Directories can be read by anyone who has access permission to read the directory. But only the kernel can write to a directory, to preserve file system sanity(心智健康)(只有内核可以写如目录来保证文件系统的正常运作).
目录的写权限和执行权限可以让我们在目录中创建新文件和移除文件。但是并不能让我们写入目录它本身。
目录的实际形式取决于Unix系统实现和文件系统的设计。早期的系统中,使用简单的结构:目录entry有16字节,14byte for filename, 2byte for inode number。随着更长的文件名加入,每个entry都是可变的长度。
为简化读目录操作,POSIX1规定了一系列directory routines。许多实现访问应用程序使用read来访问目录的内容。
opendir, fdopendir - open a directory
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
DIR *opendir(const char *name);
DIR *fdopendir(int fd);
//Return: pointer if OK, NULL on erroropendir
用于初始化,这样第一次调用readdir会返回目录中第一个entry。
fdopendir
提供file decriptor转换为DIR结构的方法。
DIR由fdopendir创建的时候,readdir返回的第一个entry,取决于传递给fdopendir的参数file descriptor相关的file offset 文件偏移量。
a set of directory routines
#include <dirent.h>
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);//read a directory
//Returns: pointer if OK, NULL at end of directory or error
long telldir(DIR *dirp);
//Return: current location in directory stream(associated with dirp)
void rewinddir(DIR *dp);
int closedir(DIR *dp);
//Returns: 0 if OK, −1 on error
void seekdir(DIR *dirp, long loc);
//set the position of the next readdir() call in the directory stream.telldir, seekdir不是基础POSIX1标准的一部分,他们被包含在(single UNIX specification)单一UNIX规范的XSI选项中。
Recall our use of several of these functions in the program shown in Figure 1.3, our bare-bones(裸骨) implementation of thels command.(1.3节的ls实现,我这里也把代码贴上,如下图)
结构体:dirent
该结构体定义在dirent.h中,依赖于具体实现,但所有实现都会包含d_ino,d_name
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */
char d_name[256]; /* filename */
off_t d_off; /* not an offset; see NOTES */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported
by all filesystem types */
};
d_name至少包含NAME_MAX个字符,在Linux中为256个,如上图。
TheDIR structure is an internal structure used by these seven functions to maintain information about the directory being read. The purpose of the DIR structure is similar to that of the FILE structure maintained by the standard I/O library, which we describe in Chapter 5.(DIR结构与FILE结构目的是类似的,DIR适用于保存所有目录的信息)
Note that the ordering of entries within the directory is implementation dependent and is usually not alphabetical(字母顺序).(在目录中entries的顺序是依赖与实现的,不是字母顺序的)
Example
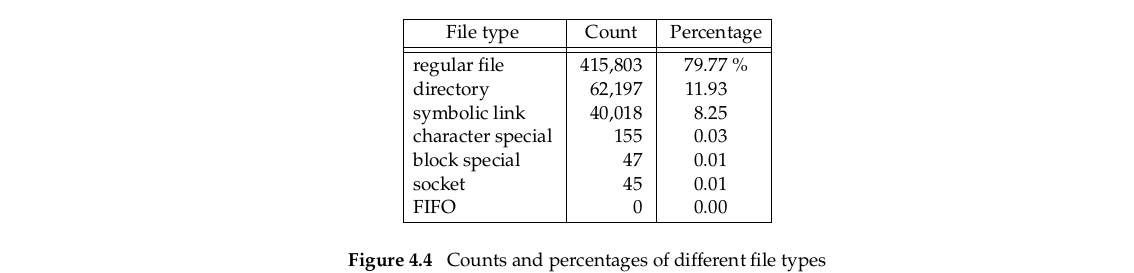
我们编写代码完成遍历整个文件结构(file hierarchy),最后效果如图4.4
系统提供了ftw(3)从一点迭代进入文件结构。但是ftw 调用了stat,这会产生问题,因为stat会跟着链接符号进入follow symbolic links。例如我们开始在根目录,然后/usr/lib拥有链接/bin,这样会导致/usr/lib被计算了两次。为了避免这个问题,有另外的函数nftw(3),拥有一个选项来决定是否跟随symbolic links。尽管我们可以使用nftw,但我们还是编写自己的代码来练习directory routines的使用。























 661
661











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










