参考:http://chiffon.gitcafe.io/2014/12/28/cluster-analysis.html
聚类算法可以分为:中心点方法、层次聚类方法、基于密度方法、基于网格、基于模型方法。
其中最为经典的是K-means算法
K-means
K-means属于中心点方法(也有叫划分方法),算法经典简单。
算法
- 人工选取K值,并选取K个点作为K个簇的质心
- 对所有样本分别计算到K个簇的质心的距离(欧式或者曼哈顿),取最近距离的质心,并将该样本归于最近质心所在的簇。
- 更新K个簇的质心
- Until质心位置不再发生变化(也就是每个簇中的样本不再发生变化)
算法的复杂度为O(tnK),t代表迭代次数,n代表样本个数,K代表簇个数。由此看来它的复杂度只和样本大小线性相关,因此是一种非常有效的大数据聚类算法。
问题
K-means存在几个问题:1、对聚类中心的初始化比较敏感,不同的初始化带来不同的聚类结果。2、K值需要首先人工确定(启发式)。3、只能处理服从标准正太分布的聚类。4、K-means对于噪声比较敏感。
如何设置K值和如何选择初始簇的K个点可以参考
对于非标准正太分布和非均匀分布样本集合聚类时,可以使用Kernel K-means和谱聚类Spectral Clustering。
对于噪声的处理,可以使用K-mediods。这是一种K-means的简单改进,区别在于对于质心的选择。K-means的质心是同簇下所有点的平均值,K-mediods则将簇中的某点选为质心,条件是此点到簇内其他点距离和最小。
仿真实验
from numpy import *
#select k sample using kmeans++
def initCent(dataSet,k):
numSamples,dim=dataSet.shape
indexlist=[int(random.uniform(0,numSamples))]
loop=1
while loop<k:
maxD=0
maxIndex=0
for i in xrange(numSamples):
d=0
for j in indexlist:
d+=eucleanDistance(dataSet[j],dataSet[i])
if d>maxD:
maxD=d
maxIndex=i
loop+=1
indexlist.append(maxIndex)
centroids=zeros((k,dim))
for i in range(k):
centroids[i]=dataSet[indexlist[i]]
return centroids
#random select k sample
def initRandomCent(dataSet,k):
numSamples,dim=dataSet.shape
centroids=zeros((k,dim))
for i in range(k):
index=int(random.uniform(0,numSamples))
centroids[i,:]=dataSet[index,:]
return centroids
def eucleanDistance(x1,x2):
return sqrt(sum(power(x1-x2,2)))
def kmeans(dataSet,k):
numSamples,dim=dataSet.shape
clusterAssment=zeros(numSamples)
#random select k sample
#centroids=initRandomCent(dataSet,k)
centroids=initCent(dataSet,k)
clusterChanged=True
count=0
while clusterChanged:
clusterChanged=False
#go through all samples
for i in xrange(numSamples):
minDist=float('inf')
minIndex=0
#get the minDistance and which cluster belong to
for j in range(k):
distance=eucleanDistance(centroids[j,:],dataSet[i,:])
if distance<minDist:
minDist=distance
minIndex=j
#update cluster infomation: cluster center , distance
if clusterAssment[i]!=minIndex:
clusterChanged=True
clusterAssment[i]=minIndex
#go through k cluster
for j in range(k):
#get cluster j dataSet
pointsInCluster=dataSet[nonzero(clusterAssment[:]==j)[0]]
centroids[j,:]=mean(pointsInCluster,axis=0)
count+=1
print 'iterate:%d' % count
return centroids,clusterAssment
from skimage import io,color
from scipy import misc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
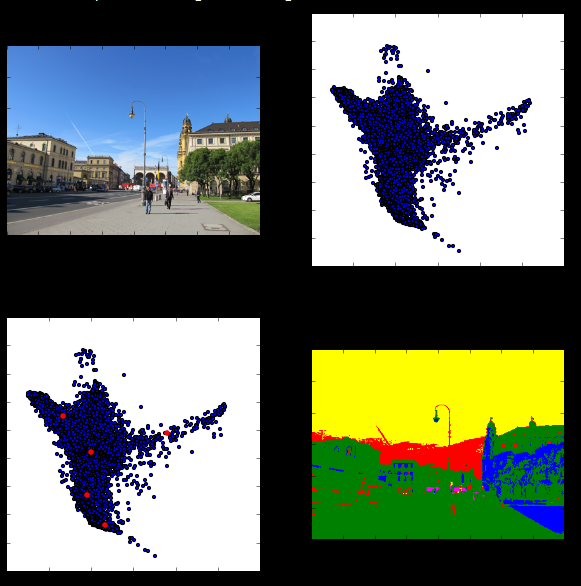
rgb=io.imread('E:\BaiduYunDownload\ML\project\city.jpg')
rows=rgb.shape[0]
cols=rgb.shape[1]
lab=color.rgb2lab(rgb)
ab=lab[:,:,1:3]
plt.figure(figsize(10,10))
plt.subplot(2,2,1)
plt.imshow(rgb)
plt.subplot(2,2,2)
plt.scatter(ab[:,:,0],ab[:,:,1],10)
k=5
centroids,clusterAssment=kmeans(ab.reshape(ab.shape[0]*ab.shape[1],ab.shape[2]),k)
plt.subplot(2,2,3)
plt.scatter(ab[:,:,0],ab[:,:,1],10)
plt.scatter(centroids[:,0],centroids[:,1],20,color='r')
rgblabel=color.label2rgb(clusterAssment.reshape(rows,cols))
plt.subplot(2,2,4)
plt.imshow(rgblabel)二分K-means聚类
Kernel K-means
Spectral Clustering





 本文详细介绍了经典的K-means聚类算法及其工作原理,包括算法步骤、复杂度分析及存在的问题。此外还探讨了K-means算法的几种变种如二分K-means、Kernel K-means和Spectral Clustering等。
本文详细介绍了经典的K-means聚类算法及其工作原理,包括算法步骤、复杂度分析及存在的问题。此外还探讨了K-means算法的几种变种如二分K-means、Kernel K-means和Spectral Clustering等。
















 10万+
10万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








