【0】README
0.1)本文总结于 数据结构与算法分析, 源代码均为原创, 旨在实现 对不相交集合的路径压缩操作;
0.2)对求并后的集合进行路径压缩,目的是降低集合(合并树)的深度,减少find 操作的时间复杂度;
0.3) for introduction to non-intersect set ADT ,please refet to http://blog.csdn.net/PacosonSWJTU/article/details/49716905 , and for details of finding or unionSet operations towards non-intersect set , please refer to http://blog.csdn.net/pacosonswjtu/article/details/49717009
【1】 路径压缩相关
1.1)基于这样的观察:执行 Union操作 的任何算法都将产生相同的最坏情形的树,因为它必然会随意打破树间的平衡。因此,无需对整个数据结构重新加工而使算法加速的唯一方法是: 对Find 操作做些更聪明的工作;
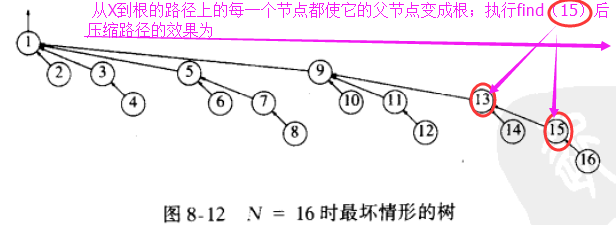
1.2)路径压缩定义:设操作是Find(X), 此时路径压缩的效果是, 从X到根的路径上的每一个节点都使它的父节点变成根;执行find(15)后压缩路径的效果为:
 |  |
对路径压缩算法的分析(Analysis)
- A1)路径压缩的实施在于 使用额外的两次指针移动, 节点13和14 现在离根近了一个位置, 而节点15和16离根近了两个位置;
- A2)因此, 对这些节点未来的快速访问将由于花费 额外的工作来进行路径压缩而得到补偿;
1.3)路径压缩对 基本的 Find操作改变不大。对 Find 操作来说,唯一的变化是 使得 S[X] 等于 由Find 返回的值;这样,在集合的根被递归地找到以后, X 就直接指向了它, 对通向根的路径上的每一个节点这将递归地出现,因此实现了路径压缩;
1.4)路径压缩可以和 大小求并完全兼容,这就使得两个例程可以同时实现;
1.5)路径压缩不完全与 按高度求并兼容,因为路径压缩可以改变树的高度;
【2】source code + printing results
2.1)download source code:
https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/blob/master/chapter8/p206_pathCompression.c
- souce code statements:路径压缩源代码中使用的集合求并方法是: 按大小求并:
2.2)source code at a glance:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define ElementType int
#define Error(str) printf("\n error: %s \n",str)
struct UnionSet;
typedef struct UnionSet* UnionSet;
// we adopt the child-sibling expr
struct UnionSet
{
int parent;
int size;
ElementType value;
};
UnionSet makeEmpty();
UnionSet* initUnionSet(int size, ElementType* data);
void printSet(UnionSet* set, int size);
void printArray(ElementType data[], int size);
int find(int index, UnionSet* set);
void pathCompress(int, UnionSet*);
// initialize the union set
UnionSet* initUnionSet(int size, ElementType* data)
{
UnionSet* set;
int i;
set = (UnionSet*)malloc(size * sizeof(UnionSet));
if(!set)
{
Error("out of space, from func initUnionSet");
return NULL;
}
for(i=0; i<size; i++)
{
set[i] = makeEmpty();
if(!set[i])
return NULL;
set[i]->value = data[i];
}
return set;
}
// allocate the memory for the single UnionSet and evaluate the parent and size -1
UnionSet makeEmpty()
{
UnionSet temp;
temp = (UnionSet)malloc(sizeof(struct UnionSet));
if(!temp)
{
Error("out of space, from func makeEmpty!");
return NULL;
}
temp->parent = -1;
temp->size = 1;
return temp;
}
// merge set1 and set2 by size
void setUnion(UnionSet* set, int index1, int index2)
{
//judge whether the index1 or index2 equals to -1 ,also -1 represents the root
if(index1 != -1)
index1 = find(index1, set);
if(index2 != -1)
index2 = find(index2, set);
