本节是网卡驱动的入门基础部分,移植移植DM9000C网卡驱动程序
请看下节:移植DM9000C网卡驱动程序http://blog.csdn.net/fengyuwuzu0519/article/details/72821567
一、嵌入式linux驱动主要分为三部分:
- 字符设备驱动
- 块设备驱动
- 网络设备驱动
字符设备驱动:
APP:open、read、write。。。
驱动:drv_open、drv_read、drv_write。。。
框架:
(1)主设备号
(2)file_operation结构体
(3)regist_chrdev(主设备号,name,file_operation)
(4)入口函数
(5)出口函数
二、网卡设备驱动
1、框架分析
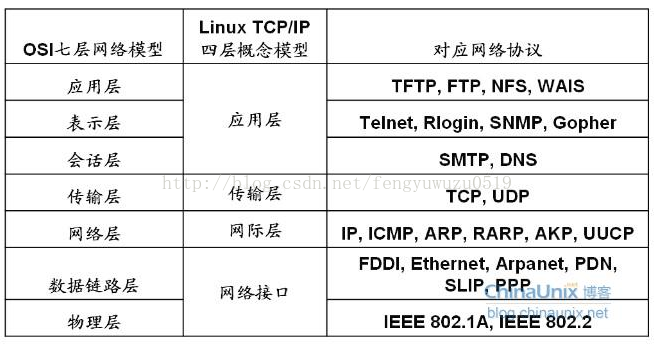
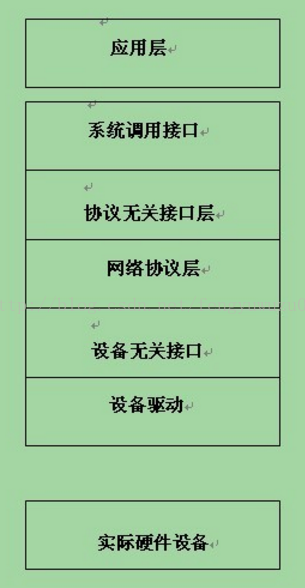
网络协议分可为七层等等。我们 只关心硬件部分。就是底层的网卡部分的内容。应用通过socket就可以传输数据。
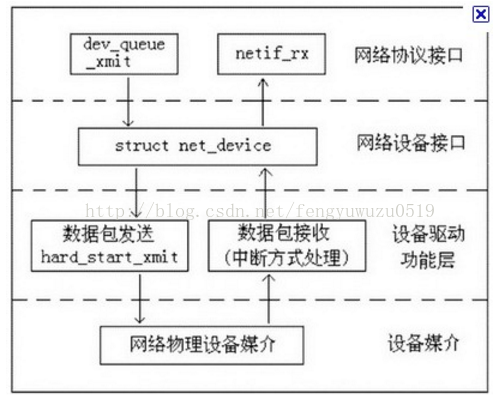
下面,我们说一下实际的网络包究竟经过怎样一个流程从用户空间发送到驱动,再到实际的硬件设备的,或者怎样由实际的设备接收之后,经由设备驱动层传递到用户空间的。上图:
- 接收过程,如上如,网络上的数据包到达网卡后,网卡产生中断,然后设备驱动层收到中断后,开始进行网络包的接收,接收完之后调用一个netif_rx函数交给网络协议层(层次结构上图一),然后就是一层一层的网上传到用户空间了
- 发送过程,从用户空间过来的数据包,经过层层穿越之后,到达网络协议层,然后调用一个dev_queue_xmit()函数之后就不管了,剩下的交给驱动层经过处理后,使用函数hard_start_xmit()函数发送,然后硬件上网卡开始发送数据包了
1)、网络协议接口层向网络层协议提供提供统一的数据包收发接口,不论上层协议为ARP还是IP,都通过dev_queue_xmit()函数发送数据,并通过netif_rx()函数接受数据。这一层的存在使得上层协议独立于具体的设备。
2)、网络设备接口层向协议接口层提供统一的用于描述具体网络设备属性和操作的结构体net_device,该结构体是设备驱动功能层中各函数的容器。实际上,网络设备接口层从宏观上规划了具体操作硬件的设备驱动功能层的结构。
3)、设备驱动功能层各函数是网络设备接口层net_device数据结构的具体成员,是驱使网络设备硬件完成相应动作的程序,他通过hard_start_xmit()函数启动发送操作,并通过网络设备上的中断触发接受操作。
4)、网络设备与媒介层是完成数据包发送和接受的物理实体,包括网络适配器和具体的传输媒介,网络适配器被驱动功能层中的函数物理上驱动。对于Linux系统而言,网络设备和媒介都可以是虚拟的。
5)、网络协议接口层:主要进行数据包的收发。
2、分析内核中的驱动代码
(1)参考:Cs89x0.c (drivers\net)
(2)入口函数init_module
int __init init_module(void)
{
struct net_device*dev =alloc_etherdev(sizeof(struct net_local));
/* 设置默认MAC地址,
* MAC地址可以由CS8900A外接的EEPROM设定(有些单板没接EEPROM),
* 或者启动系统后使用ifconfig修改
*/
dev->dev_addr[0] = 0x08;
dev->dev_addr[1] = 0x89;
dev->dev_addr[2] = 0x89;
dev->dev_addr[3] = 0x89;
dev->dev_addr[4] = 0x89;
dev->dev_addr[5] = 0x89;
ret = cs89x0_probe1(dev, io, 1);
}
(3)cs89x0_probe1中
cs89x0_probe1(struct net_device *dev, int ioaddr, int modular)
{
dev->open = net_open;
dev->stop = net_close;
dev->tx_timeout= net_timeout;
dev->watchdog_timeo= HZ;
dev->hard_start_xmit= net_send_packet;
dev->get_stats= net_get_stats;
dev->set_multicast_list = set_multicast_list;
dev->set_mac_address = set_mac_address;
retval = register_netdev(dev);
}
static int net_send_packet(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev)
(4)看一看中断函数net_interrupt
static irqreturn_t net_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
net_rx(dev);
}
net_rx(struct net_device *dev)
{
struct sk_buff *skb;
skb = dev_alloc_skb(length + 2);
netif_rx(skb);
}
(5)总结
我们可以看出协议与硬件之间就是通过这两个函数来通讯的。收发的内容是一个sk_buff结构体来描述的。
几个结构体:
sk_buff结构体:
struct sk_buff {
/* These two members must be first. */
struct sk_buff *next;
struct sk_buff *prev;
struct sock *sk;
ktime_t tstamp;
struct net_device *dev;
int iif;
/* 4 byte hole on 64 bit*/
struct dst_entry *dst;
struct sec_path *sp;
/*
* This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
*/
char cb[48];
unsigned int len,
data_len,
mac_len;
union {
__wsum csum;
struct {
__u16 csum_start;
__u16 csum_offset;
};
};
__u32 priority;
__u8 local_df:1,
cloned:1,
ip_summed:2,
nohdr:1,
nfctinfo:3;
__u8 pkt_type:3,
fclone:2,
ipvs_property:1;
__be16 protocol;
void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);
#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)
struct nf_conntrack *nfct;
struct sk_buff *nfct_reasm;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER
struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
__u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */
#endif
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_DMA
dma_cookie_t dma_cookie;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK
__u32 secmark;
#endif
__u32 mark;
sk_buff_data_t transport_header;
sk_buff_data_t network_header;
