=====================================================
最简单的基于FFmpeg的libswscale的示例系列文章列表:
最简单的基于FFmpeg的libswscale的示例(YUV转RGB)
最简单的基于FFmpeg的libswscale的示例附件:测试图片生成工具
=====================================================
本文记录一个基于FFmpeg的libswscale的示例。Libswscale里面实现了各种图像像素格式的转换,例如YUV与RGB之间的转换;以及图像大小缩放(例如640x360拉伸为1280x720)功能。而且libswscale还做了相应指令集的优化,因此它的转换效率比自己写的C语言的转换效率高很多。
本文记录的程序将像素格式为YUV420P,分辨率为480x272的视频转换为像素格式为RGB24,分辨率为1280x720的视频。
流程
简单的初始化方法
Libswscale使用起来很方便,最主要的函数只有3个:
(1) sws_getContext():使用参数初始化SwsContext结构体。
(2) sws_scale():转换一帧图像。
(3) sws_freeContext():释放SwsContext结构体。
其中sws_getContext()也可以用另一个接口函数sws_getCachedContext()取代。
复杂但是更灵活的初始化方法
初始化SwsContext除了调用sws_getContext()之外还有另一种方法,更加灵活,可以配置更多的参数。该方法调用的函数如下所示。
(1) sws_alloc_context():为SwsContext结构体分配内存。
(2) av_opt_set_XXX():通过av_opt_set_int(),av_opt_set()…等等一系列方法设置SwsContext结构体的值。在这里需要注意,SwsContext结构体的定义看不到,所以不能对其中的成员变量直接进行赋值,必须通过av_opt_set()这类的API才能对其进行赋值。
(3) sws_init_context():初始化SwsContext结构体。
这种复杂的方法可以配置一些sws_getContext()配置不了的参数。比如说设置图像的YUV像素的取值范围是JPEG标准(Y、U、V取值范围都是0-255)还是MPEG标准(Y取值范围是16-235,U、V的取值范围是16-240)。
几个知识点
下文记录几个图像像素数据处理过程中的几个知识点:像素格式,图像拉伸,YUV像素取值范围,色域。
像素格式
像素格式的知识此前已经记录过,不再重复。在这里记录一下FFmpeg支持的像素格式。有几点注意事项:
(1) 所有的像素格式的名称都是以“AV_PIX_FMT_”开头
(2) 像素格式名称后面有“P”的,代表是planar格式,否则就是packed格式。Planar格式不同的分量分别存储在不同的数组中,例如AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P存储方式如下:
data[0]: Y1, Y2, Y3, Y4, Y5, Y6, Y7, Y8……
data[1]: U1, U2, U3, U4……
data[2]: V1, V2, V3, V4……
Packed格式的数据都存储在同一个数组中,例如AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24存储方式如下:
data[0]: R1, G1, B1, R2, G2, B2, R3, G3, B3, R4, G4, B4……
(3) 像素格式名称后面有“BE”的,代表是Big Endian格式;名称后面有“LE”的,代表是Little Endian格式。
FFmpeg支持的像素格式的定义位于libavutil\pixfmt.h,是一个名称为AVPixelFormat的枚举类型,如下所示。
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- enum AVPixelFormat {
- AV_PIX_FMT_NONE = -1,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUYV422,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV410P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV411P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8,
- AV_PIX_FMT_MONOWHITE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_MONOBLACK,
- AV_PIX_FMT_PAL8,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ422P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ444P,
- #if FF_API_XVMC
- AV_PIX_FMT_XVMC_MPEG2_MC,
- AV_PIX_FMT_XVMC_MPEG2_IDCT,
- #define AV_PIX_FMT_XVMC AV_PIX_FMT_XVMC_MPEG2_IDCT
- #endif /* FF_API_XVMC */
- AV_PIX_FMT_UYVY422,
- AV_PIX_FMT_UYYVYY411,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR8,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR4,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR4_BYTE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB8,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB4,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB4_BYTE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_NV12,
- AV_PIX_FMT_NV21,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_ARGB,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