if(set[index1]->size > set[index2]->size)
{
set[index2]->parent = index1;
set[index1]->size += set[index2]->size;
}
else
{
set[index1]->parent = index2;
set[index2]->size += set[index1]->size;
}
}
//find the root of one set whose value equals to given value
int find(int index, UnionSet* set)
{
UnionSet temp;
while(1)
{
temp = set[index];
if(temp->parent == -1)
break;
index = temp->parent;
}
return index;
}
// conducting path compression towards union set with given index
void pathCompress(int index, UnionSet* set)
{
int root;
int i;
int parent;
//1st step: find the top root contains the element under index
root = find(index, set);
//2nd step: path compression begins
i = set[index]->parent;
set[index]->parent = root;
while(i != -1)
{
parent = set[i]->parent;
if(parent == root)
break;
set[i]->parent = root;
i = parent;
}
}
int main()
{
int size;
UnionSet* unionSet;
ElementType data[] = {110, 245, 895, 658, 321, 852, 147, 458, 469, 159, 347, 28};
size = 12;
printf("\n\t====== test for conducting path compression towards union set by size ======\n");
//printf("\n\t=== the initial array is as follows ===\n");
//printArray(data, depth);
printf("\n\t=== the init union set are as follows ===\n");
unionSet = initUnionSet(size, data); // initialize the union set over
//printSet(unionSet, size);
printf("\n\t=== after union(0, 1) + union(2, 3) + union(4, 5) + union(6, 7) + union(8, 9) + union(10 ,11) ===\n");
setUnion(unionSet, 0, 1);
setUnion(unionSet, 2, 3);
setUnion(unionSet, 4, 5);
setUnion(unionSet, 6, 7);
setUnion(unionSet, 8, 9);
setUnion(unionSet, 10, 11);
//printSet(unionSet, size);
printf("\n\t=== after union(1, 3) + union(5, 7) + union(9, 11) ===\n");
setUnion(unionSet, 1, 3);
setUnion(unionSet, 5, 7);
setUnion(unionSet, 9, 11);
//printSet(unionSet, size);
printf("\n\t=== after union(3, 7) + union(7, 11) ===\n");
setUnion(unionSet, 3, 7);
setUnion(unionSet, 7, 11);
printSet(unionSet, size);
printf("\n\t=== after pathCompress(0, unionSet) + pathCompress(8, unionSet) ===\n");
pathCompress(0, unionSet) ;
pathCompress(8, unionSet);
printSet(unionSet, size);
return 0;
}
void printArray(ElementType data[], int size)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("\n\t data[%d] = %d", i, data[i]);
printf("\n\n");
}
void printSet(UnionSet* set, int size)
{
int i;
UnionSet temp;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
temp = set[i];
printf("\n\t parent[%d] = %d", i, temp->parent);
}
printf("\n");
}
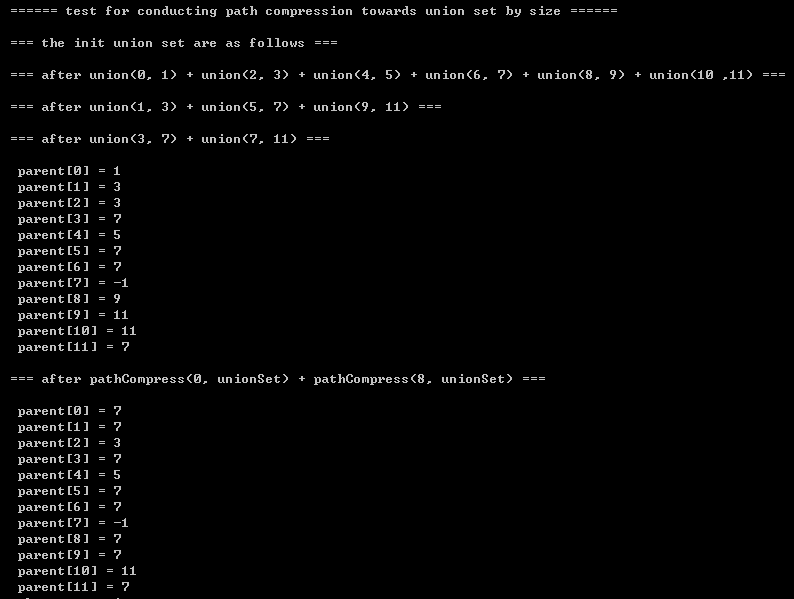
2.3)printing results:






















 3726
3726

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