sk_buff_data_t mac_header;
/* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
sk_buff_data_t tail;
sk_buff_data_t end;
unsigned char *head,
*data;
unsigned int truesize;
atomic_t users;
};net_device结构体
struct net_device
{
/*
* This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure
* (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name
* the interface.
*/
char name[IFNAMSIZ];
/* device name hash chain */
struct hlist_node name_hlist;
/*
* I/O specific fields
* FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one
*/
unsigned long mem_end; /* shared mem end */
unsigned long mem_start; /* shared mem start */
unsigned long base_addr; /* device I/O address */
unsigned int irq; /* device IRQ number */
/*
* Some hardware also needs these fields, but they are not
* part of the usual set specified in Space.c.
*/
unsigned char if_port; /* Selectable AUI, TP,..*/
unsigned char dma; /* DMA channel */
unsigned long state;
struct list_head dev_list;
/* The device initialization function. Called only once. */
int (*init)(struct net_device *dev);
/* ------- Fields preinitialized in Space.c finish here ------- */
/* Net device features */
unsigned long features;
#define NETIF_F_SG 1 /* Scatter/gather IO. */
#define NETIF_F_IP_CSUM 2 /* Can checksum only TCP/UDP over IPv4. */
#define NETIF_F_NO_CSUM 4 /* Does not require checksum. F.e. loopack. */
#define NETIF_F_HW_CSUM 8 /* Can checksum all the packets. */
#define NETIF_F_HIGHDMA 32 /* Can DMA to high memory. */
#define NETIF_F_FRAGLIST 64 /* Scatter/gather IO. */
#define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_TX 128 /* Transmit VLAN hw acceleration */
#define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_RX 256 /* Receive VLAN hw acceleration */
#define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_FILTER 512 /* Receive filtering on VLAN */
#define NETIF_F_VLAN_CHALLENGED 1024 /* Device cannot handle VLAN packets */
#define NETIF_F_GSO 2048 /* Enable software GSO. */
#define NETIF_F_LLTX 4096 /* LockLess TX */
/* Segmentation offload features */
#define NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT 16
#define NETIF_F_GSO_MASK 0xffff0000
#define NETIF_F_TSO (SKB_GSO_TCPV4 << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_UFO (SKB_GSO_UDP << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_GSO_ROBUST (SKB_GSO_DODGY << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_TSO_ECN (SKB_GSO_TCP_ECN << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_TSO6 (SKB_GSO_TCPV6 << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
/* List of features with software fallbacks. */
#define NETIF_F_GSO_SOFTWARE (NETIF_F_TSO | NETIF_F_TSO_ECN | NETIF_F_TSO6)
#define NETIF_F_GEN_CSUM (NETIF_F_NO_CSUM | NETIF_F_HW_CSUM)
#define NETIF_F_ALL_CSUM (NETIF_F_IP_CSUM | NETIF_F_GEN_CSUM)
struct net_device *next_sched;
/* Interface index. Unique device identifier */
int ifindex;
int iflink;
struct net_device_stats* (*get_stats)(struct net_device *dev);
struct net_device_stats stats;
#ifdef CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT
/* List of functions to handle Wireless Extensions (instead of ioctl).
* See <net/iw_handler.h> for details. Jean II */
const struct iw_handler_def * wireless_handlers;
/* Instance data managed by the core of Wireless Extensions. */
struct iw_public_data * wireless_data;
#endif
const struct ethtool_ops *ethtool_ops;
/*
* This marks the end of the "visible" part of the structure. All
* fields hereafter are internal to the system, and may change at
* will (read: may be cleaned up at will).
