Android标准架构实例分析之编写最简单的hello驱动
摘要:
本文主要实现了一个虚拟的字符设备驱动–hello_device 。这个设备驱动会创建相关的cdev数据结构和file_operations,并通过class_create和device_create在sys文件系统上创建相关的目录和文件,为udev创建相关的设备文件提供资源。最终会在/dev/下面创建/dev/hello这个文件节点。并提供文件节点测试程序和测试方法。
- udev工作原理
- 创建并初始化cdev加入到链表中
- 测试代码分析和编译
- 详细代码列表
udev工作原理
udev实现了用户空间动态的方法管理/dev目录。/dev目录是设备目录,里面的文件就是设备文件。udev文件系统在用户空间工作,它可以根据sysfs文件系统导出的信息(设备号(dev)等),动态建立和删除设备文件。而不再需要使用mknod来手动建立设备文件,也不必为查找设备号(尤其是驱动中动态申请产生的设备号)而头疼。
为了能让udev能够正常工作,一个设备驱动程序要做的事情是:通过sysfs将驱动程序所控制设备的主设备号和此设备号导出到用户空间。对于那些使用子系统分配主设备号和次设备号的驱动程序,该工作已经有子系统完成,驱动程序不做任何事情。这样的子系统有:tty,misc,usb,input,scsi,block,i2c,network,framebuffer子系统。如果驱动程序通过调用cdev_init函数,自己处理获得主设备号和次设备号,那么为了能正确的使用udev,需要对驱动程序进行修改。Udev在sysfs中的/class/目录树下搜索名为dev的文件,这样内核通过/sbin/hotplug接口调用它的时候,就能获得分配给特定设备的主设备号和次设备号。
*注:
/dev,设备文件存储目录,应用程序通过对这些文件的读写和控制,可以访问实际的设备;
/sys/devices目录,按照设备挂接的总线类型,组织成层次结构,保存了系统所有的设备;是文件系统管理设备的最重要的目录结构;
/sys/dev下有两个子目录,block和char,存放的是块设备和字符设备的主次号码,形式为(major:minor),它指向/sys/devices目录下的设备。*
字符设备驱动的分析和编译
①主设备编号和次设备编号的申请:
传统上, 主编号标识设备相连的驱动,大部分设备仍然按照一个主编号一个驱动的原则来组织.
次编号被内核用来决定引用哪个设备.
在内核中, dev_t 类型,用来持有设备编号 – 主次部分都包括.
下面的例子是一个动态申请设备编号的过程代码:
/* the major device number */
static int hello_major = 0;//主设备编号
static int hello_minor = 0;//次设备编号
dev_t devno = 0;//devno = MKDEV(int major, int minor);
/*动态分配主设备和从设备号*/
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, hello_minor, DEVICE_SUM, "hello");
hello_major = MAJOR(devno);
hello_minor = MINOR(devno);
通过 /proc/devices 或者 ls -l /dev/ 可以查看设备号和设备信息。
②创建并初始化cdev加入到链表中
struct cdev 是内核的内部结构, 代表字符设备。
下面是一个字符设备最简单的初始化和添加到链表的方式:
/* init the file_operations structure */
struct file_operations hello_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_open,
.release = hello_release,
.read = hello_read,
.write = hello_write,
};
struct cdev *cdev;
cdev = cdev_alloc();
cdev->owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev->ops = &hello_fops;
但是, 偶尔你会想将 cdev 结构嵌入一个你自己的设备特定的结构; scull 这样做了. 在这种情况下, 你应当初始化你已经分配的结构, 使用:
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev, struct file_operations *fops);
下面是将初始化好的cdev添加到字符设备到链表:
if ((ret = cdev_add(cdev, devno, 1)))
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "hello:Error %d adding hello.\n", ret);
return 0;
}
这里, dev 是 cdev 结构, num 是这个设备响应的第一个设备号, count 是应当关联到设备的设备号的数目. 常常 count 是 1。
③在sysfs中创建一些必要的数据结构
前面已经分析了udev的工作原理,只是①②两个操作是不足以完成设备节点在/dev下面生成,必须要操作sysfs进行一些必要的设备目录和文件的创建,下面是具体的代码:
struct device* temp = NULL;
static struct class* hello_class = NULL;
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello");
/*在/dev/目录和/sys/class/hello目录下分别创建设备文件hello*/
temp = device_create(hello_class, NULL, devno, "%s", "hello");
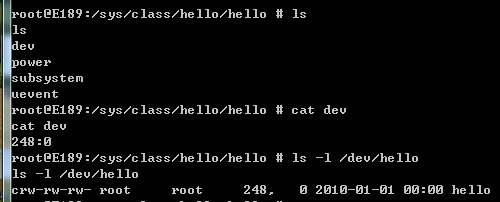
如果/sys/class/hello/hello创建成功,udev会导入这些信息并创建/dev/hello设备节点。
测试结果如下图:
④ copy_to_user & copy_from_user
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
这个包含文件声明内核代码使用的函数来移动数据到和从用户空间.
unsigned long copy_from_user (void *to, const void *from, unsigned long count);
unsigned long copy_to_user (void *to, const void *from, unsigned long count);
在用户空间和内核空间拷贝数据.
