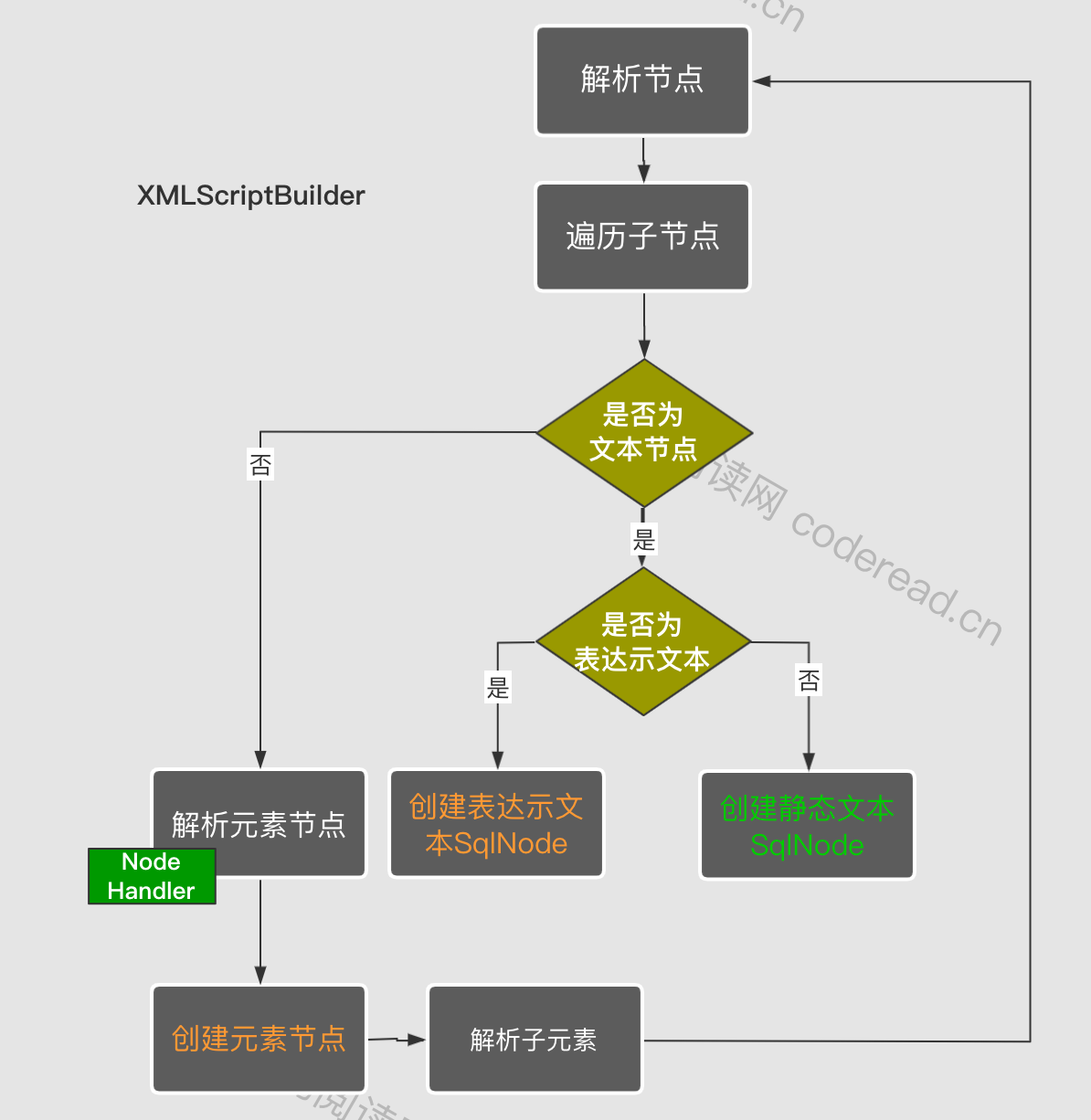
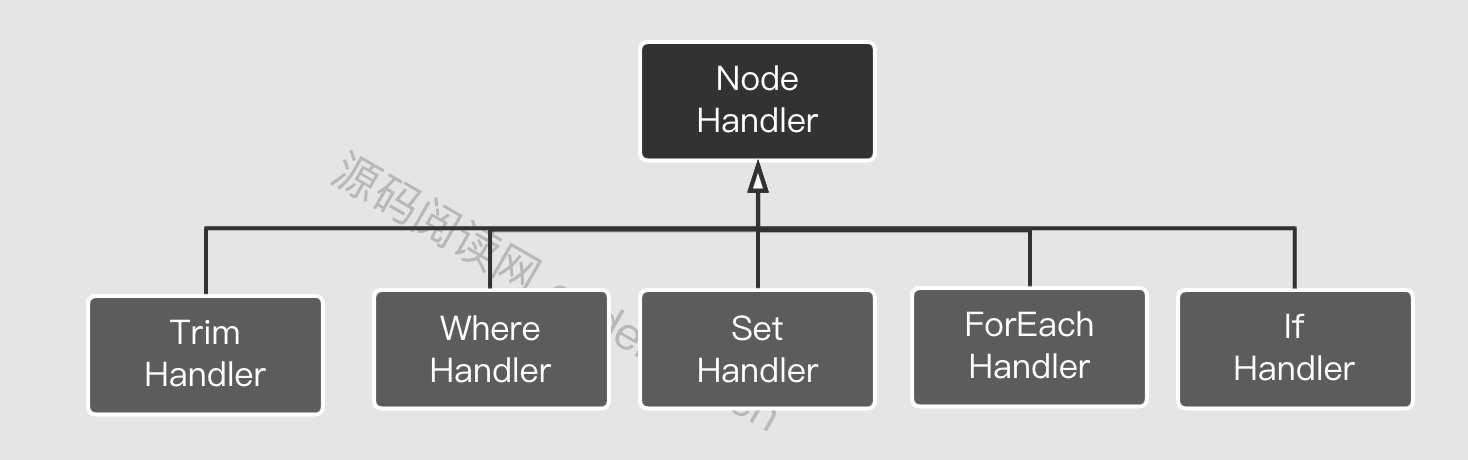
从图中可以看出这是一种递归式的访问 所有节点,如果是文本节点就会直接创建TextNode 或StaticSqlNode。否则就会创建动态脚本节点如IfSqlNode等。这里每种动态节点都会对应的处理器(NodeHandler)来创建。创建好之后又会继续访问子节点,让递归继续下去。当然子节点所创建的SqNode 也会作为当前所创建的元素的子节点而存在。























 230
230











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