*/
unsigned int flags; /* interface flags (a la BSD) */
unsigned short gflags;
unsigned short priv_flags; /* Like 'flags' but invisible to userspace. */
unsigned short padded; /* How much padding added by alloc_netdev() */
unsigned char operstate; /* RFC2863 operstate */
unsigned char link_mode; /* mapping policy to operstate */
unsigned mtu; /* interface MTU value */
unsigned short type; /* interface hardware type */
unsigned short hard_header_len; /* hardware hdr length */
struct net_device *master; /* Pointer to master device of a group,
* which this device is member of.
*/
/* Interface address info. */
unsigned char perm_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* permanent hw address */
unsigned char addr_len; /* hardware address length */
unsigned short dev_id; /* for shared network cards */
struct dev_mc_list *mc_list; /* Multicast mac addresses */
int mc_count; /* Number of installed mcasts */
int promiscuity;
int allmulti;
/* Protocol specific pointers */
void *atalk_ptr; /* AppleTalk link */
void *ip_ptr; /* IPv4 specific data */
void *dn_ptr; /* DECnet specific data */
void *ip6_ptr; /* IPv6 specific data */
void *ec_ptr; /* Econet specific data */
void *ax25_ptr; /* AX.25 specific data */
struct wireless_dev *ieee80211_ptr; /* IEEE 802.11 specific data,
assign before registering */
/*
* Cache line mostly used on receive path (including eth_type_trans())
*/
struct list_head poll_list ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
/* Link to poll list */
int (*poll) (struct net_device *dev, int *quota);
int quota;
int weight;
unsigned long last_rx; /* Time of last Rx */
/* Interface address info used in eth_type_trans() */
unsigned char dev_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw address, (before bcast
because most packets are unicast) */
unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw bcast add */
/*
* Cache line mostly used on queue transmit path (qdisc)
*/
/* device queue lock */
spinlock_t queue_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
struct Qdisc *qdisc;
struct Qdisc *qdisc_sleeping;
struct list_head qdisc_list;
unsigned long tx_queue_len; /* Max frames per queue allowed */
/* Partially transmitted GSO packet. */
struct sk_buff *gso_skb;
/* ingress path synchronizer */
spinlock_t ingress_lock;
struct Qdisc *qdisc_ingress;
/*
* One part is mostly used on xmit path (device)
*/
/* hard_start_xmit synchronizer */
spinlock_t _xmit_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
/* cpu id of processor entered to hard_start_xmit or -1,
if nobody entered there.
*/
int xmit_lock_owner;
void *priv; /* pointer to private data */
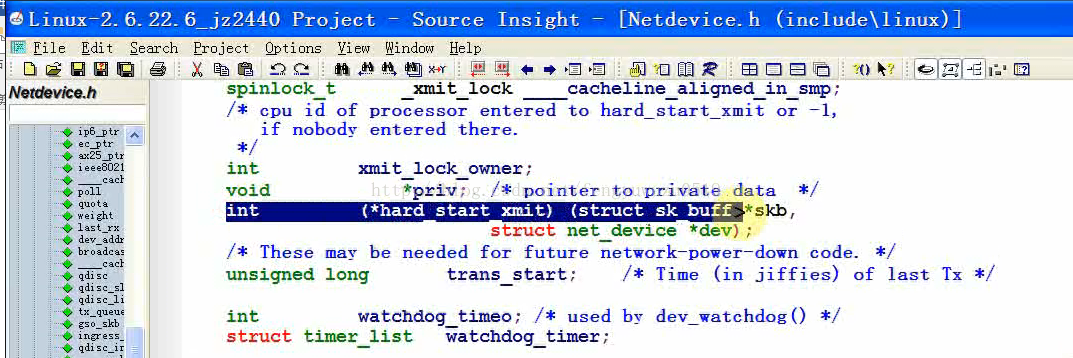
int (*hard_start_xmit) (struct sk_buff *skb,
struct net_device *dev);
/* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */
unsigned long trans_start; /* Time (in jiffies) of last Tx */
int watchdog_timeo; /* used by dev_watchdog() */
struct timer_list watchdog_timer;
/*
* refcnt is a very hot point, so align it on SMP
*/
/* Number of references to this device */
atomic_t refcnt ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
/* delayed register/unregister */
struct list_head todo_list;
/* device index hash chain */
struct hlist_node index_hlist;
struct net_device *link_watch_next;
/* register/unregister state machine */
enum { NETREG_UNINITIALIZED=0,
NETREG_REGISTERED, /* completed register_netdevice */
NETREG_UNREGISTERING, /* called unregister_netdevice */
NETREG_UNREGISTERED, /* completed unregister todo */
NETREG_RELEASED, /* called free_netdev */
} reg_state;
/* Called after device is detached from network. */
void (*uninit)(struct net_device *dev);
/* Called after last user reference disappears. */
void (*destructor)(struct net_device *dev);
/* Pointers to interface service routines. */
int (*open)(struct net_device *dev);
int (*stop)(struct net_device *dev);
#define HAVE_NETDEV_POLL
int (*hard_header) (struct sk_buff *skb,
struct net_device *dev,
unsigned short type,
void *daddr,
void *saddr,
unsigned len);
int (*rebuild_header)(struct sk_buff *skb);
#define HAVE_MULTICAST
void (*set_multicast_list)(struct net_device *dev);
#define HAVE_SET_MAC_ADDR
int (*set_mac_address)(struct net_device *dev,
void *addr);
#define HAVE_PRIVATE_IOCTL
int (*do_ioctl)(struct net_device *dev,
struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd);
#define HAVE_SET_CONFIG
int (*set_config)(struct net_device *dev,
struct ifmap *map);
#define HAVE_HEADER_CACHE
int (*hard_header_cache)(struct neighbour *neigh,
struct hh_cache *hh);
void (*header_cache_update)(struct hh_cache *hh,
struct net_device *dev,
unsigned char * haddr);
#define HAVE_CHANGE_MTU
int (*change_mtu)(struct net_device *dev, int new_mtu);
#define HAVE_TX_TIMEOUT
void (*tx_timeout) (struct net_device *dev);
void (*vlan_rx_register)(struct net_device *dev,
struct vlan_group *grp);
void (*vlan_rx_add_vid)(struct net_device *dev,
unsigned short vid);
void (*vlan_rx_kill_vid)(struct net_device *dev,
unsigned short vid);
int (*hard_header_parse)(struct sk_buff *skb,
unsigned char *haddr);
int (*neigh_setup)(struct net_device *dev, struct neigh_parms *);
#ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
struct netpoll_info *npinfo;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_POLL_CONTROLLER
void (*poll_controller)(struct net_device *dev);
#endif
/* bridge stuff */
struct net_bridge_port *br_port;
/* class/net/name entry */
struct device dev;
/* space for optional statistics and wireless sysfs groups */
struct attribute_group *sysfs_groups[3];
};三、虚拟网卡设备驱动编写
(1)步骤,怎么写网卡驱动程序?
