逻辑斯谛回归LogisticRegression
逻辑斯谛回归
逻辑斯谛回归(Logistic Regression, LR)是统计学习中的经典分类方法。常见的逻辑斯谛回归模型包括二项逻辑斯谛回归、多项逻辑斯谛回归(多项逻辑斯谛回归可以看做是二项LR的扩展).
定义 逻辑斯谛回归模型
二项逻辑斯谛回归
二项逻辑斯谛回归模型是如下条件概率分布:
(1)
P
(
Y
=
1
∣
x
)
=
exp
(
w
⋅
x
+
b
)
1
+
exp
(
w
⋅
x
+
b
)
{P(Y=1|x)=\frac{\exp(w \cdot x+b)}{1+\exp(w \cdot x+b)} \tag{1}}
P(Y=1∣x)=1+exp(w⋅x+b)exp(w⋅x+b)(1)
(2)
P
(
Y
=
0
∣
x
)
=
1
1
+
exp
(
w
⋅
x
+
b
)
{P(Y=0|x)=\frac{1}{1+\exp(w \cdot x+b)}\tag{2}}
P(Y=0∣x)=1+exp(w⋅x+b)1(2)
其中
x
∈
R
n
x\in \mathcal{R}^{n}
x∈Rn是输入,
Y
∈
{
0
,
1
}
Y\in \{0,1\}
Y∈{0,1}是输出,
w
∈
R
n
w \in \mathcal{R}^{n}
w∈Rn是权值向量参数,
b
∈
R
b\in \mathcal{R}
b∈R称为偏置,
w
⋅
x
w\cdot x
w⋅x为
w
w
w和
x
x
x的内积。
将权值向量和输入向量加以扩充,仍记作 w w w, x x x,即 w = ( w ( 1 ) , w ( 2 ) , . . . , w ( n ) , b ) T w=\left(w^{(1)},w^{(2)},...,w^{(n)},b \right)^{T} w=(w(1),w(2),...,w(n),b)T, x = ( x ( 1 ) , x ( 2 ) , . . . , x ( n ) ) x=\left(x^{(1)},x^{(2)},...,x^{(n)}\right) x=(x(1),x(2),...,x(n)),则二项逻辑斯谛回归模型如下:
(3) P ( Y = 1 ∣ x ) = exp ( w ⋅ x ) 1 + exp ( w ⋅ x ) {P(Y=1|x)=\frac{\exp(w\cdot x)}{1+\exp(w\cdot x)} \tag{3}} P(Y=1∣x)=1+exp(w⋅x)exp(w⋅x)(3)
(4) P ( Y = 0 ∣ x ) = 1 1 + exp ( w ⋅ x ) {P(Y=0|x)=\frac{1}{1+\exp(w\cdot x)}\tag{4}} P(Y=0∣x)=1+exp(w⋅x)1(4)
多项逻辑斯谛回归
二项逻辑斯谛回归常用于二分类,可以将二项逻辑斯谛回归扩展为多项逻辑斯谛回归模型,用于多分类任务。
设离散型随机变量
Y
Y
Y的取值集合为
{
1
,
2
,
.
.
.
,
K
}
\{1,2,...,K\}
{1,2,...,K},则多项逻辑斯谛回归模型为:
(5)
P
(
Y
=
k
∣
x
)
=
exp
(
w
k
⋅
x
)
1
+
∑
k
=
1
K
−
1
exp
(
w
k
⋅
x
)
{P(Y=k|x)=\frac{\exp(w_k \cdot x)}{1+\sum_{k=1}^{K-1} \exp(w_k \cdot x)}\tag{5}}
P(Y=k∣x)=1+∑k=1K−1exp(wk⋅x)exp(wk⋅x)(5)
其中,
x
∈
R
n
+
1
,
w
k
∈
R
n
+
1
x \in \mathcal{R}^{n+1},w_k \in \mathcal{R}^{n+1}
x∈Rn+1,wk∈Rn+1
代码案例
LogisticRegression算法案例 python实现(iris数据)
案例代码已上传:Github地址
from math import exp
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
定义LR回归模型分类器
class LogisticReression:
def __init__(self, max_iter=200, learning_rate=0.01):
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
def sigmoid(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + exp(-x))
def data_matrix(self, X):
data_mat = []
for d in X:
data_mat.append([1.0, *d])
return data_mat
#训练
def train(self, X, y):
# label = np.mat(y)
data_mat = self.data_matrix(X) # m*n
self.weights = np.zeros((len(data_mat[0]), 1), dtype=np.float32)
for iter_ in range(self.max_iter):
for i in range(len(X)):
result = self.sigmoid(np.dot(data_mat[i], self.weights))
error = y[i] - result
self.weights += self.learning_rate * error * np.transpose(
[data_mat[i]])
print('LR模型学习率={},最大迭代次数={}'.format(