- AV_PIX_FMT_ABGR,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGRA,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV440P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ440P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA420P,
- #if FF_API_VDPAU
- AV_PIX_FMT_VDPAU_H264,
- AV_PIX_FMT_VDPAU_MPEG1,
- AV_PIX_FMT_VDPAU_MPEG2,
- AV_PIX_FMT_VDPAU_WMV3,
- AV_PIX_FMT_VDPAU_VC1,
- #endif
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB48BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB48LE,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB565BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB565LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB555BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB555LE,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR565BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR565LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR555BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR555LE,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_VAAPI_MOCO,
- AV_PIX_FMT_VAAPI_IDCT,
- AV_PIX_FMT_VAAPI_VLD,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P16BE,
- #if FF_API_VDPAU
- AV_PIX_FMT_VDPAU_MPEG4,
- #endif
- AV_PIX_FMT_DXVA2_VLD,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB444LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB444BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR444LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR444BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8A,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR48BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR48LE,
-
-
-
-
-
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P9BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P9LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P10BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P10LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P10BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P10LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P9BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P9LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P10BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P10LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P9BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P9LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_VDA_VLD,
-
- #ifdef AV_PIX_FMT_ABI_GIT_MASTER
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA64BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA64LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGRA64BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGRA64LE,
- #endif
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP9BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP9LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP10BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP10LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP16LE,
-
-
-
-
-