1. 分配一个net_device结构体
2. 设置:
2.1 发包函数: hard_start_xmit
2.2 收到数据时(在中断处理函数里)用netif_rx上报数据
2.3 其他设置
3. 注册: register_netdevice
(2)代码:参考Cs89x0.c (drivers\net)拷贝其头文件等,做出框架
现在最简单的网卡驱动程序就写好了,我们可以做实验测试一下。
(3)驱动代码
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/netdevice.h>
#include <linux/etherdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/ioport.h>
#include <linux/in.h>
#include <linux/skbuff.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/spinlock.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/bitops.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <asm/system.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
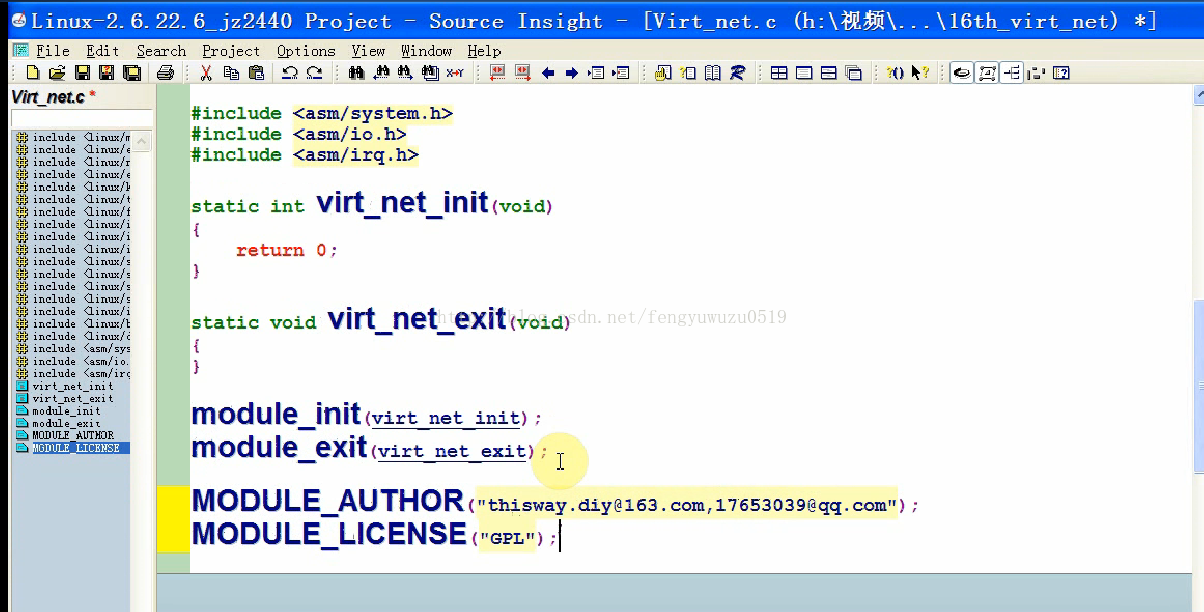
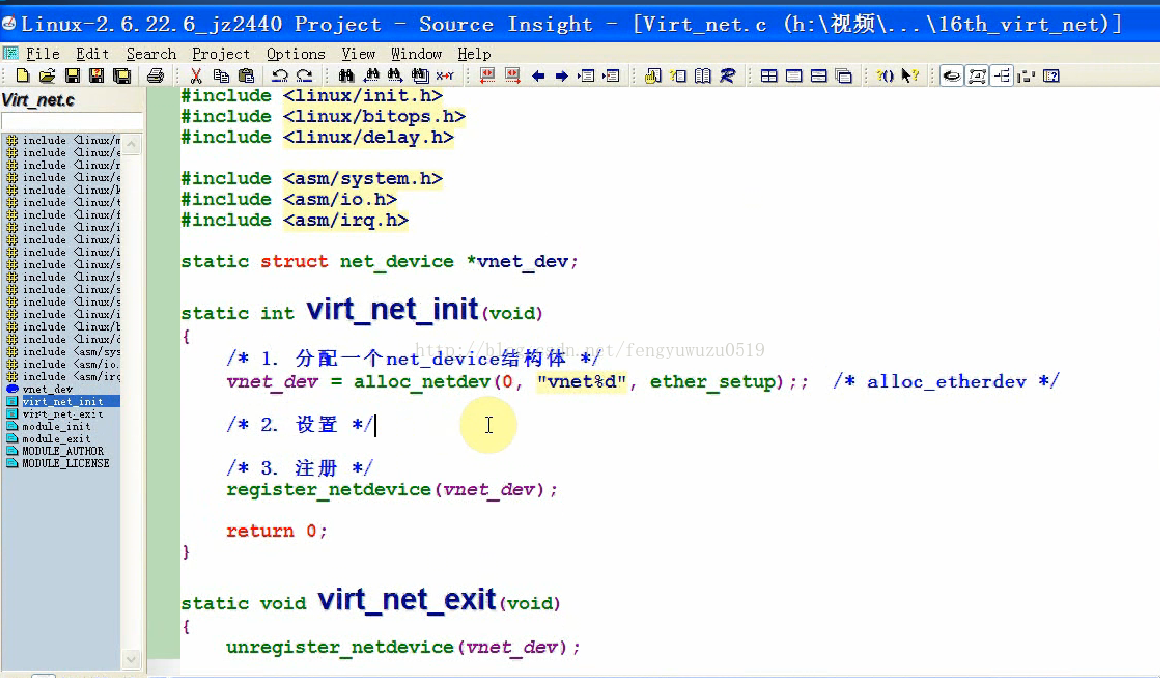
static struct net_device *vnet_dev;
static int virt_net_init(void)
{
/* 1. 分配一个net_device结构体 */
vnet_dev = alloc_netdev(0, "vnet%d", ether_setup);; /* alloc_etherdev */
/* 2. 设置 */
/* 3. 注册 */
//register_netdevice(vnet_dev);
register_netdev(vnet_dev);
return 0;
}
static void virt_net_exit(void)
{
unregister_netdev(vnet_dev);
free_netdev(vnet_dev);
}
module_init(virt_net_init);
module_exit(virt_net_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("xxx");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");(4)makefile
KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-2.6.22.6
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
obj-m += virt_net.o
(5)实验结果
测试1th/2th:
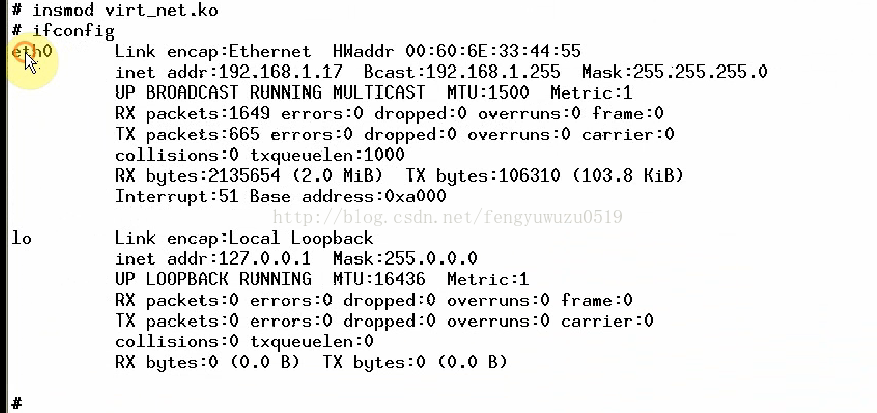
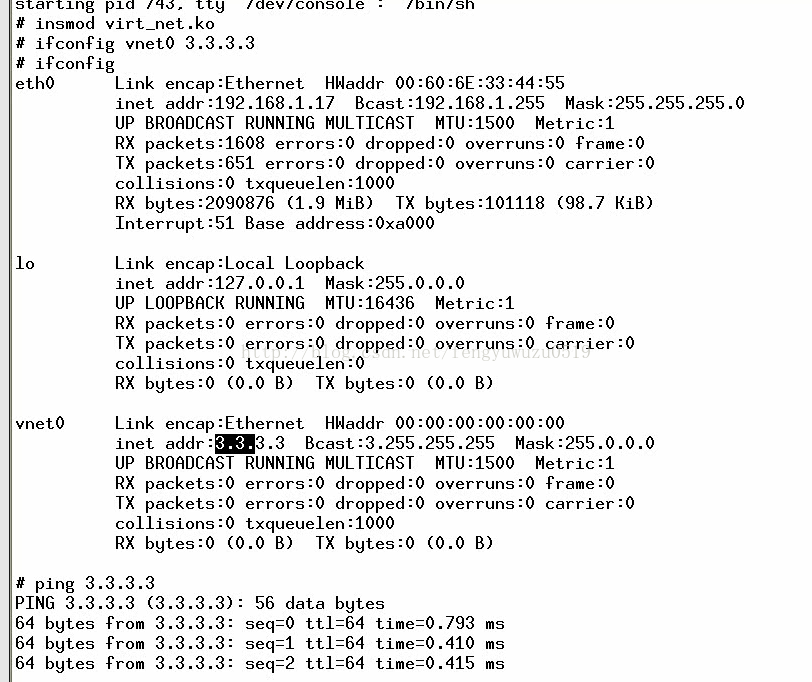
1. insmod virt_net.ko
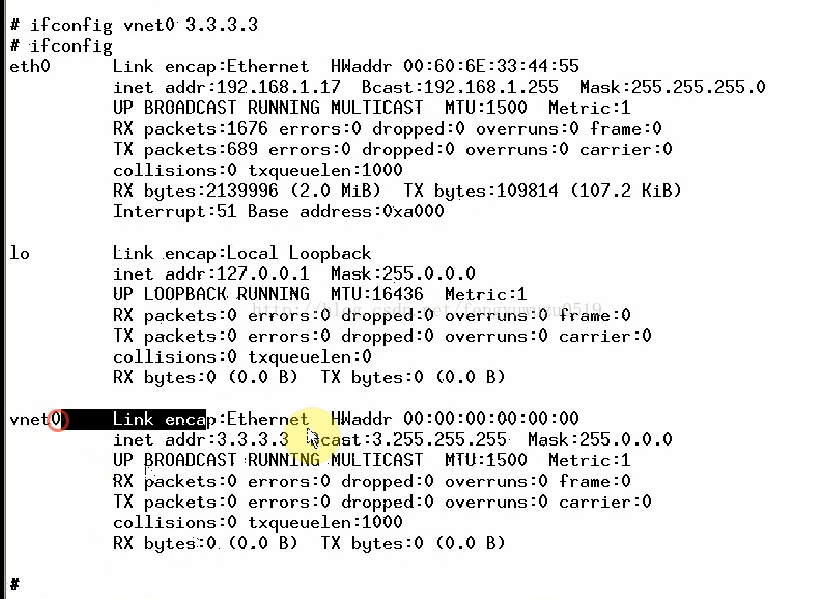
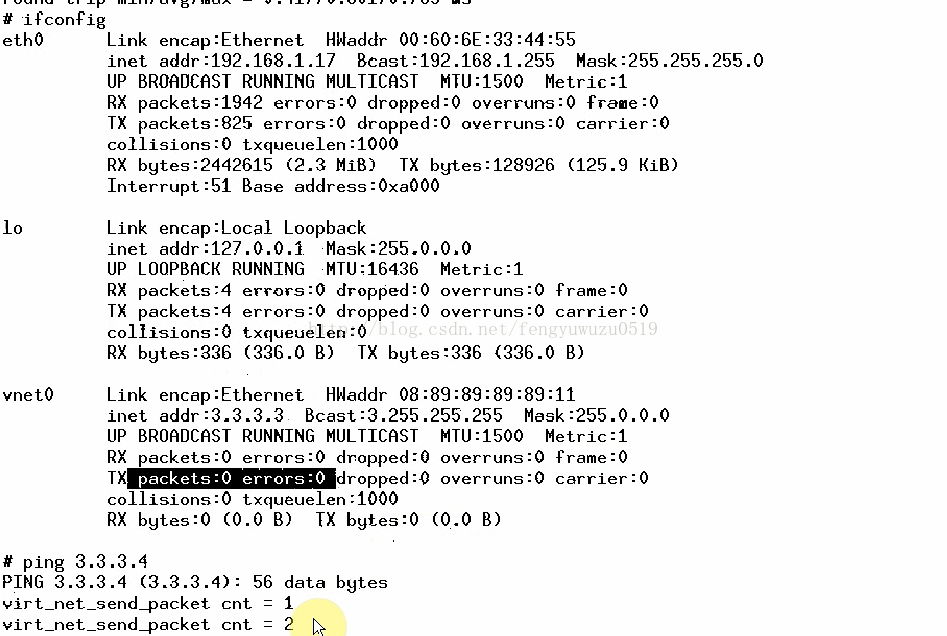
2. ifconfig vnet0 3.3.3.3
ifconfig // 查看
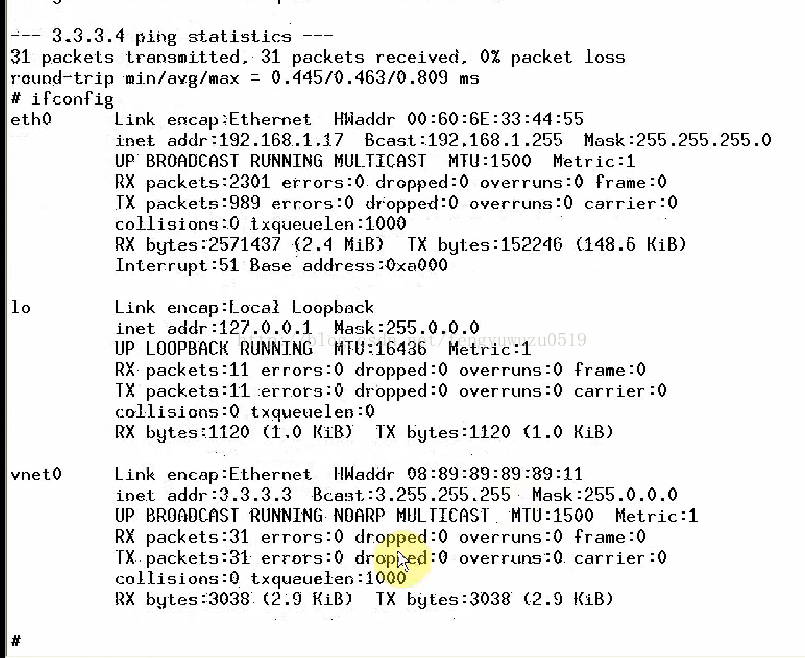
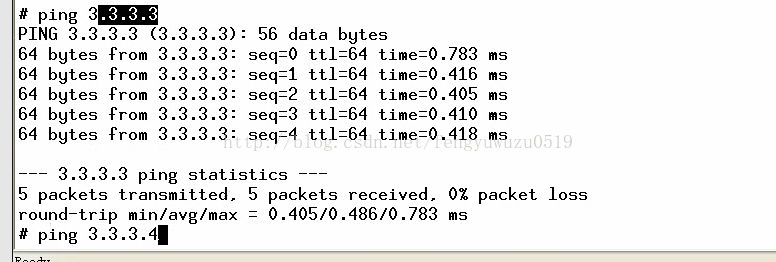
3. ping 3.3.3.3 // 成功
ping 3.3.3.4 // 死机
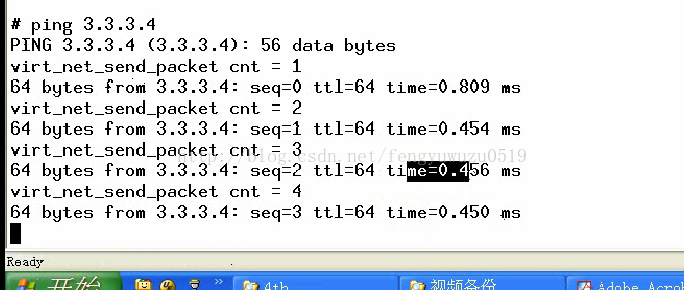
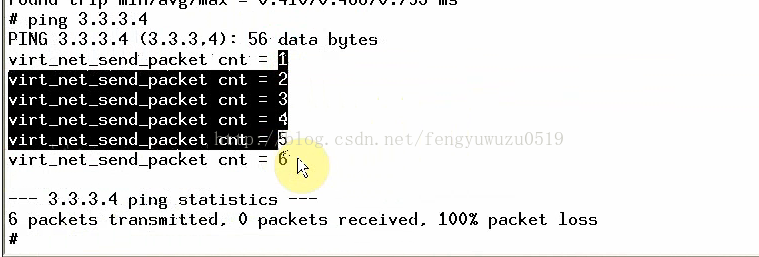
(6)死机是因为没有hard_start_xmit,加入后 可以ping通ping 3.3.3.4
static struct net_device *vnet_dev;
static int virt_net_send_packet(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev)
{
static int cnt = 0;
printk("virt_net_send_packet cnt = %d\n", ++cnt);
return 0;
}
static int virt_net_init(void)
{
/* 1. 分配一个net_device结构体 */
vnet_dev = alloc_netdev(0, "vnet%d", ether_setup);; /* alloc_etherdev */
/* 2. 设置 */
vnet_dev->hard_start_xmit = virt_net_send_packet;
/* 3. 注册 */
//register_netdevice(vnet_dev);
register_netdev(vnet_dev);
return 0;
}

(7)加入统计信息,设置mac地址
