AcDreamer博客原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/7851144
二分解决自然是因为幂次太大,用公式远超int范围,无法求解
今天我们学习如何有效地求表达式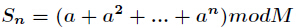
(1)当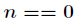
(2)当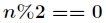
(3)当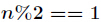
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int M = 1000000007;
typedef long long LL;
LL power(LL a,LL b)
{
LL ans = 1;
a %= M;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = ans * a % M;
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = a * a % M;
}
return ans;
}
LL sum(LL a,LL n)
{
if(n == 1) return a;
LL t = sum(a,n/2);
if(n & 1)
{
LL cur = power(a,n/2+1);
t = (t + t * cur % M) % M;
t = (t + cur) % M;
}
else
{
LL cur = power(a,n/2);
t = (t + t * cur % M) % M;
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
LL a,n;
while(cin>>a>>n)
cout<<sum(a,n)<<endl;
return 0;
}
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=3233
题意:矩阵求和
矩阵也满足上述等比数列二分求和方式
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N = 35;
struct Matrix
{
int m[N][N];
};
Matrix I;
int n, k, MOD;
Matrix add(Matrix a, Matrix b)
{
Matrix c;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
c.m[i][j] = (a.m[i][j] + b.m[i][j]) % MOD;
return c;
}
Matrix multi(Matrix a, Matrix b)
{
Matrix c;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
c.m[i][j] = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
c.m[i][j] += a.m[i][k] * b.m[k][j];
c.m[i][j] %= MOD;
}
return c;
}
Matrix Power(Matrix A, int n)
{
Matrix ans = I, p = A;
while(n)
{
if(n & 1)
ans = multi(ans, p);
n >>= 1;
p = multi(p, p);
}
return ans;
}
Matrix sum(Matrix A, int k)
{
if(k == 1) return A;
Matrix t = sum(A, k / 2);
if(k & 1)
{
Matrix cur = Power(A, k/2 + 1);
t = add(t, multi(t, cur));
t = add(t, cur);
}
else
{
Matrix cur = Power(A, k/2);
t = add(t, multi(t, cur));
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &k, &MOD) != EOF)
{
Matrix A;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &A.m[i][j]);
A.m[i][j] %= MOD;
I.m[i][j] = (i == j);
}
Matrix ans = sum(A, k);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
printf("%d%c", ans.m[i][j], j == n - 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
}
return 0;
}







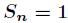
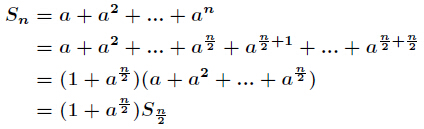
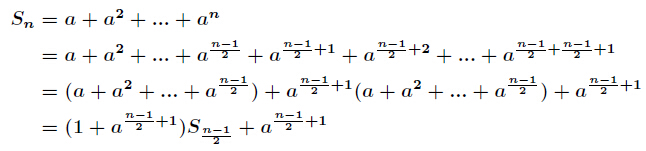
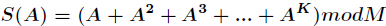
















 270
270

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