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA422P_LIBAV,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA444P_LIBAV,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA420P9BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA420P9LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA422P9BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA422P9LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA444P9BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA444P9LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA420P10BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA420P10LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA422P10BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA422P10LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA444P10BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA444P10LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA420P16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA420P16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA422P16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA422P16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA444P16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA444P16LE,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_VDPAU,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_XYZ12LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_XYZ12BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_NV16,
- AV_PIX_FMT_NV20LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_NV20BE,
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA64BE_LIBAV,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA64LE_LIBAV,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGRA64BE_LIBAV,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGRA64LE_LIBAV,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_YVYU422,
-
- #ifndef AV_PIX_FMT_ABI_GIT_MASTER
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA64BE=0x123,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA64LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGRA64BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGRA64LE,
- #endif
- AV_PIX_FMT_0RGB=0x123+4,
- AV_PIX_FMT_RGB0,
- AV_PIX_FMT_0BGR,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BGR0,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA444P,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVA422P,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P12BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P12LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P14BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P14LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P12BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P12LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P14BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P14LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P12BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P12LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P14BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P14LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP12BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP12LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP14BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRP14LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRAP,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRAP16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_GBRAP16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ411P,
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_BGGR8,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_RGGB8,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_GBRG8,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_GRBG8,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_BGGR16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_BGGR16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_RGGB16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_RGGB16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_GBRG16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_GBRG16BE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_GRBG16LE,
- AV_PIX_FMT_BAYER_GRBG16BE,
- #if !FF_API_XVMC
- AV_PIX_FMT_XVMC,
- #endif /* !FF_API_XVMC */
-
- AV_PIX_FMT_NB,
-
- #if FF_API_PIX_FMT
- #include "old_pix_fmts.h"
- #endif
- };
FFmpeg有一个专门用于描述像素格式的结构体AVPixFmtDescriptor。该结构体的定义位于libavutil\pixdesc.h,如下所示。
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- typedef struct AVPixFmtDescriptor{
- const char *name;
- uint8_t nb_components;
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- uint8_t log2_chroma_w;
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- uint8_t log2_chroma_h;
- uint8_t flags;
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- AVComponentDescriptor comp[4];
- }AVPixFmtDescriptor;
关于AVPixFmtDescriptor这个结构体不再做过多解释。它的定义比较简单,看注释就可以理解。通过av_pix_fmt_desc_get()可以获得指定像素格式的AVPixFmtDescriptor结构体。
-
-
-
-
- const AVPixFmtDescriptor *av_pix_fmt_desc_get(enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt);
通过AVPixFmtDescriptor结构体可以获得不同像素格式的一些信息。例如下文中用到了av_get_bits_per_pixel(),通过该函数可以获得指定像素格式每个像素占用的比特数(Bit Per Pixel)。
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- int av_get_bits_per_pixel(const AVPixFmtDescriptor *pixdesc);
其他的API在这里不做过多记录。
图像拉伸
FFmpeg支持多种像素拉伸的方式。这些方式的定义位于libswscale\swscale.h中,如下所示。
- #define SWS_FAST_BILINEAR 1
- #define SWS_BILINEAR 2
- #define SWS_BICUBIC 4
- #define SWS_X 8
- #define SWS_POINT 0x10
- #define SWS_AREA 0x20
- #define SWS_BICUBLIN 0x40
- #define SWS_GAUSS 0x80
- #define SWS_SINC 0x100
- #define SWS_LANCZOS 0x200
- #define SWS_SPLINE 0x400
其中SWS_BICUBIC性能比较好;SWS_FAST_BILINEAR在性能和速度之间有一个比好好的平衡,
而SWS_POINT的效果比较差。
有关这些方法的评测可以参考文章:
《ffmpeg中的sws_scale算法性能测试》
简单解释一下SWS_BICUBIC、SWS_BILINEAR和SWS_POINT的原理。
SWS_POINT(Nearest-neighbor interpolation, 邻域插值)
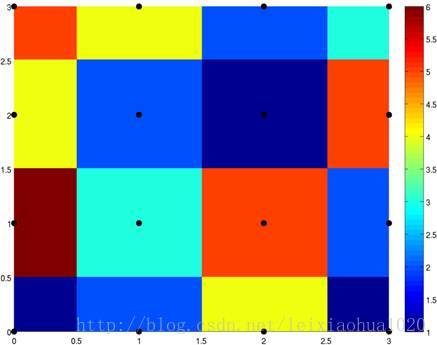
领域插值可以简单说成“1个点确定插值的点”。例如当图像放大后,新的样点根据距离它最近的样点的值取得自己的值。换句话说就是简单拷贝附近距离它最近的样点的值。领域插值是一种最基础的插值方法,速度最快,插值效果最不好,一般情况下不推荐使用。一般情况下使用邻域插值之后,画面会产生很多的“锯齿”。下图显示了4x4=16个彩色样点经过邻域插值后形成的图形。
SWS_BILINEAR(Bilinear interpolation, 双线性插值)
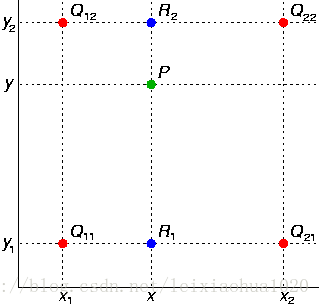
双线性插值可以简单说成“4个点确定插值的点”。它的计算过程可以简单用下图表示。图中绿色的P点是需要插值的点。首先通过Q11,Q21求得R1;Q12,Q22求得R2。然后根据R1,R2求得P。
其中求值的过程是一个简单的加权计算的过程。
设定Q11 = (x1, y1),Q12 = (x1, y2),Q21 = (x2, y1),Q22 = (x2, y2)则各点的计算公式如下。
可以看出距离插值的点近一些的样点权值会大一些,远一些的样点权值要小一些。
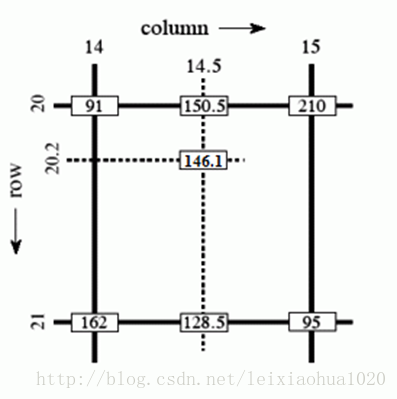
下面看一个维基百科上的双线性插值的实例。该例子根据坐标为(20, 14), (20, 15), (21, 14),(21, 15)的4个样点计算坐标为(20.2, 14.5)的插值点的值。