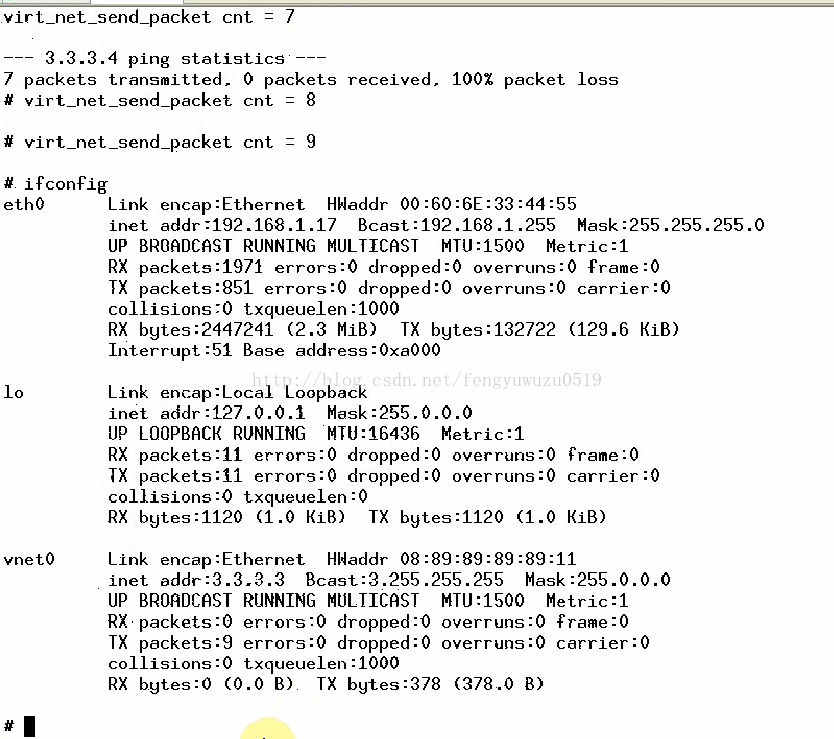
(8)不死机了,但是ping不同设备,因为不存3.3.3.4,没有回复,现在做一个假的回复。
/*
* 参考 drivers\net\cs89x0.c
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/netdevice.h>
#include <linux/etherdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/ioport.h>
#include <linux/in.h>
#include <linux/skbuff.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/spinlock.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/bitops.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ip.h>
#include <asm/system.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
static struct net_device *vnet_dev;
static void emulator_rx_packet(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev)
{
/* 参考LDD3 */
unsigned char *type;
struct iphdr *ih;
__be32 *saddr, *daddr, tmp;
unsigned char tmp_dev_addr[ETH_ALEN];
struct ethhdr *ethhdr;
struct sk_buff *rx_skb;
// 从硬件读出/保存数据
/* 对调"源/目的"的mac地址 */
ethhdr = (struct ethhdr *)skb->data;
memcpy(tmp_dev_addr, ethhdr->h_dest, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(ethhdr->h_dest, ethhdr->h_source, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(ethhdr->h_source, tmp_dev_addr, ETH_ALEN);
/* 对调"源/目的"的ip地址 */
ih = (struct iphdr *)(skb->data + sizeof(struct ethhdr));