示例代码:
static int global_var = 0; /* global var */
if(copy_to_user(buf, &global_var, sizeof(int)))
{
return -EFAULT;
}
if(copy_from_user(&global_var, buf, sizeof(int)))
{
return -EFAULT;
}
⑤编译
创建同级目录下的Makefile文件,文件内容为:
obj-y += hello.o
在上一级Makefile中添加:
obj-y += hello/
测试代码分析和编译
测试代码主要是对文件节点/dev/hello进行open,read,write操作,主要注意文件的权限问题,使用
adb shell chmod 777 /dev/hello //修改权限
文件的操作详细参考:百度或者谷歌,搜索:Linux 文件操作 系统调用;
编译过程:
将测试代码放在Android /external/hello/文件夹下,编写Android.mk
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional
LOCAL_MODULE := hello
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(call all-subdir-c-files)
include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE)
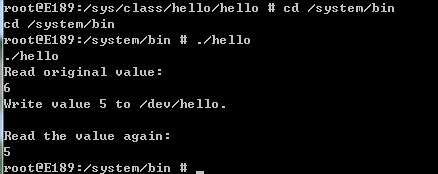
执行:mmm external/hello/ 会在system/bin/下面生成测试程序可执行文件:hello
执行: make snod打包system.img 下载后,执行测试程序结果:
详细代码列表
驱动文件hello.c
/*
* hello.c -- A simple virtual char device driver
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("eliot shao");
#define DEVICE_SUM 1
static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp);
static int hello_release(struct inode *, struct file *filp);
static ssize_t hello_read(struct file*, char*, size_t, loff_t*);
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file*, const char*, size_t, loff_t*);
/* the major device number */
static int hello_major = 0;
static int hello_minor = 0;
static struct class* hello_class = NULL;
/* init the file_operations structure */
struct file_operations hello_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_open,
.release = hello_release,
.read = hello_read,
.write = hello_write,
};
/* define a cdev device */
struct cdev *cdev;
static int global_var = 0; /* global var */
/* module init */
static int __init hello_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
struct device* temp = NULL;
dev_t devno = 0;
printk("hello:hello_init .\n");
/*动态分配主设备和从设备号*/
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, hello_minor, DEVICE_SUM, "hello");
if(ret < 0) {
printk(KERN_ALERT"hello:Failed to alloc char dev region.\n");
goto fail;
}
hello_major = MAJOR(devno);
hello_minor = MINOR(devno);
cdev = cdev_alloc();
cdev->owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev->ops = &hello_fops;
if ((ret = cdev_add(cdev, devno, 1)))
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "hello:Error %d adding hello.\n", ret);
return 0;
}
else
printk("hello:hello register success.\n");
/*在/sys/class/目录下创建设备类别目录hello*/
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello");
if(IS_ERR(hello_class)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(hello_class);
printk(KERN_ALERT"Failed to create hello class.\n");
goto destroy_cdev;
}
/*在/dev/目录和/sys/class/hello目录下分别创建设备文件hello*/
temp = device_create(hello_class, NULL, devno, "%s", "hello");
if(IS_ERR(temp)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(temp);
printk(KERN_ALERT"Failed to create hello device.");
goto destroy_class;
}
return ret;
destroy_class:
class_destroy(hello_class);
destroy_cdev:
cdev_del(cdev);
fail:
return ret;
}
/* module exit */
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
{
dev_t devno = MKDEV(hello_major, 0);
/* remove cdev from kernel */
cdev_del(cdev);
/* unregister the device driver */
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1);
/* free the dev structure */
if(cdev)
kfree(cdev);
cdev = NULL;
}
/* open device */
static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
int ret = 0;
printk("KERNEL:open success.\n");
return ret;
}
/* release device */
static int hello_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("KERNEL:release success.\n");
return 0;
}
/* read device */
static ssize_t hello_read(struct file *filp, char *buf, size_t len, loff_t *off)
{
printk("KERNEL:reading...\n");
if(copy_to_user(buf, &global_var, sizeof(int)))
{
return -EFAULT;
}
return sizeof(int);
}
/* write device */
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char *buf, size_t len, loff_t *off)
{
printk("KERNEL:writing...\n");
if(copy_from_user(&global_var, buf, sizeof(int)))
{
return -EFAULT;
}
return sizeof(int);
}
/* module register */
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);测试程序hello.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define DEVICE_NAME "/dev/hello"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int fd = -1;
int val = 0;
fd = open(DEVICE_NAME, O_RDWR);
if(fd == -1) {
printf("Failed to open device %s\n", DEVICE_NAME);
return -1;
}
printf("Read original value:\n");
read(fd, &val, sizeof(val));
printf("%d\n", val);
val = 5;
printf("Write value %d to %s.\n\n", val, DEVICE_NAME);
write(fd, &val, sizeof(val));
printf("Read the value again:\n");
read(fd, &val, sizeof(val));
printf("%d\n", val);
close(fd);
return 0;
}























 1801
1801

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