SWS_BICUBIC(Bicubic interpolation, 双三次插值)
双三次插值可以简单说成“16个点确定插值的点”。该插值算法比前两种算法复杂很多,插值后图像的质量也是最好的。有关它的插值方式比较复杂不再做过多记录。它的差值方法可以简单表述为下述公式。
其中aij的过程依赖于插值数据的特性。
维基百科上使用同样的样点进行邻域插值,双线性插值,双三次插值对比如下图所示。

Nearest-neighbor interpolation,邻域插值
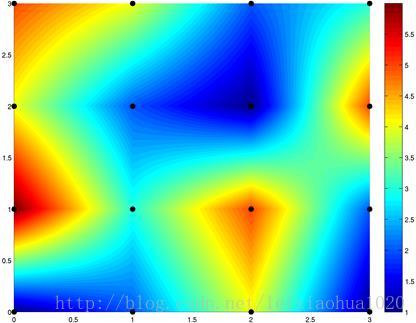
Bilinear interpolation,双线性插值
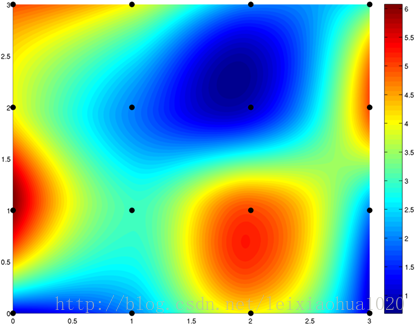
Bicubic interpolation,双三次插值
YUV像素取值范围
FFmpeg中可以通过使用av_opt_set()设置“src_range”和“dst_range”来设置输入和输出的YUV的取值范围。如果“dst_range”字段设置为“1”的话,则代表输出的YUV的取值范围遵循“jpeg”标准;如果“dst_range”字段设置为“0”的话,则代表输出的YUV的取值范围遵循“mpeg”标准。下面记录一下YUV的取值范围的概念。
与RGB每个像素点的每个分量取值范围为0-255不同(每个分量占8bit),YUV取值范围有两种:
(1) 以Rec.601为代表(还包括BT.709 / BT.2020)的广播电视标准中,Y的取值范围是16-235,U、V的取值范围是16-240。FFmpeg中称之为“mpeg”范围。
(2) 以JPEG为代表的标准中,Y、U、V的取值范围都是0-255。FFmpeg中称之为“jpeg” 范围。
实际中最常见的是第1种取值范围的YUV(可以自己观察一下YUV的数据,会发现其中亮度分量没有取值为0、255这样的数值)。很多人在这个地方会有疑惑,为什么会去掉“两边”的取值呢?
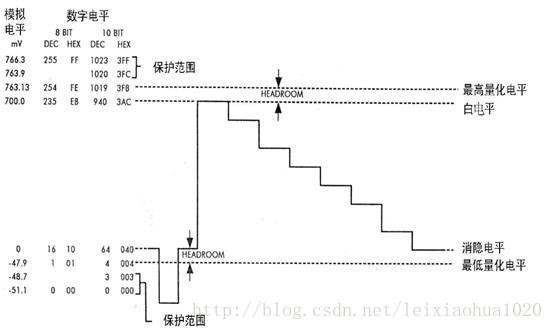
在广播电视系统中不传输很低和很高的数值,实际上是为了防止信号变动造成过载,因而把这“两边”的数值作为“保护带”。下面这张图是数字电视中亮度信号量化后的电平分配图。从图中可以看出,对于8bit量化来说,信号的白电平为235,对应模拟电平为700mV;黑电平为16,对应模拟电平为0mV。信号上方的“保护带”取值范围是236至254,而信号下方的“保护带”取值范围是1-15。最边缘的0和255两个电平是保护电平,是不允许出现在数据流中的。与之类似,10bit量化的时候,白电平是235*4=940,黑电平是16*4=64。
下面两张图是数字电视中色度信号量化后的电平分配图。可以看出,色度最大正电平为240,对应模拟电平为+350mV;色度最大负电平为16,对应模拟电平为-350mV。需要注意的是,色度信号数字电平128对应的模拟电平是0mV。
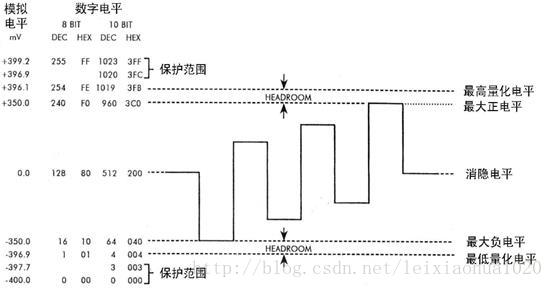
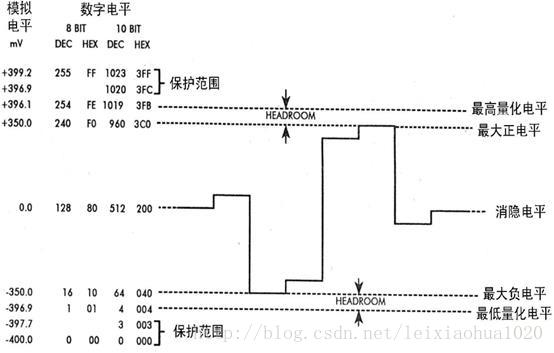
色域
Libswscale支持色域的转换。有关色域的转换我目前还没有做太多的研究,仅记录一下目前最常见的三个标准中的色域:BT.601,BT.709,BT.2020。这三个标准中的色域逐渐增大。
在这里先简单解释一下CIE 1931颜色空间。这个空间围绕的区域像一个“舌头”,其中包含了自然界所有的颜色。CIE 1931颜色空间中的横坐标是x,纵坐标是y,x、y、z满足如下关系:
x + y + z = 1
“舌头”的边缘叫做“舌形曲线”,代表着饱和度为100%的光谱色。“舌头”的中心点(1/3,1/3)对应着白色,饱和度为0。
受显示器件性能的限制,电视屏幕是无法重现所有的颜色的,尤其是位于“舌形曲线”上的100% 饱和度的光谱色一般情况下是无法显示出来的。因此电视屏幕只能根据其具体的荧光粉的配方,有选择性的显示一部分的颜色,这部分可以显示的颜色称为色域。下文分别比较标清电视、高清电视和超高清电视标准中规定的色域。可以看出随着技术的进步,色域的范围正变得越来越大。
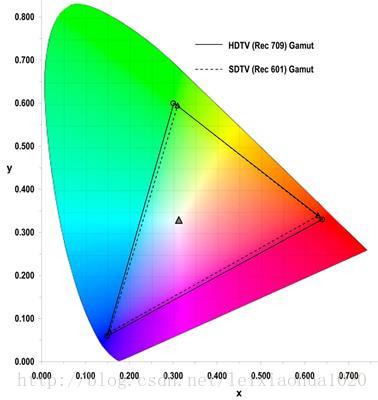
标清电视(SDTV)色域的规定源自于BT.601。高清电视(HDTV)色域的规定源自于BT.709。他们两个标准中的色域在CIE 1931颜色空间中的对比如下图所示。从图中可以看出,BT.709和BT.601色域差别不大,BT.709的色域要略微大于BT.601。
超高清电视(UHDTV)色域的规定源自于BT.2020。BT.2020和BT.709的色域在CIE 1931 颜色空间中的对比如下图所示。从图中可以看出,BT.2020的色域要远远大于BT.709。
从上面的对比也可以看出,对超高清电视(UHDTV)的显示器件的性能的要求更高了。这样超高清电视可以还原出一个更“真实”的世界。
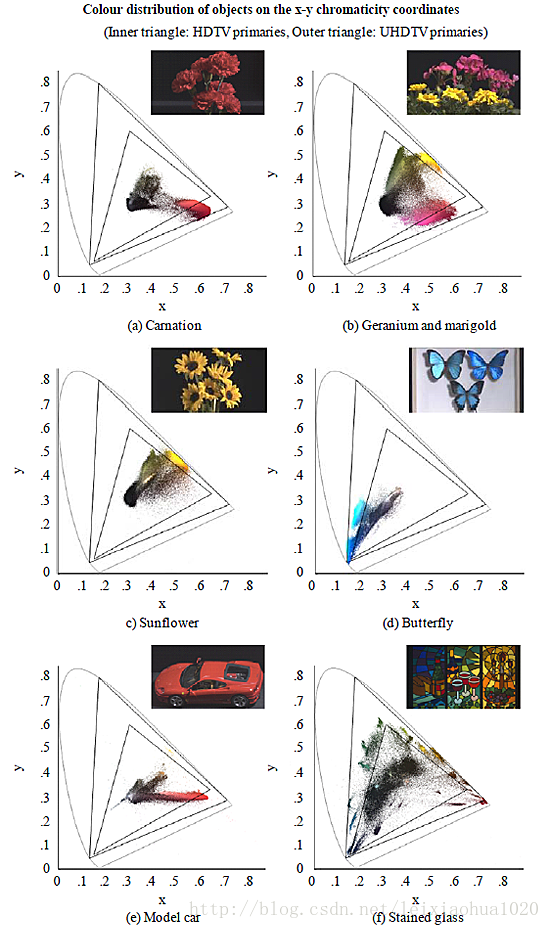
下面这张图则使用实际的例子反映出色域范围大的重要性。图中的两个黑色三角形分别标识出了BT.709(小三角形)和BT.2020(大三角形)标准中的色域。从图中可以看出,如果使用色域较小的显示设备显示图片的话,将会损失掉很多的颜色。
源代码
本示例程序包含一个输入和一个输出,实现了从输入图像格式(YUV420P)到输出图像格式(RGB24)之间的转换;同时将输入视频的分辨率从480x272拉伸为1280x720。
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- #include <stdio.h>
-
- #define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS
-
- #ifdef _WIN32
-
- extern "C"
- {
- #include "libswscale/swscale.h"
- #include "libavutil/opt.h"
- #include "libavutil/imgutils.h"
- };
- #else
-
- #ifdef __cplusplus
- extern "C"
- {
- #endif
- #include <libswscale/swscale.h>
- #include <libavutil/opt.h>
- #include <libavutil/imgutils.h>
- #ifdef __cplusplus
- };
- #endif
- #endif
-
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
-
- FILE *src_file =fopen("sintel_480x272_yuv420p.yuv", "rb");
- const int src_w=480,src_h=272;
- AVPixelFormat src_pixfmt=AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
-