saddr = &ih->saddr;
daddr = &ih->daddr;
tmp = *saddr;
*saddr = *daddr;
*daddr = tmp;
//((u8 *)saddr)[2] ^= 1; /* change the third octet (class C) */
//((u8 *)daddr)[2] ^= 1;
type = skb->data + sizeof(struct ethhdr) + sizeof(struct iphdr);
//printk("tx package type = %02x\n", *type);
// 修改类型, 原来0x8表示ping
*type = 0; /* 0表示reply */
ih->check = 0; /* and rebuild the checksum (ip needs it) */
ih->check = ip_fast_csum((unsigned char *)ih,ih->ihl);
// 构造一个sk_buff
rx_skb = dev_alloc_skb(skb->len + 2);
skb_reserve(rx_skb, 2); /* align IP on 16B boundary */
memcpy(skb_put(rx_skb, skb->len), skb->data, skb->len);
/* Write metadata, and then pass to the receive level */
rx_skb->dev = dev;
rx_skb->protocol = eth_type_trans(rx_skb, dev);
rx_skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY; /* don't check it */
dev->stats.rx_packets++;
dev->stats.rx_bytes += skb->len;
// 提交sk_buff
netif_rx(rx_skb);
}
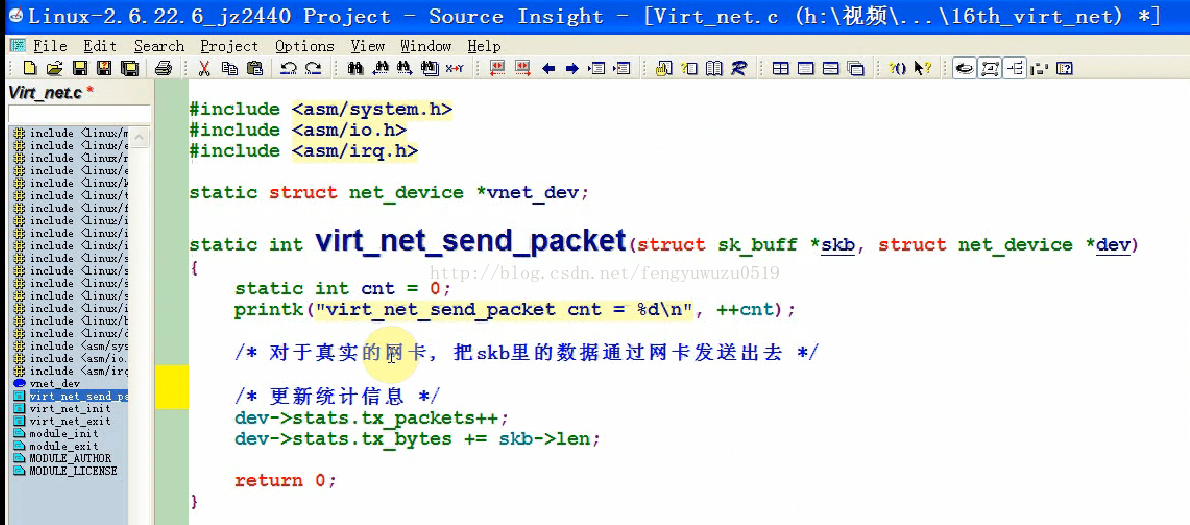
static int virt_net_send_packet(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev)
{
static int cnt = 0;
printk("virt_net_send_packet cnt = %d\n", ++cnt);
/* 对于真实的网卡, 把skb里的数据通过网卡发送出去 */
netif_stop_queue(dev); /* 停止该网卡的队列 */