self.learning_rate, self.max_iter))
# 准确率
def accuracy(self, X_test, y_test):
right = 0
X_test = self.data_matrix(X_test)
for x, y in zip(X_test, y_test):
result = np.dot(x, self.weights)
if (result > 0 and y == 1) or (result < 0 and y == 0):
right += 1
return right / len(X_test)
第一步:构建数据
def create_data():
iris = load_iris()
df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
df['label'] = iris.target
df.columns = ['sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label']
data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0,1,-1]])
return data[:,:2], data[:,-1]
X, y = create_data()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3)
第二步:训练并测试精度
LR = LogisticReression()
LR.train(X_train, y_train)
LR.accuracy(X_test, y_test)
LR模型学习率=0.01,最大迭代次数=200
精度:1.0
第三步:效果展示
x_ponits = np.arange(3, 9)
y_ = -(LR.weights[1]*x_ponits + LR.weights[0])/LR.weights[2]
plt.plot(x_ponits, y_)
#绘制图
plt.scatter(X[:50,0],X[:50,1], label='0')
plt.scatter(X[50:,0],X[50:,1], label='1')
plt.legend()
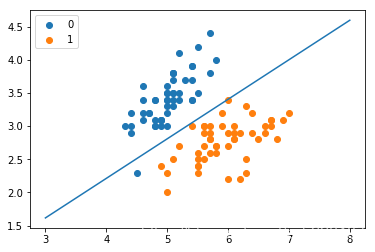
sklearn中的LogisticRegression案例代码
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn import metrics
import seaborn as sn
第一步:构建数据集
candidates = {'gmat': [780,750,690,710,680,730,690,720,740,690,610,690,710,680,770,610,580,650,540,590,620,600,550,550,570,670,660,580,650,660,640,620,660,660,680,650,670,580,590,690],
'gpa': [4,3.9,3.3,3.7,3.9,3.7,2.3,3.3,3.3,1.7,2.7,3.7,3.7,3.3,3.3,3,2.7,3.7,2.7,2.3,3.3,2,2.3,2.7,3,3.3,3.7,2.3,3.7,3.3,3,2.7,4,3.3,3.3,2.3,2.7,3.3,1.7,3.7],
'work_experience': [3,4,3,5,4,6,1,4,5,1,3,5,6,4,3,1,4,6,2,3,2,1,4,1,2,6,4,2,6,5,1,2,4,6,5,1,2,1,4,5],
'admitted': [1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(candidates,columns= ['gmat', 'gpa','work_experience','admitted'])
df[:10]

X = df[['gmat', 'gpa','work_experience']]
y = df['admitted']
# 75%的数据用来做训练集,25%的数据用作测试集
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.25,random_state=0)
logistic_regression= LogisticRegression()
#训练
logistic_regression.fit(X_train,y_train)
#预测
y_pred=logistic_regression.predict(X_test)
#绘制热力图
confusion_matrix = pd.crosstab(y_test, y_pred, rownames=['Actual'], colnames=['Predicted'])
sn.heatmap(confusion_matrix, annot=True)
print('精度: ',metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))

案例地址
案例代码已上传:Github地址
参考资料:
[1] 《统计学习方法》
Github地址https://github.com/Vambooo/lihang-dl
更多技术干货在公众号:深度学习学研社



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