- int src_bpp=av_get_bits_per_pixel(av_pix_fmt_desc_get(src_pixfmt));
-
- FILE *dst_file = fopen("sintel_1280x720_rgb24.rgb", "wb");
- const int dst_w=1280,dst_h=720;
- AVPixelFormat dst_pixfmt=AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24;
- int dst_bpp=av_get_bits_per_pixel(av_pix_fmt_desc_get(dst_pixfmt));
-
-
- uint8_t *src_data[4];
- int src_linesize[4];
-
- uint8_t *dst_data[4];
- int dst_linesize[4];
-
- int rescale_method=SWS_BICUBIC;
- struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx;
- uint8_t *temp_buffer=(uint8_t *)malloc(src_w*src_h*src_bpp/8);
-
- int frame_idx=0;
- int ret=0;
- ret= av_image_alloc(src_data, src_linesize,src_w, src_h, src_pixfmt, 1);
- if (ret< 0) {
- printf( "Could not allocate source image\n");
- return -1;
- }
- ret = av_image_alloc(dst_data, dst_linesize,dst_w, dst_h, dst_pixfmt, 1);
- if (ret< 0) {
- printf( "Could not allocate destination image\n");
- return -1;
- }
-
-
- img_convert_ctx =sws_alloc_context();
-
- av_opt_show2(img_convert_ctx,stdout,AV_OPT_FLAG_VIDEO_PARAM,0);
-
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"sws_flags",SWS_BICUBIC|SWS_PRINT_INFO,0);
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"srcw",src_w,0);
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"srch",src_h,0);
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"src_format",src_pixfmt,0);
-
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"src_range",1,0);
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"dstw",dst_w,0);
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"dsth",dst_h,0);
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"dst_format",dst_pixfmt,0);
- av_opt_set_int(img_convert_ctx,"dst_range",1,0);
- sws_init_context(img_convert_ctx,NULL,NULL);
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- while(1)
- {
- if (fread(temp_buffer, 1, src_w*src_h*src_bpp/8, src_file) != src_w*src_h*src_bpp/8){
- break;
- }
-
- switch(src_pixfmt){
- case AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8:{
- memcpy(src_data[0],temp_buffer,src_w*src_h);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P:{
- memcpy(src_data[0],temp_buffer,src_w*src_h);
- memcpy(src_data[1],temp_buffer+src_w*src_h,src_w*src_h/4);
- memcpy(src_data[2],temp_buffer+src_w*src_h*5/4,src_w*src_h/4);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P:{
- memcpy(src_data[0],temp_buffer,src_w*src_h);
- memcpy(src_data[1],temp_buffer+src_w*src_h,src_w*src_h/2);
- memcpy(src_data[2],temp_buffer+src_w*src_h*3/2,src_w*src_h/2);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P:{
- memcpy(src_data[0],temp_buffer,src_w*src_h);
- memcpy(src_data[1],temp_buffer+src_w*src_h,src_w*src_h);
- memcpy(src_data[2],temp_buffer+src_w*src_h*2,src_w*src_h);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_YUYV422:{
- memcpy(src_data[0],temp_buffer,src_w*src_h*2);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24:{
- memcpy(src_data[0],temp_buffer,src_w*src_h*3);
- break;
- }
- default:{
- printf("Not Support Input Pixel Format.\n");
- break;
- }
- }
-
- sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, src_data, src_linesize, 0, src_h, dst_data, dst_linesize);