/* ...... */ /* 把skb的数据写入网卡 */
/* 构造一个假的sk_buff,上报 */
emulator_rx_packet(skb, dev);
dev_kfree_skb (skb); /* 释放skb */
netif_wake_queue(dev); /* 数据全部发送出去后,唤醒网卡的队列 */
/* 更新统计信息 */
dev->stats.tx_packets++;
dev->stats.tx_bytes += skb->len;
return 0;
}
static int virt_net_init(void)
{
/* 1. 分配一个net_device结构体 */
vnet_dev = alloc_netdev(0, "vnet%d", ether_setup);; /* alloc_etherdev */
/* 2. 设置 */
vnet_dev->hard_start_xmit = virt_net_send_packet;
/* 设置MAC地址 */
vnet_dev->dev_addr[0] = 0x08;
vnet_dev->dev_addr[1] = 0x89;
vnet_dev->dev_addr[2] = 0x89;
vnet_dev->dev_addr[3] = 0x89;
vnet_dev->dev_addr[4] = 0x89;
vnet_dev->dev_addr[5] = 0x11;
/* 设置下面两项才能ping通 */
vnet_dev->flags |= IFF_NOARP;
vnet_dev->features |= NETIF_F_NO_CSUM;
/* 3. 注册 */
//register_netdevice(vnet_dev);
register_netdev(vnet_dev);
return 0;
}
static void virt_net_exit(void)
{
unregister_netdev(vnet_dev);
free_netdev(vnet_dev);
}
module_init(virt_net_init);
module_exit(virt_net_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("thisway.diy@163.com,17653039@qq.com");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");





























 8449
8449

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