- printf("Finish process frame %5d\n",frame_idx);
- frame_idx++;
-
- switch(dst_pixfmt){
- case AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8:{
- fwrite(dst_data[0],1,dst_w*dst_h,dst_file);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P:{
- fwrite(dst_data[0],1,dst_w*dst_h,dst_file);
- fwrite(dst_data[1],1,dst_w*dst_h/4,dst_file);
- fwrite(dst_data[2],1,dst_w*dst_h/4,dst_file);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P:{
- fwrite(dst_data[0],1,dst_w*dst_h,dst_file);
- fwrite(dst_data[1],1,dst_w*dst_h/2,dst_file);
- fwrite(dst_data[2],1,dst_w*dst_h/2,dst_file);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P:{
- fwrite(dst_data[0],1,dst_w*dst_h,dst_file);
- fwrite(dst_data[1],1,dst_w*dst_h,dst_file);
- fwrite(dst_data[2],1,dst_w*dst_h,dst_file);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_YUYV422:{
- fwrite(dst_data[0],1,dst_w*dst_h*2,dst_file);
- break;
- }
- case AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24:{
- fwrite(dst_data[0],1,dst_w*dst_h*3,dst_file);
- break;
- }
- default:{
- printf("Not Support Output Pixel Format.\n");
- break;
- }
- }
- }
-
- sws_freeContext(img_convert_ctx);
-
- free(temp_buffer);
- fclose(dst_file);
- av_freep(&src_data[0]);
- av_freep(&dst_data[0]);
-
- return 0;
- }
运行结果
程序的输入为一个名称为“sintel_480x272_yuv420p.yuv”的视频。该视频像素格式是YUV420P,分辨率为480x272。
程序的输出为一个名称为“sintel_1280x720_rgb24.rgb”的视频。该视频像素格式是RGB24,分辨率为1280x720。
下载
Simplest FFmpeg Swscale
项目主页
SourceForge:https://sourceforge.net/projects/simplestffmpegswscale/
Github:https://github.com/leixiaohua1020/simplest_ffmpeg_swscale
开源中国:http://git.oschina.net/leixiaohua1020/simplest_ffmpeg_swscale
CDSN下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/leixiaohua1020/8292175
本教程是最简单的基于FFmpeg的libswscale进行像素处理的教程。它包含了两个工程:
simplest_ffmpeg_swscale: 最简单的libswscale的教程。
simplest_pic_gen: 生成各种测试图片的工具。
更新-1.1 (2015.2.13)=========================================
这次考虑到了跨平台的要求,调整了源代码。经过这次调整之后,源代码可以在以下平台编译通过:
VC++:打开sln文件即可编译,无需配置。
cl.exe:打开compile_cl.bat即可命令行下使用cl.exe进行编译,注意可能需要按照VC的安装路径调整脚本里面的参数。编译命令如下。
- ::VS2010 Environment
- call "D:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\VC\vcvarsall.bat"
- ::include
- @set INCLUDE=include;%INCLUDE%
- ::lib
- @set LIB=lib;%LIB%
- ::compile and link
- cl simplest_ffmpeg_swscale.cpp /link swscale.lib avutil.lib /OPT:NOREF
MinGW:MinGW命令行下运行compile_mingw.sh即可使用MinGW的g++进行编译。编译命令如下。
- g++ simplest_ffmpeg_swscale.cpp -g -o simplest_ffmpeg_swscale.exe \
- -I /usr/local/include -L /usr/local/lib -lswscale -lavutil
GCC:Linux或者MacOS命令行下运行compile_gcc.sh即可使用GCC进行编译。编译命令如下。
- gcc simplest_ffmpeg_swscale.cpp -g -o simplest_ffmpeg_swscale.out -I /usr/local/include -L /usr/local/lib \
- -lswscale -lavutil
PS:相关的编译命令已经保存到了工程文件夹中
CSDN下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/leixiaohua1020/8445671
SourceForge上已经更新。
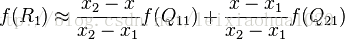


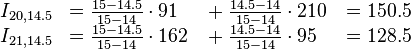
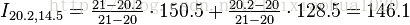
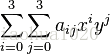




























 205
205

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








